Yachting World
- Digital Edition


Dinghy sailing: why it’s great for beginners and keelboat sailors
- Toby Heppell
- June 30, 2022
Dinghy sailing helps improve your understanding of a wide variety of skills, whether you are just starting out or a seasoned keelboat sailor, sailing a dinghy is a hugely rewarding pastime

Dinghy sailing – whether racing or as a leisure activity – is one of the best ways to improve your skill level whether you’ve no experience of sailing, race 50ft yachts offshore or cruise the coast in a 30ft bilge-keeler.
It is no coincidence that some of the world’s top sailors either started out dinghy sailing or continue to dinghy sail as a pastime. But many sailors, particularly those who come to the sport of sailing as an adult will only have limited dinghy sailing experience.
Though keelboat sailing and dinghy sailing are ostensibly the same sport, the two have a number of small differences, which transfer from one to the other to make you a better sailor generally.
However, this does also mean that no matter how good a keelboat sailor you are, jumping straight into a dinghy may come as something of a shock and vice versa.
What is a dinghy?
The difference between a dinghy and a keelboat can be difficult to define simply. Typically a sailing dinghy does not have a weighted keel in order to keep it upright.
However, there are boats many would consider to be a dinghy that do have a weighted keel, so this is not a strict definition.
Dinghies are also typically under 20ft and are not designed to sail in ocean going conditions. This, alongside the lack of a keel, typically means dinghies are much more manoeuvrable, faster to accelerate and more responsive to body position.
It’s these traits that make dinghy sailing such a boon in terms of improving your understanding of sailing when on a keelboat.
Sit in the wrong place on a dinghy at the wrong time and you might well capsize. Do the same on a keelboat and the effect will be negative but not in quite so stark a manner – in fact, it can often be an almost imperceptible reduction in performance.
The same is true of sail trim, accelerating and slowing down and a whole raft of other boat handling and sail handling skills that are vital to understanding how best to control a boat.
Finally, in terms of the difference between the two, dinghies usually only have one or two sailors onboard, meaning that all the jobs need to be either undertaken by one person or shared equally between two. This, in turn, means that a day out sailing a dinghy provides more opportunity to practise a wider variety of skills as compared to being one of a wider number of crew on a keelboat.

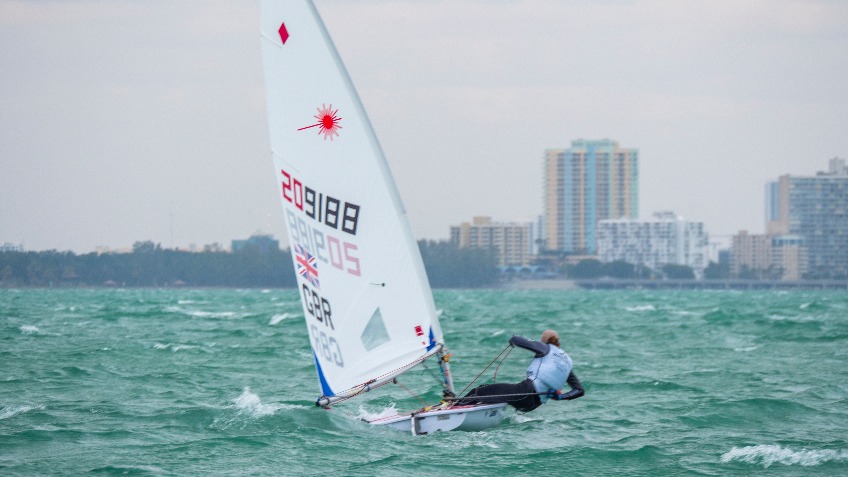
Laser/ILCA dinghies in Antigua racing as part of Bart’s Bash, the worldwide sailing charity race, raising funds for sailing communities affected by the 2017 hurricanes
Where to go dinghy sailing
In theory you can sail a dinghy on almost any publicly accessible piece of water, but publicly owned launching facilities tend to be few and far between.
Given their lack of communication equipment and their relative lack of self-sufficiency as compared to a keelboat, it’s advisable to have some sort of safety cover available should you get into trouble.
For this reason, the traditional way to go dinghy sailing is to join your nearest sailing club on an annual or trial membership and borrow a club boat (if they are available) to start sailing regularly.
Article continues below…

RS Aero – A Game Changer?
Lighter than most people’s launching trolleys, RS’ new single hander could prove to be a game changer – I found…
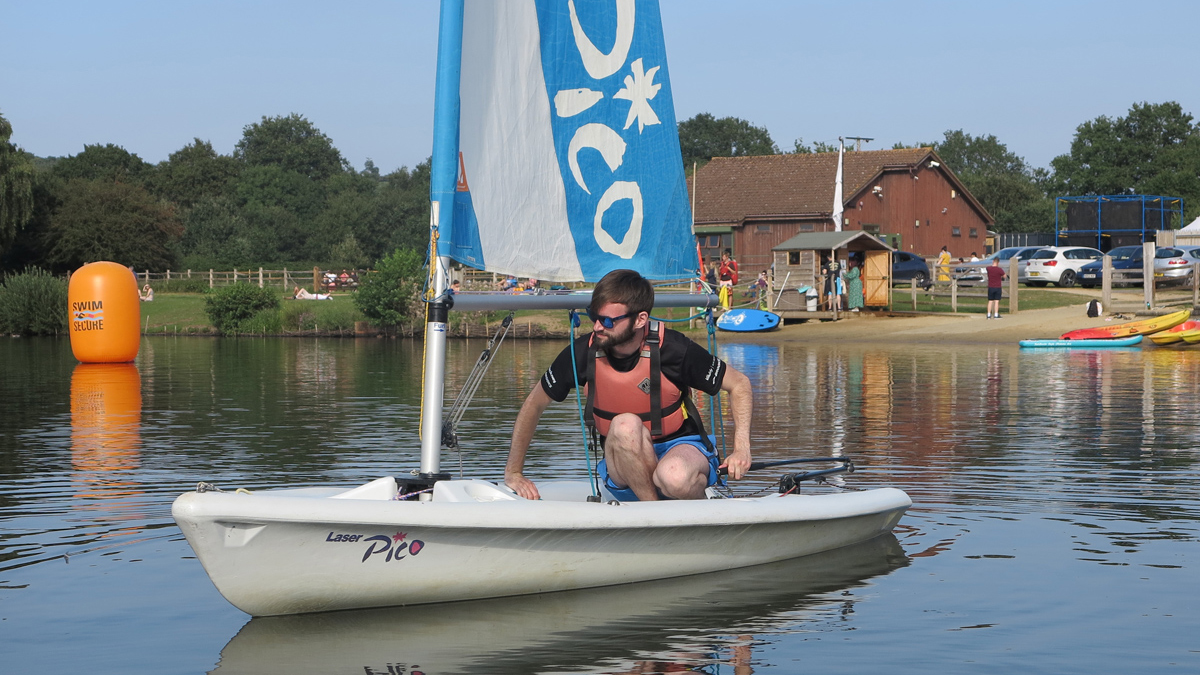

Learn to sail: What to expect from the RYA Dinghy Level 1 Start Sailing course
There can be few more forgiving places to learn to sail than Horseshoe Lake Activity Centre in Berkshire. This inland…
It’s not the most flexible system in the world and, increasingly, clubs are offering memberships on a pay-to-play basis.
Queen Mary Sailing Club in the UK based just west of London is one such club, which offers a gym-style membership of a monthly subscription which allows you to sail a wide variety of boats as often as you like (subject to booking etc.).
This can be a great way to go dinghy sailing or to try out dinghy sailing before making the commitment to an annual membership at a sailing club, or committing to the purchase of a boat.

A typical dinghy sailing club in the UK. Photo: David George / Getty Images
Although this is a growing area and there are plenty of sailing clubs offering a gym-style membership, it’s a long way from ubiquity, so the annual membership model is likely to be the best option for most.
It’s worth looking around you and seeing what options are available in the local area. In the UK, you will usually be living within easy access of a number of clubs, so you will be able to pick the club that is right for you.
If you are dinghy sailing in the USA, then your options will be limited, with sailing clubs being relatively fewer and further between.
What dinghy to buy
The first and easiest question to ask yourself is whether you plan on sailing alone or with another person and thus whether you are looking for a single or doublehanded boat (or something that can do both).
Ideally before taking the plunge and buying a dinghy you will have the chance to sail a variety of types of dinghy at a club you have joined, which should help you make your choice.
Most dinghies have an optimum weight so your size is a factor, but this is less of an issue if you are not planning on racing your dinghy.
Construction of the boat is a key consideration. Wood was the traditional dinghy material but this requires significant maintenance and is susceptible to rot if not well-kept – but it does look nice and is repairable with some simple wood-working skills.
Fibreglass and foam sandwich builds offer stiffness and are great for racing, but can become easily scratched or damaged and require a working knowledge of resin and glass fibre work to fix damage – or get a local boat builder to do it for you.
In the last 20 years, many beginner dinghies have been built from polyurethane or polyethylene and are rotomoulded. This process involves pouring liquid ‘plastic’ into a mould and rotating it while it sets to get an even distribution of the material, which forms the boats hull once cooled and released from the mould.

The Laser Pico is a rotomoulded boat, popular with sailing schools and beginners
Rotomoulding is not exactly new, so there are plenty of second hand examples on the market. These boats are very resistant to damage and are typically seen as ideal for the rental or beginner market.
Globally speaking, the Laser (recently being sold under the name ILCA) and the Sunfish are two of the most popular singlehanded dinghies. Both are fibreglass, but crucially wherever you are in the world there are likely to be plenty on the market at a variety of price points – the Sunfish being much more popular in the USA than Europe and the Laser/ILCA having a slightly more global presence.
Both these boats will also hold their second hand value reasonably well, so are good options for taking the plunge.
Catamarans are faster and more inherently stable than monohull dinghies, so can often be a good option for the starter sailor. It should be noted, however, that multihull sailing is, a slightly different skill to monohull sailing, so if you are looking to improve your skills on a monohull it might not be the very best option.

Catamarans lined up on the banks of the Swan River in Perth, Australia. Photo: lkonya / Getty Images
If you are considering racing, then the best advice would be to see what boats are being sailed at your local club. It might be that a slightly obscure boat is popular near where you live and sailing alongside others in the same type of boat is usually more fun than sailing around alone.

Sailing alongside others in the same type of boat can be more rewarding than sailing alone. Photo: Tim Platt / Getty Images
Dinghy Sailing Kit
Dinghy sailing is a pretty wet sport, with launching and retrieval usually seeing sailors in the water, regular soaking from waves and the possibility of capsizing all factors.
As such, particularly for those not blessed with warm warters and balmy breezes, buying a wetsuit is a pretty important thing to do.
You can go dinghy sailing in old trainers and a pair of trousers that you don’t mind getting wet, but these will be uncomfortable over an extended period of time on the water and will not keep you warm.
A buoyancy aid is also absolutely essential to help you float in the water should you fall out or capsize. Buoyancy aids are better than lifejackets for dinghy sailing as it’s entirely possible that you will be in the water more than once in a dinghy sailing session, so a manually inflating lifejacket will get in the wat after it has been set off once, and an automatically inflating one is likely to go off while you are in the boat itself if there is enough spray.
While a wetsuit and lifejackets are, in my opinion, must have items, trainers will be fine for a while – though you will probably want to invest in a pair of wetboots after not too long, which will be comfort and much warmer.
If you enjoyed this….
Yachting World is the world’s leading magazine for bluewater cruisers and offshore sailors. Every month we have inspirational adventures and practical features to help you realise your sailing dreams. Build your knowledge with a subscription delivered to your door. See our latest offers and save at least 30% off the cover price.

The 5 Best Sailboats For Beginners

Sailing is a fun activity for people of all experience levels. In fact, learning to sail a basic boat is relatively easy—in the right environment, you can start cruising with minimal experience.
However, the idea of a beginner commanding a 55-foot ketch in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean is a bit ridiculous. Even though virtually everyone can sail, beginners should learn the basics in a controlled environment—and on the correct boat.
Boat size doesn’t necessarily affect its beginner-friendliness, because sailors need to take into account factors such as rig simplicity and handling characteristics.
Many beginners make the mistake of picking the wrong boat to begin with, which can lead to frustration and turn them off of sailing forever.
To mitigate these issues, this article will cover the best sailboats for beginners —so you can get on the water and start sailing safely and comfortably.
Table of contents
Best Rigs for Beginners
There are many types of sailboat rigging , and some are more beginner-friendly than others. Unfortunately, some of the most aesthetically pleasing rigs are also the most complicated.
Eventually, sailors can acquire enough skill to master complex rigs, but it’s best to start simple.
Arguably, one of the simplest sailing rigs is the Lateen Rig. This rig consists of a mast, boom, and spar, along with a single halyard and mainsheet. With only two ropes in its simplest configuration, the Lateen Rig makes an excellent starter sailboat, and it will be featured on this list.
For larger boats, the Bermuda Sloop rig is an excellent choice. This rig is quite common and includes a jib for a larger sail plan.
For those who desire a slightly more robust (but single sail) layout, the gaff-rigged catboat is also an excellent choice. This versatile craft (and rig) has a large and relatively simple single sail, which is easier to handle than multiple sails.
Top Five Sailboats for Beginners
Now, we’ll go over the top five sailboats for beginners . These boats will descend in order from smallest to largest, but not by the level of experience needed.
Remember, just because you’re new to sailing doesn’t mean you have to settle for a boat that’s too small. Beginners can handle larger boats with some training, and some are easier to handle than their smaller counterparts.
The following boats were chosen because of their handling characteristics, low cost-of-ownership, and simplicity, as all of these factors are important for choosing the best beginner sailboat.
5) Sailing Dinghy
The sailing dinghy is the quintessential starter sailboat. These tiny, lightweight, popular, and highly affordable little craft is easy to operate and relatively difficult to capsize. The popular Optimist Sailing Dinghy, while designed for children up to the age of about 15, can be used (sometimes hilariously) by adults as well. An Optimist-style dingy is a great option for beginners over the age of 15, as boats of this style can be found in a variety of sizes. The sailing dinghy is a very popular youth racing sailboat, especially in the United States and the United Kingdom. While it’s not particularly fast, this little boat has wonderful handling characteristics and is relatively difficult to capsize. This open-cockpit boat uses a centerboard and detachable tiller and can be beached or carried atop a car without much hassle. The mast is removable, and all parts are easily stowed. Overall, the Optimist and its copycats are a remarkable little craft, equally useful as a tender for a larger boat or a standalone beginner sailboat.
Dinghy rigs vary between builders, but many use the simple Spirit Rig. The rig consists of a single sail and mainsheet, along with one mast, boom, and spar. The leech is stiffened by battens, and ties along the luff secure it all to the mast. Hoisting and securing the rig is easy, and lines are secured to the boat by a cleat. This simple rig has plenty of sail area for most places, and sailors can secure the mainsheet to a block or simply hold it in their hands.
The price of sailing dinghies can vary widely depending on multiple factors. Professionally-made sailing dinghies start around $3,500 new, and plywood kits are available for around $1,000 to $2,000. Used dinghies (including Optimist sailing dinghies) can be found on Craigslist for as low as a few hundred dollars.
{{boat-info="/boats/vanguard-sunfish"}}
The Sunfish is a brilliant little sailboat, and a very fast boat indeed. This little racing dinghy, while only 13 feet in length, can be an enormous amount of fun for beginners and experienced sailors alike. The best way to describe the handling of a Sunfish is, ‘tender,’ though it’s not difficult to master this little boat. For its size, the Sunfish has a relatively large sail area and a very shallow draft. This boat has a small cockpit and can be controlled easily by a single person. The large sail plan of the Lateen-Rigged Sunfish makes for excellent performance in light winds and amazing speed on windy days. The Sunfish is a lightweight fiberglass boat with a simple rig and is a great step-up from a sailing dinghy. It’s possible to learn how to sail on this boat, but every sailor who’s spent time on a Sunfish will probably recommend bringing a towel. The boat is relatively easy to capsize for beginners and it heels aggressively, but these characteristics can teach sailors some important lessons. The heeling characteristics of the Sunfish can help beginners get accustomed to the feeling and help them understand the limits of a sailboat and how to avoid capsizing.
The Sunfish features a Lateen Rig, which has some shared characteristics with the simple Spirit Rig. The Lateen Rig has a single spar, mast, and boom, and is easy to set up and dismantle. The mast is removable as well, making stowing and transportation relatively easy. The large sail plan of the Sunfish makes it ideal for lakes and other areas where the wind is sporadic or very low, and the boat can be safely handled in many conditions. The boat is great for racing and learning and is also available in a Bermuda rig. The Sunfish is recognizable by the distinctive fish logo in the top corner of the sail, and the classic rainbow sails striping.
The Sunfish is still commercially manufactured. You can purchase one new from the factory for around $5,000 today, and options are available to make the boat your own. While the boat is designed to be sailed by a single person, two adults can purchase this boat and use it together comfortably. Used Sunfish prices vary, but a fully-outfitted boat in good condition can cost upwards of $1,000. They hold their value well, and they’re a great choice for beginners.
{{boat-info="/boats/vanguard-laser"}}
The Laser is considered by many to be the Sunfish’s main competitor. The two boats are the same length (13 feet 9 inches) and share many of the same handling characteristics. However, the boats do have some notable differences. Many people consider the Laser to be a step-up from the Sunfish in difficulty, as the boat handles much more like a racer. The Laser has been used in the Olympics for racing. The laser is small and simple enough for beginners but requires skill to operate. Beginners can learn a lot from sailing a Laser and have an enormous amount of fun in the process. This fast little boat is simple and easy to set up but handles like a racecar. If you’re a beginner on a laser, you’ll probably capsize at some point—which isn’t always a problem if you’re in a controlled environment, as the boat can be righted easily.
The laser is a Cat Rigged boat. This means it has only one mainsail and no headsails. The simple rig has a mast and a boom and is very easy to set up. The sail area of the laser is relatively large and designed for speed in high winds. The rig combined with the overall design of the sailboat makes it handle tenderly, which may be off-putting to some beginners. Regardless, it’s still a blast to sail for beginners with some experience.
New Laser sailboats start around $6,000 which is slightly more than the Sunfish. This simple centerboard cruiser is constructed as a race boat, which can explain some of the price increase. Used Laser sailboats are available on the market, though usually not as common as the Sunfish. Used Laser prices vary widely.
2) Gaff-Rigged Catboat
The gaff-rigged catboat isn’t a brand of boat—it’s a style of a sailboat that was once a popular workboat on the New England coast. This boat, which has only one mainsail and no headsails, is available in a wide range of designs. Catboats are famous for their handling and power and make a great sailboat for beginners. These vessels are available with centerboards, keels, cabins, and in open designs. Most catboats range from 15 to 19-feet long and can be built from wood or fiberglass. Catboats are easy to handle, and one who learns on a small catboat can easily transition to a larger one. Besides being one of the most easily recognizable sailboats, catboats are also some of the most versatile. A catboat can be just as suitable for lake cruising as it is for coastal waters.
The most common type of catboat rig is the Gaff Rig. This classic and robust rig is more complex than the simple Spirit and Lateen rig, but it’s more suitable for a ‘proper ship.’ The Gaff Rig can provide similar power as an equivalent Bermuda Rig, with much more elegance and a shorter mast. Many sailors prefer the classic Gaff Rig for its handling characteristics and durability.
It’s impossible to specify the price of catboats because they vary so much in design and size. New catboats (between 15 and 25-feet) can be purchased for less than $20,000, and used boats are numerous and varied. Cabin catboats tend to cost more, especially new—some run for more than $50,000 with a high level of amenities, including a head and galley. Numerous catboat plans are available online, and sailors report constructing them (usually of plywood) for just a few thousand dollars.
1) West Wight Potter 19
{{boat-info="/boats/west-wight-potter-19"}}
The West Wight Potter 19 is a fiberglass sailboat designed for safety, easy handling, and beginner-friendliness. This 19-foot trailer-sailor features a cabin with a vee-berth, a simple rig, and a retractable keel. The West Wight Potter 19 could potentially be the best cabin sailboat for beginners, and certainly one of the safest—the West Wight Potter 19, according to the manufacturer, is quite literally unsinkable. The hull is filled with buoyant materials, allowing the boat to be flooded and remain afloat. However, unsinkability isn’t the only characteristic of this boat that makes it ideal for beginners. The rig is simple and easy to set up, and the handling characteristics are excellent. The boat is not prone to aggressive heeling and handles confidently in a variety of conditions. While one generally wouldn’t consider it to be a blue-water cruiser, it’s still extremely capable—one sailor even sailed this vessel from California to Hawaii , which is over 2,000 nautical miles. The theoretical hull speed of this boat is around 5.4 knots, but it actually has a tendency to plane and achieve higher speeds. It’s a flat-bottomed cruiser, making it easy to beach and transport with its retractable keel and removable rudder. The West Wight Potter 19 is a great introduction to large sailboats and carries amenities normally reserved for boats at least 1/3 larger.
The West Wight Potter 19 is a Bermuda-Rigged sloop. The sail plan is sufficiently large to propel the boat in a variety of conditions, but not so large that it overpowers the boat. Sailors can single-hand the boat with ease, and set up and takedown are easy and require no special tools. The boat handles well in a variety of conditions and is well-known for its superior stability. The rig comes apart easily and can be stowed and trailered by one person.
The West Wight Potter 19 has been produced and sold commercially since the 1970s, and the used market has plenty of boats available, generally starting around $5,000. New West Wight Potter 19 sailboats are remarkably affordable compared to other boats with comparable characteristics. The West Wight Potter 19 is manufactured by International Marine in California. New sailboats start at just shy of $25,000. Owners can add an enormous range of extra features to their boats, including a hull-strengthening ‘blue water’ package, a stove, a head, electrical power, spare parts, and much more. The boats are highly customizable and can be outfitted for weekender sailing or long-term liveaboard cruising.
How to Pick a Sailboat
Picking a sailboat for beginners doesn’t have to be difficult. Before deciding on a boat, consider your experience level and location.
If you only have access to rough ocean, it may not be the best idea to get an open dinghy.
If you live near a lake, a Sunfish could be a great way to start.
Also, consider your budget. If you’re looking for a $50 sailboat, you can probably find one, but it won’t be ideal.
If you have just a few thousand dollars to spend, you can set yourself up nicely with a little research .
Also, consider what you want to do with the sailboat. Recreation, fishing , cruising , and exploration are options, and require different kinds of boats.
Whichever you end up choosing, make sure you try it out and can sail it comfortably.
Related Articles
How To Buy A Beginner Sailboat
Sail Maintenance For Beginners
Can a Novice Sail Around the World?
Daniel Wade
I've personally had thousands of questions about sailing and sailboats over the years. As I learn and experience sailing, and the community, I share the answers that work and make sense to me, here on Life of Sailing.
by this author
Best Sailboats
Most Recent

What Does "Sailing By The Lee" Mean?
October 3, 2023

The Best Sailing Schools And Programs: Reviews & Ratings
September 26, 2023
Important Legal Info
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies.
Similar Posts

Affordable Sailboats You Can Build at Home
September 13, 2023

Best Small Sailboats With Standing Headroom
December 28, 2023

Best Bluewater Sailboats Under $50K
Popular posts.

Best Liveaboard Catamaran Sailboats

Elizabeth O'Malley
June 15, 2022

4 Best Electric Outboard Motors

How Long Did It Take The Vikings To Sail To England?

10 Best Sailboat Brands (And Why)
December 20, 2023

7 Best Places To Liveaboard A Sailboat
Get the best sailing content.
Top Rated Posts
© 2024 Life of Sailing Email: [email protected] Address: 11816 Inwood Rd #3024 Dallas, TX 75244 Disclaimer Privacy Policy

- Find A School
- Certifications
- North U Sail Trim
- Inside Sailing with Peter Isler
- Docking Made Easy
- Study Quizzes
- Bite-sized Lessons
- Fun Quizzes
- Sailing Challenge

Dinghy Sailing vs. Yacht Sailing
By: American Sailing Sailboats
The kind of boat you choose to sail will define your relationship with the sport as a whole. Like wind and weather conditions, the boat is one part of the entire sailing experience. So what kind of boats are there, and which type is right for you? Many sailors transition from boat to boat depending on where they are and what sailboats they have access to, but many also stick to the same kind of boat for their entire lives! Here’s a quick overview of the two most common types of sailboats: dinghies and yachts.

Dinghy Pros:
- Athletic, good for keeping in shape
- Close to the water, exhilarating
- Builds skill set that allows you to sail any boat properly and even competitively
- There are tons of dinghy regattas, and rentals are available in many places for fun day sailing!
Dinghy Cons:
- Difficult for larger people who may not be able to fit comfortably in certain boats
- Can cause soreness and injury because of athleticism required, and can be difficult for older or less active people
- Less mid-level sailing available for adults. Fun, noncompetitive sailing and high level regattas are most common.

Yacht Pros:
- Fun and social because there are multiple people on board
- Open ocean sailing and longer races
- Chartering and traveling is possible with keelboat skills
- Many yacht clubs have weekly “beer can races,” fostering a strong yachting community
Yacht Cons:
- Much more difficult to store and maneuver
- Can be difficult to fully understand sailing by doing just your job on the boat
- Expensive to own and upkeep a keelboat
Make your own list of pros and cons to figure out what kind of boat you want to sail! Don’t let that list sit on our desk forever, though. Go sailing!
Related Posts:

- Learn To Sail
- Mobile Apps
- Online Courses
- Upcoming Courses
- Sailor Resources
- ASA Log Book
- Bite Sized Lessons
- Knots Made Easy
- Catamaran Challenge
- Sailing Vacations
- Sailing Cruises
- Charter Resources
- International Proficiency Certificate
- Find A Charter
- All Articles
- Sailing Tips
- Sailing Terms
- Destinations
- Environmental
- Initiatives
- Instructor Resources
- Become An Instructor
- Become An ASA School
- Member / Instructor Login
- Affiliate Login
- Paddle Board

A Guide to Dinghy Boats
Are you looking for an affordable boat for your fishing trips or watersports? The dinghy offers you the best options for a low-cost, versatile watercraft. There are several dinghy designs to suit any watersports activity.
Typically, dinghies are the best choice for watersports like skiing and diving. However, some models are good for cruising or light sailing, with options for motors or sails. A dinghy can range in size, but most of them are suitable for carrying two to six people.
Dinghies are available in models suiting use in freshwater or saltwater, with inflatables, solid boats, and more options. Is a dinghy the right choice for your boat? Let’s unpack everything you need to know about these watercraft.
What Is a Dinghy Boat?
A dinghy is a small boat, usually and inflatable, and most models are around five to ten feet long. A dinghy is easy to transport, and it offers versatile utility for fishing and watersports. You also have options for motors, sales, or you can use oars to propel the boat.
Dinghies can feature fiberglass construction, or they may use inflatable pontoons, similar to a pontoon boat. The inflatable models typically feature design and construction with Hypalon or PVC. These polymers provide UV resistance, tough resistance against punctures, and easy repairs.
The sides on inflatables also act as seats, allowing fishing directly from all sides of the boat. Dinghies are not really built for speed; they usually come with low-powered trolling motors with a 3-hp to 5-hp output. However, they are ideal for moving through estuaries and lakes, allowing for silent movement so you don’t disturb the fish.
What are the best beginner sailing dinghies?
If you’re just getting into sailing, there are several dinghy options for enjoying your time out on the water. Whether you want to sail solo or with a friend, there is a boat for you.
Training Sailing Dinghies
These models are easy to master, giving beginners the chance to master the complexities of sailboats. They are simple to operate, safe, and offer you the best option for learning to master sailing techniques.
Doublehanded Sailing Dinghies
These models cater to two passengers for handling the sail and rigging. They are great for learners, allowing them to take an experienced sailor out on the water to learn the ropes.
Singlehanded Sailing Dinghies
These models have a design for one person. Typically, they are smaller boats, and you’ll already have to know how to sail. However, they are easy to master, and spending time out on the water will familiarize you with the aspects of sailboats.
These dinghies feature double or triple hulls. They are typically the best choice for racing, and they offer excellent stability in all water conditions.
Different Types of Dinghy Models
As mentioned, there are several models of dinghies for different watersports activities. Here are the most common options; we categorized them into sailing dinghies and inflatable dinghies.
Sailing Dinghies
A sailing dinghy is a small sailboat with no fixed keel and a shallow draft. These models are ideal for sailing in lagoons, estuaries, and lakes, navigating shallow waters. The sailing dinghy typically features a fiberglass design, with an open-plan seating area and a mast. These boats usually accommodate anywhere from one to five passengers.

High-Performance Dinghies
High-performance sailing dinghies are another sail-based model that’s ideal for racing. They are fast and cut through the water with ease. You get excellent maneuverability on the water with a low-profile design and an open-plan deck with a mast. The Fireball, International 505, and Thistle are a few examples of leading racing and high-performance dinghies.
Cruising Dinghies
A cruising dinghy is another sail-based model that’s a great choice for cruising out in calm ocean conditions or inland water bodies. They are a recreational vessel equipped with sails and rudders, and you have more passenger capacity than the other sailing models. As a result, they are the ideal choice for family’s that enjoy the sailing lifestyle.
Cruiser-Racer Dinghies
These models are hybrids that come with a focus on performance and stability. They have the ability to race or to cruise, providing excellent stability in the water. They are a great choice for someone that wants to start sailing competitively, and they also work for fun recreational sailing days on the lake with the family. The GP14 is an example of a cruiser-racer offering high-performance standards and stable cruising.
Classic Dinghies
These boats had an original design featuring wood finishes using materials like plywood and cedar. However, modern dinghies feature fiberglass construction. The classic dinghy sailboat focuses on versatility over sailing performance. The Minto is a great example of a classic dinghy.
Inflatable Dinghies
Inflatables are gaining in popularity thanks to the affordable price tag and versatility offered by the boat. Inflatables are easy to carry, and some might even fit on the back of a truck. Inflatables have side pontoons, and many of them are suitable for diving activities or spearfishing. These dinghies usually feature low-powered trolling motors; they don’t have a design for speed.

Features and Benefits of Dinghy Boat
Dinghies are versatile and affordable. There are plenty of benefits for choosing this boat beyond just the savings you make over other models.
The dinghy is one of the few boats left that offer a sailing configuration. If you’re into boating on lakes or thinking about sailing competitively, the dinghy is the best choice. Any of the sailing models listed above are a great choice. Pick the boat that offers you the best utility for your sailing needs.
Minimal Noise
Most dinghies are sailing options, so you don’t have to worry about gas fumes from the motor or noise. They offer a serene sailing experience on inland waters. Inflatable models may use a trolling engine for moving through calm, shallow waters when fishing. The low noise and churn produced by the motors won’t scare off the fish. You also have options for poling and oars for moving around without engines.
Trailerable
Dinghies are compact boats with sailing and inflatable models offering you easy trailering. Some of the smaller inflatables can fit in the back of a panel van or on the load bed of your single-cab truck. They offer you easy transport between lakes and estuaries, with a lightweight design that’s easy to launch and trailer.
Options for Inflatables or Fiberglass
As mentioned, the dinghy comes in sailing and inflatable options. Some fiberglass models also feature a wood finish on the deck for an added aesthetic that looks like a classic dinghy.
Ideal as an Excursion Boat for Yachts
Many superyachts use inflatable dinghies allowing the passengers to reach the shore. Yachts can’t enter shallow water, and the dinghy makes the ideal transfer boat for reaching the coast from open water. Most of these models feature low-powered motors.
No Need for Registration
Larger vessels require registration before you can take them out on the water. However, dinghies are small, and they don’t need any registration or licensing before you can take them out on the water. As long as the boat doesn’t have a fixed motor and is less than eight feet in length, you don’t have to worry about doing the paperwork. Regulations differ between California and Florida, so check with your local authorities before taking your boat to the lake or slip.
Lightweight
The dinghy is a lightweight boat. The fiberglass and inflatable models offer you a lightweight watercraft that’s easy to launch and pull from the water. They are also easy to repair, with basic fiberglass or polymer patching.
Easy to Maneuver
The dinghy is a super-maneuverable boat. The sailing models are easy to tack in the wind, allowing for sharp turning radiuses and easy maneuverability on the water.
Complete sailing systems
Most sailing dinghies come with options for sail systems. If you want to learn the art of sailing or teach your kids about sailboats, the dinghy is the ideal starter vessel.
Suitable for use in Shallow Waters
The dinghy usually has a high draft and a shallow keel, allowing for sailing in shallow water, such as lakes. These boats won’t run aground, and the low hull design allows for less friction on the water, increasing speed and performance.
Save on Fuel
Sailing dinghies don’t have motors, so you save on fuel costs for your boating trips. Those inflatable models with trolling motors have low-capacity engines, and they are economical with fuel consumption.
Disadvantages of Dinghy Boat
The dinghy is a great choice for your first boat, especially if you want to tackle the art of sailing. However, they do come with some drawbacks.
Minimal Power and Small Motors
Since most models are sailboats, they rely on the wind for performance. Sure, some models can reach high speeds when the winds are right, but they lack a speed boat’s torque and on-demand power. Even those dinghy models relying on trolling motors don’t move very fast.
Limited Standing Room
The sailing dinghy doesn’t offer you any standing room. Sure, you can stand on the deck, but you’ll have to duck and manage the sail, and that could mean the boat tosses you overboard. The small size of the dinghy also means that you’ll unbalance the vessel if you stand on the deck.
Limited Seating
Dinghies are small boats designed for one to five passengers. Sure, you get bigger models, but these dinghies are more like proper sailboats. The seating may also be somewhat uncomfortable, as most models rely on a cast fiberglass deck with molded seats and no cushions.
No Crossover Function
Most dinghies are for sailing, and they don’t offer you crossover functions for fishing and watersports. It’s impossible to tow a skier, and the sail gets in the way of angling. The inflatable models are okay for fishing in shallow waters or inland water bodies, but the seating setup isn’t comfortable. The low-power trolling motors available for inflatable models don’t reach high speeds, making them unsuitable for watersports.
Limited Storage Space
Most dinghy models, especially sailing types, don’t come with consoles or storage systems. Some inflatables might have storage bins in the bow of the dinghy, but they typically don’t offer much storage space.
Top Dinghy Boat Brands and Models
Intex excursion 5.
The Intex Excursion 5 is a great example of an inflatable dinghy. You can seat up to five people in this model, and it has a rubber design with all the fishing accessories you need to get out on the water and enjoy a few hour’s angling in the lake.

You get four rod-holders, a bench-style seat in the boat’s center, and two inflatable seats.
This model comes with an affordable price tag and oars included with your purchase. There’s also the option of attaching a trolling motor for effortless navigation.
However, the boat is not suitable for standing, so don’t expect to cast far with this model. The boat comes with a three-chambered design and a 1,300-lbs capacity.
The Laser is the best choice for a single-hander sailboat dinghy. This boat is ideal for cruising or competitive racing, and they hold their resale value.
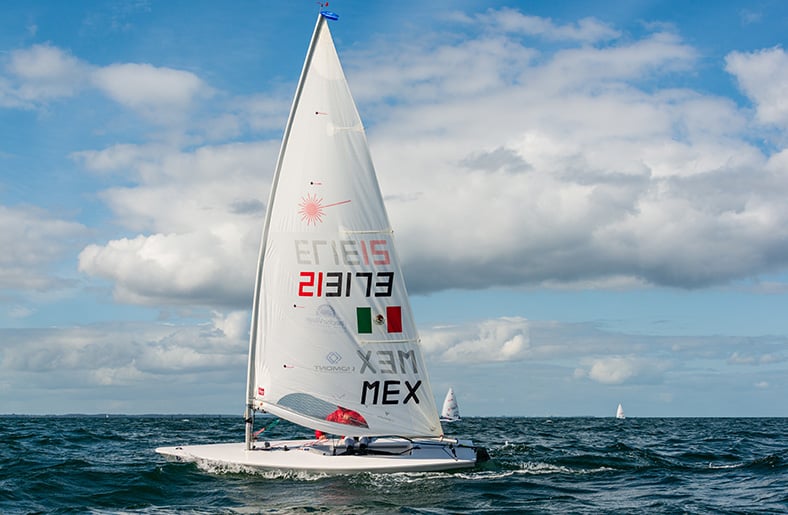

You get options for three rig sizes, the 4.7, Standard, and the Radial model. These boats feature fiberglass design and low hulls for easy navigation through shallow waters.
The RS Vision
This family sailboat makes a fantastic trainer, club racer, or cruising model. This boat can accommodate up to eight sailors, and the new RS Quest model features both trapeze and spinnaker options.
Wrapping Up
Dinghies are the ideal boat for learning how to sail, and they also make inexpensive boats for recreational fishing in inland water or calm ocean conditions.
They are not the most durable boats, and they don’t accommodate many people. However, there are plenty of models to suit your sailing experience or watercraft needs. However, they offer lightweight design, user-friendly operation, and choices for inflatable or fiberglass models.
If you’re looking to learn how to sail, you won’t find a better boat available.

John is an experienced journalist and veteran boater. He heads up the content team at BoatingBeast and aims to share his many years experience of the marine world with our readers.
A Complete Guide to Micro Skiffs: All You Need to Know!
A complete guide to narrow boats: all you need to know, a guide to aluminum fishing boats.
Comments are closed.
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.
Become the Confident Skipper of Your Own Sailboat
What’s a dinghy sailboat 5 things to consider.
- Post author: Anns
- Post published: October 25, 2022
- Post category: Uncategorized
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Introduction
Sailing is a great way to get outside and enjoy the sun. But if you don’t want to spend thousands of dollars on a boat that’s too big for your lake or river, then a dinghy sailboat might be the perfect solution. A dinghy sailboat is small enough for one person to sail but can also hold multiple passengers if necessary. They’re also easy to store when not in use, which makes them ideal for those with limited storage space or limited funds—or both!
What is a Dinghy Sailboat?
Dinghy sailboats are small, single-person boats with a sail to add power. Dinghies can be rowed or sailed, but if you’re new to the sport of dinghy sailing, it’s best to find a boat that has both options. Most dinghies have a rudder for steering and are made of lightweight materials like aluminum or fiberglass. The design of dinghies makes them easy to transport from one place to another because they don’t take up much space when deflated and stored away in bags until you want them again.
A dinghy sailboat is similar in many ways to a kayak: both types of boats are small enough for one person at a time; both have flat bottoms so they won’t tip over easily; both can float on water; and neither require much storage space once deflated (a major plus). However, there are some key differences between these two boats as well:
1. Do I want to sail or row?
The first question to ask yourself is whether you want to row or sail. Both types of boats are great, but they have their own advantages. Sailboats are faster and more fun to take out on the water, while rowing boats tend to be more efficient at transporting people across large bodies of water (and thus better for reaching destinations).
2. How many people will be sailing?
A dinghy sailboat should be able to hold at least one person. If you’re planning on sailing alone, or with just a friend, then the boat will need to accommodate both of you without being too cramped. On the other hand, if you want to row with three people (or more), then your dinghy sailboat should be large enough for everyone to sit comfortably and relax while rowing.
If there are no other sailors in your life who share your love of sailing and boating, don’t worry! It’s not uncommon for people who have never gone sailing before to purchase a single-person dinghy sailboat. These boats are smaller than most others in this category but still provide an exciting adventure that can be enjoyed by all ages!
3. Where will I store the boat?
It’s important to consider where you will store your boat. If you have a dinghy sailboat, there are two options: storing it on land or at sea.
If you choose to store your dinghy sailboat on land, then you’ll need a place that is protected from the elements and theft.
However, if you choose to store it at sea, then there are no worries about losing something valuable and having to replace it because everything was submerged in water when someone stole them!
4. What are the maintenance requirements of a dinghy sailboat?
A dinghy sailboat is a great option for anyone looking to purchase a boat that’s both fun and easy to use. While the upkeep of a dinghy may seem minimal, there are still some things you should know about before purchasing one.
- Regular cleaning: You should clean your dinghy at least once per week or after every time you use it, just like with any other boat on the water. A good way to do this is using mild soap and warm water, followed by rinsing with fresh water and then drying off everything completely before storing it away so as not to trap any moisture inside where mold could grow later on down the road (mold loves warm environments).
- Replacing sails and rigging: Sails can wear down over time due to UV damage from being exposed outside all day long in direct sunlight every single day during summer months; therefore they will eventually need replaced at some point during ownership if not sooner than later depending on how much exposure they’ve had throughout their lifetime thus far.”
5. Do I want to build my own or purchase one?
If you’re a DIYer, then building your own dinghy sailboat may be the best option. In fact, many people find that building their own is the most rewarding part of owning one. You can build it from scratch and customize it to fit your needs and style. There are many resources available online that can help you create the perfect dinghy sailboat for you!
However, if building isn’t really your thing and all you want is something functional and affordable (and maybe even faster than other dinghies), then purchasing one would be better suited for you! If you do want to purchase a dinghy sailboat instead of making one yourself, just make sure that they have all of the features listed above before buying so that they will work well with what type of water sports activities or hobbies they’ll be used for most often!
A dinghy sailboat is a small, easy-to-sail boat with a single mast and three sails. They’re best for single-person sailing but can hold multiple passengers if necessary.
The boat is usually stored on a trailer or on shore.
We hope this guide has given you a better understanding of what a dinghy sailboat is, how they work and what they’re used for. If you’re looking to purchase one, we recommend going with a reputable dealer who can answer all your questions about maintenance requirements before buying one.
You Might Also Like
10 benefits of sailing, some interesting things to consider when buying a sailboat, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Dinghy Guide 101
- Dinghies 101
Dinghies, also known as sailing dinghies or dinghy sailboats, are versatile and agile boats that have gained immense popularity among sailing enthusiasts worldwide. These small watercraft offer a thrilling experience on the water, making them a perfect choice for both beginners and seasoned sailors. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the world of dinghies, exploring different types, their benefits, and everything you need to know about sailing these charming vessels.
What are Dinghies?
Dinghies are small, open boats that are usually carried or towed by larger vessels. They serve a variety of purposes, such as transportation between a larger boat and the shore, recreation, racing, and as training boats for novice sailors. Due to their compact size, they are easy to handle and maneuver, making them ideal for navigating narrow waterways and crowded harbors.
Types of Sailing Dinghies
1. dinghy sailboats.
Dinghy sailboats are the most traditional and widely used type of dinghies. They come in various designs and materials, such as fiberglass, wood, or aluminum. Dinghy sailboats use the wind as their primary means of propulsion, with a main sail and, in some cases, a jib. These boats offer an excellent opportunity for learning to sail due to their simplicity and responsiveness to wind shifts.
2. Inflatable Dinghies
Inflatable dinghies, as the name suggests, are made from inflatable materials like PVC or Hypalon. These dinghies are incredibly lightweight and easily portable, making them popular among boaters who need a dinghy that can be deflated and stowed when not in use. Inflatable dinghies are also known for their stability and durability, making them suitable for various water conditions.
3. Rigid Dinghies
Rigid dinghies, often constructed from materials like fiberglass or aluminum, offer a stable and reliable sailing experience. They are sturdy and can handle rough waters with ease. Rigid dinghies are commonly used for fishing and exploring shallow waters, making them a versatile option for those who love to venture into remote areas.
Advantages of Dinghy Sailing
1. versatility and maneuverability.
Dinghies are incredibly versatile boats that can navigate in waters where larger vessels cannot venture. Their maneuverability allows sailors to explore hidden coves, creeks, and inlets that are off-limits to bigger boats, providing an opportunity for a unique sailing experience.
2. Learning to Sail
Dinghy sailing is an excellent way to learn the art of sailing. The smaller size and direct control over sails and rudder help beginners grasp sailing techniques quickly. Aspiring sailors can gain confidence in their skills, which can be later applied to larger boats.
3. Accessibility and Portability
Dinghies are easy to transport, launch, and retrieve, making them accessible to sailing enthusiasts without access to large marinas. Inflatable dinghies, in particular, can be deflated, folded, and stored in a compact bag, enabling sailors to take their dinghies wherever they go.
Dinghies for Sale: Finding the Perfect Boat
When considering purchasing a dinghy, several factors need to be taken into account.
1. New vs. Used Dinghies
New dinghies offer the advantage of warranty and customization, while used dinghies may come at a more affordable price. Evaluate your budget and preferences before making a decision.
2. Factors to Consider Before Buying
Consider the boat's size, material, and intended use. If you plan to sail in calm waters, inflatable dinghies might be a suitable choice. For more adventurous journeys, rigid dinghies might be the better option.
3. Top Brands for Dinghy Sailboats
Some renowned brands in the dinghy sailboat market include XYZ Sailboats, ABC Marine, and QRS Boats. Researching reputable brands can help you find a high-quality dinghy that meets your requirements.
Inflatable Dinghies: The Ideal Choice for Some
Inflatable dinghies offer unique benefits that make them the ideal choice for certain boaters.
1. Benefits of Inflatable Dinghies
Inflatable dinghies are lightweight, making them easy to carry and transport. They are also stable on the water, which is especially advantageous for anglers and divers who need a steady platform.
2. Top Features to Look for
When choosing an inflatable dinghy, consider features like reinforced hulls, multiple air chambers for safety, and convenient accessories such as oars and air pumps.
Sailing Dinghies Maintenance and Care
Proper maintenance is crucial to ensure the longevity and performance of your dinghy.
1. Cleaning and Storage Tips
Rinse your dinghy with fresh water after each use to remove salt and debris. Store it in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight to prevent damage to the material.
2. Common Repairs and Maintenance Tasks
Inspect your dinghy regularly for signs of wear and tear, and address any issues promptly. Common repairs may include patching inflatable dinghies or fixing minor cracks in rigid dinghies.
Read our top notch articles on topics such as sailing, sailing tips and destinations in our Magazine .
Check out our latest sailing content:
How to sail a dinghy: a beginner's guide.
Sailing a dinghy is a rewarding experience, but it requires some basic knowledge and skills.
1. Essential Sailing Techniques
Learn the fundamental sailing techniques, including tacking, jibing, and adjusting sails according to wind conditions.
2. Safety Measures and Precautions
Always wear a life jacket and familiarize yourself with safety procedures. Be aware of weather conditions and avoid sailing in rough waters or adverse weather.
Exploring the World of Dinghy Racing
Dinghy racing is a thrilling and competitive sport that attracts sailors of all ages.
1. Dinghy Racing Basics
Dinghy racing involves navigating a set course as quickly as possible, using tactical skills and wind knowledge to gain an advantage over competitors.
2. Joining Dinghy Racing Clubs
Many sailing clubs offer dinghy racing programs, providing an opportunity to socialize, improve sailing skills, and compete with like-minded individuals.
The Rising Popularity of Inflatable Sailing Catamarans
In recent years, inflatable sailing catamarans have gained popularity for their unique design and features.
1. Advantages of Inflatable Catamarans
Inflatable catamarans offer increased stability and a spacious deck, making them suitable for leisurely sailing and family outings.
2. Top Inflatable Catamaran Models
Notable inflatable catamaran models include the XYZ SailCat 2000 and ABC Marine CataraYacht. These innovative designs provide an exceptional sailing experience.
Dinghies offer a world of adventure and excitement for sailors of all skill levels. Whether you're exploring serene lakes or embarking on thrilling races, the versatility and accessibility of dinghies make them an ideal choice for water enthusiasts. With the information provided in this guide, you can confidently set sail on your journey to embrace the joy of dinghy sailing.
So what are you waiting for? Take a look at our range of charter boats and head to some of our favourite sailing destinations.
I can help you choose the right boat for your holiday. Contact me.

Denisa Kliner Nguyenová
Faq for dinghies and sailboats, can i sail a dinghy alone, are inflatable dinghies safe for open waters, what is the average cost of a dinghy sailboat.
Better Sailing

Dinghy Sailing: Beginner’s Guide
Sailing on a Dinghy or Small Boat is a good choice in learning how to sail. This is because Dinghies are simple, easy to maneuver, and very responsive to your actions as well as to Wind conditions. Sailing on a Dinghy will give beginners a sort of training ground – they will learn the basics and understand the different important aspects of the sport.
Learn what this Sailing Variation is all about. The following sections will give you some insights on the various features of Dinghy Sailing:
Dinghies – Types and Classes
Sailing History indicates that Sailing was used for trade and transportation before it became a source of enjoyment. It was in the late 1900s that people began using Small Boats for leisure and sport.
The term ‘Dinghy’ is from India, which means ‘small’. A Dinghy is a small Sailboat designed to accommodate one or two persons and is usually used in recreational Sailing. It is powered by wind, outboard motor, or paddles.
In general, Dinghies are classified according to their purpose. They come in many types and features which suit different conditions.
In this section, know the numerous Dinghy Types and Classes:
Basic Types
- General – Purpose Dinghies : Dinghies under this type are most appropriate when learning the very basics of Sailing. These are usually used for leisure and enjoyment. Wayfarer is an example of a General-Purpose Dinghy. It is less than 16 feet long and is often used for short trips. Other examples include Mirror and Enterprise.
- Skiffs : Considered as the fastest Dinghy Type, a Skiff is a flat-hulled open Dinghy which can accommodate one or two persons. It can be powered using oars or a motor. Examples of Skiffs are Musto Skiff, 49er, Jersey Skiff, and 18ft. Skiff.
- High-Performance Dinghies : Dinghies under this type are fast and are used primarily for Racing.
- Racing Dinghies : As the name suggests, Dinghies under this type are used primarily for Dinghy Racing.
Here are some Classes of Dinghies:
- Laser Radial
- Jersey Skiff
These are the basic Dinghy Types and Classes. Take note that each one has its own features and is designed for a particular purpose.
Dinghies – Care and Maintenance
A Dinghy can be subjected to a lot of elements that can contribute to wear and tear over time. Thus, make the necessary steps to take care of your Dinghy after sailing in order to maintain its good performance every time you go onboard.
There are several things to do as far as proper care and maintenance is concerned. In this section, know some guidelines on how to take good care of your Dinghy:
- Once the Dinghy is ashore, rinse it thoroughly with fresh water.
- After washing the Rudder, Centerboard, and/or Daggerboard, store them in their respective bags.
- Make regular inspections so that damages or problems (if any) will be attended to before they become worse.
- Make sure to run repairs on parts that need to be fixed.
- Lay the Mainsail out on a clean, flat surface.
- Fold the top over onto the body of the Sail. Roll the Sail carefully and make sure that the roll is at right angles with the Leech.
- After rolling the entire Sail, put it in a sail bag.
- You can use a trolley to store your Dinghy. Tie the boat securely on the trolley. Put the detachable items inside the Dinghy. Fit the boat cover over the top and make sure that it is fastened firmly. Secure it under the Hull, Bow, as well as the sidedecks. To prevent your Dinghy from being blown over, tie the Sailboat down to securing points on the ground.
- Put your Dinghy in an area where it can be safe and secure. Dinghies can be left at Dinghy parks in many Sailing Clubs.
These are some tips on how to take care of your Dinghy and keep its good working condition. Regular checks and inspection on the components of your Dinghy can help ensure its good performance every time you go sailing.
Small Sailboat Buying Guide – How to Buy Dinghies
Dinghies and small Keelboats come in a wide range of features. Each is made and designed for a particular purpose to suit the needs of so many fans of Small Boat or Dinghy Sailing. However, there are many models that can be used for other types of Sailing besides the one in which it is designed for.
As a beginner, you need not buy a Dinghy or a Small Keelboat. Buy one when you have already tried different Dinghies and other Sailboats, and if you know by now the Sailing Variation that attracts you most.
In this section, know the different things to consider in buying Small Boats:
- Consider your skill and experience : Obviously, Sailing will be much more fun and a lot safer if your Sailboat is suitable to your skill as well as experience. Many Dinghies and small Keelboats have features that make them a bit more complex compared to other boats of the same type, therefore requiring more techniques. Hence, take your level of skill and know-how into consideration. Make sure that you and your Small Boat are well-matched to each other.
- Decide what Sailing Variation interests you most : Suitability is very important. As mentioned earlier, each Dinghy or Small Keelboat is designed for a particular type of Sailing. Therefore, make up your mind on what sort of Sailing attracts you most.
- Make some research : There are so many information resources available that can give you some ideas on the features of different Small Boats. Magazines and websites related to Sailing are good sources of information that you need.
- Get some advice : Experienced sailors can give you pointers on the advantages and drawbacks of a number of Small Boats. It is likely that they have tried several boats with varying features so they will be helpful in choosing the right Small Boat for you.
Make use of our Small Boat Buying Guide, as these pointers can help you in buying Dinghies. Take your time in the selection process. Look at several types and check the features of each one. Choose the one that suits your needs.
You can also read the “ How to Right a Capsized Sailboat ” article for this essential information if you thinking of starting Dinghy Sailing.
Dinghy Sailing Beginner’s Guide – Conclusion
It is obvious that knowing the essentials of Small Boat Sailing is crucial should you wish to pursue this Sailing Variation. Aside from the fact that you will learn different skills, the more important thing is that the learning process is a fun and exciting experience.
Peter is the editor of Better Sailing. He has sailed for countless hours and has maintained his own boats and sailboats for years. After years of trial and error, he decided to start this website to share the knowledge.
Related Posts

Atlantic vs Pacific: Which is More Dangerous for Sailing?

Why Do Sailboats Lean?

How Does a Boat Sail Upwind? Unveiling the Mechanics of Against the Wind Sailing

How Does Sailing Work? The Physics of Sailing
- Buyer's Guide
- Destinations
- Maintenance
- Sailing Info
Hit enter to search or ESC to close.
Types of Dinghies: How to Pick the Right One For You
While getting there is half the fun for a sailor, the other half is getting off the boat when you get there. Unless you spend every night in a marina or only go to harbors with launch services, you will need a dinghy.
So what is the right dinghy for you? If you plan to row, a hard dinghy may be the best option. For larger crews or families, inflatables with an outboard are more popular; the style will depend on storage needs. If you want to row, sail or motor, several hard dinghies fit the bill. Budget-conscious sailors should look at soft tail inflatables and inexpensive rowing dinghies.
To make an informed decision, you need to know your options and put some thought into how you will use it. Read on for an overview of your choices, and what to take into consideration as you decide.

On this page:
Types of dinghies, hard dinghies, inflatables, which is right for you.
When we're talking about a "dinghy," we're talking about a tender . This is a support boat you carry or tow to get you and your gear from land to the water and back again. We're not talking about dedicated sailing dinghies like Lasers, Optimists, or other sailing-only boats.
Technically, you can use a kayak or paddleboard to get to your boat and back, and some people do. But as a practical matter, if your boat is on a mooring or at anchor and you have to move your spouse, two kids, a cooler full of food, two bags of clothes and a sack of toys out to the boat, then get everyone off the boat to a beach with towels beach gear when you arrive, a kayak will not cut it.

A hard dinghy is the oldest and simplest style of tender, and they come in a variety of shapes, sizes, materials, and capacities. Most hard dinghies row very well, and most can be fitted with an outboard. Some hard dinghies can sail, which is a pleasant bonus and lets it double as a water toy. But a sailing dinghy as a primary choice has limitations based on winds and current, and a dinghy rigged to sail carries fewer people and less gear to make room for masts, booms, daggerboards and tillers.
When considering a hard dinghy, give serious thought to the construction material. Roto-molded plastic, PVC, fiberglass, and aluminum will usually be lighter than wood, but there are always tradeoffs. Dragging a boat up on a rocky beach will scratch all but the most rugged hulls. But many prefer the classic styling of a painted dinghy in pristine trim and have no plans to pull it over rocks or send it into a melee of splashing, rowdy cruising kids.

Materials and construction affect not only the durability of a hard dinghy, but the price. For example, you pay a premium for the near-indestructible and versatile Portland Pudgy, but a molded boat at a quarter of the cost may not last as long. Pay attention to weight and ergonomics like handles and wheels, since you may have to haul this boat up a beach or onto your boat.
Most hard dinghies have limited carrying capacity compared to similar sized inflatables and are less stable when boarding and loaded. This has much to do with the form stability of a hard hull versus tubes; a pair of big inflated tubes are hard to tip.
Hard Dinghy Pros
- Well suited to rowing and track well.
- Can usually take an engine and/or an optional sailing rig.
- Can not be punctured on docks or rocks.
- Tow very well, though you don't want to flip them.
- There are some very inexpensive options.
Hard Dinghy Cons:
- Capacity for gear and people is more limited.
- They can be tippy, especially when loaded.
- Some materials will get scraped and gouged on beaches and rocks.
- Can cause damage or get damaged by contact with the big boat.
Examples of Hard Dinghies
- Walker Bay - Injection-molded, polypropylene hull with an option sailing rig and inflatable tubes (for added stability) that can take a small engine. 8' and 10' models. Check it here.
- Portland Pudgy - Roto-molded polyethylene, a rugged dinghy which can take an outboard and has upgrade kits for sailing and use as a four-person life-raft. Check it here.
- OC Tender - Lightweight, high-performance carbon fiber planing dinghy. Not made for rowing, but stable planing with lower horsepower engines. Models from 8'9" to 11'6". Check it here.
- Fatty Knees - Traditional looking fiberglass hull with optional sailing rig. Sizes from 7' - 9', can also accommodate a small outboard. Check it here.
- Trinka - Fiberglass rowing and sailing dinghy, available in 8' and 10' models. Check it here.
Besides these, there are dozens of low-cost plastic, aluminum and wood rowing dinks available new and used. Nesting dinghies break down for compact storage, but usually must be bought as kits or plans and built.

Most cruising sailors use inflatable dinghies for their stability and carrying capacity. It's tough to beat giant rubber tubes for stability, though the tubes create a lot of drag moving through the water this is offset with engine horsepower and planing-form hulls.
An inflatable dinghy has several air tubes (from one to three, though most have multiple tubes) attached to a hull and most often floor. They also come in a variety of configurations, from soft bottomed inflatables without floors or transoms to large RIBs (Rigid Inflatable Boat) which attach the tubes to a stiff hull made of fiberglass or aluminum.
All but the lowest end inflatables will have a floor, and most will have a seat, though the tubes are usually the best seats. Some models are easier to deflate and pack, but most are kept inflated for ready use as filling and emptying them is a chore. Most inflatables row poorly, but can be rowed if the engine fails.
A major advantage of all inflatables is they bounce off the mother ship, whether you come in a little too hot with the engine or things shift in the night and the big boat bumps the dinghy. You'll be spared the hard thump in the night, but most importantly, you won't crunch fiberglass or gouge gel coat if you hit your boat or another while going too fast.
The least expensive variety. These boats do not have transoms. Even without a transom, they do have a bracket for a small outboard.
Advantages: lightweight, cheap, compact when deflated. Disadvantages: Small, low carrying capacity. Easily punctured if beached. Do not track well rowing or powering.
Soft Bottoms

Soft bottom dinghies will have a transom to take an engine and a floor. Under the floor, there is an inflatable keel to help the boat track through the water, but some may be flat and will not steer well. Lighter soft bottoms still have decent cargo capacities, and often more than a comparable length RIB as the boat is lighter. However, they cannot take the same horsepower engine so they will be slower.
Some models have slats, boards or panels for a floor over the keel tube. The hard floor is the simplest to maintain but doesn't break down for storage.
Inflatable floors are another choice for soft-bottoms; they're lighter, and you can roll the boat up without removing the floor. An inflatable floor can get punctured and must be inflated to a very high pressure to maintain stiffness.
A roll-up inflatable will have a soft bottom and inflatable keel, with a segmented, hard floor installed. The boat rolls for storage, either for passages or the offseason. From my experience owning one, getting it to roll to a neat package for a weekend trip is not as easy as you'd think.
Advantages: Lighter than RIBs, can compact when packed properly. Can plane in some conditions. Intermediate pricing compared to RIBs. Disadvantages: Floor and bottom puncture easily on rocks and sharp shells. Must be maintained at peak inflation for good operation (don't let the floor and keel get soft!).
Rigid Inflatable Boats (RIB)

The RIB has become the de facto choice for most serious cruisers. They are also popular with coastal sailors and weekenders because they are comfortable, dry, plane easily, and can be beached with little risk to the boat. They have great payload for their size and are near impossible to tip. The rigid hull allows for higher horsepower engines and greater speeds.
Since they can not be deflated and packed, the RIB is more popular on larger boats. Davits help with an always inflated boat, though they are often stored without the engine ahead of the mast, lashed upside down to the deck. Towing is a good option for shorter trips in mild conditions if you remove the engine, but is not appropriate for offshore trips.
They typically build RIB hulls from fiberglass or aluminum. Aluminum is lighter and stronger, but more expensive. Larger RIBS will have a floor for comfort, which may be sealed into a chamber or double floor on fiberglass boats. Most aluminum RIBs end the floor before the transom instead of creating a second sealed compartment.
Advantages: With a rigid hull, these boats are quicker and easier to handle. They're also rugged if beached, can plane quickly, and have great stability. Disadvantages: The heaviest of the inflatables, and the most expensive. Can't be folded up or put away, so storage and handling is more challenging.
Tube Size, Cloth Choices, and Chambers
When picking an inflatable, the tube size , cloth used in construction, and the chamber layout of the tubes is an important consideration.
For tube size, the larger the tube, the more comfortable the ride. Large tube dinghies are more comfortable to sit on, but the larger tubes also deflect more water away from the inside of the boat in splashy conditions with spray. A larger tube may have more drag and may have less interior volume for gear and people.
Two cloth materials are used in construction - PVC (polyvinyl chloride) or Hypalon, a synthetic rubber. PVC is less expensive but subject to quicker ultraviolet degradation from sunlight. Sailors in tropical climes prefer Hypalon since it lasts longer. Most seasonal sailors in more temperate climes get better life from PVC, though it still doesn't last as long as Hypalon. Dinghy chaps will extend the life of either cloth.
Finally, make sure your dinghy has at least two air chambers in the tubes, though three is better. You don't want one tube because if it punctures you have little reserve buoyancy. Over three chambers makes sense only in much larger boats than the typical cruising tender.
Inflatable Pros
- Very stable and easy to get in and out of and work on.
- High cargo capacities, up to double similar sized hard dinghies.
- Most have good performance under power.
- Won't damage or get damaged by fiberglass boats on impact.
Inflatable Cons
- Tubes can get punctured and will degrade in sunlight. Can develop hard to find and fix leaks.
- Soft bottoms are tricky to beach on anything but soft sand.
- There aren't many very low budget options.
- They row poorly.
Inflatable Examples
These are representative boats from a few manufacturers. Each one has product ranges covering almost all the inflatable types mentioned above, though not everyone makes a soft tail.
- Achilles LT Series - Soft tail dinghy with oars and an engine mount for up to 3Hp. Check it here.
- Zodiac Cadet - Soft bottom hull with several options for rolling or rigid floor. Check it here.
- West Marine PHP-275 Performance Air Floor - Lightweight air-floored PVC boat with a soft bottom and decent cargo capacity. Check it here.
- Highfield CL310 - Aluminum hulled RIB, available in Hypalon or PVC. Check it here.
The best call for you comes down to these questions:
- What is your budget? Don't forget to include an engine in that figure.
- How many adults and children are you moving?
- Do you want to row, power, and/or sail?
- Do you expect to anchor or moor some distance from shore landings?
- How often do you expect to use it?
- Do you plan other activities for your tender, like watersports, exploring distant locations, fishing, or sailing?
- How big is your primary pleasure craft? Do you have room to store a boat on board or install a storage system like davits?
- What type of waters do you sail? Inshore and protected, or offshore in larger waves?
These are questions only you can answer. A fifty-foot boat with a family of five will want a sturdy rib, but a solo sailor in a twenty-six-foot boat who likes to row for exercise will have a very different need. So pick what works for you and your boat.
If you're thinking about buying a dinghy, be sure to check out my article on How Much a Dinghy Costs (with 14 examples ). There, I'll discuss fourteen good dinghies, go over their properties, and list the price.

Leave a comment

Dinghy Sailing vs. Sailboat Sailing
Dinghy sailing vs sailboat sailing are very similar, but there are a few key differences. Dinghy sailing is done in small boats, while sailboat sailing is on larger boats. Dinghy sailing utilizes much smaller sails or no sails at all, while sailboat sailing requires much larger sails.
Dinghy sailing is typically done in only 1 to 2 feet of water, while sailboat sailing can be done in almost any water level. Dinghies are typically much easier to maneuver than sailboats and can make tight turns without tipping over.
Dinghy and sailboat sailing are two popular types of water sports. So which is better and you’ll enjoy it more? Well, if you want to know, then read this article because this article has covered everything dinghy sailing vs sailboat sailing.
What Is Dinghy Sailing?
Dinghy sailing is a form of sailing in which a small, lightweight boat is used. Dinghies are typically between eight and twelve feet in length and can be sailed by one or two people.
Dinghy sailing is a popular sport in many parts of the world and is often used as a training ground for larger yacht racing. Dinghies are relatively easy to sail and can be sailed in a variety of conditions.
Dinghy racing is a competitive sport, with races being held at both club and national levels. There are a variety of different classes of dinghy, with the most popular being the Laser, Optimist, and 420.
Dinghy sailing is a great way to enjoy the outdoors and can be a very rewarding experience. It is also a great way to meet new people and make new friends.
Types of Dinghy Sailing
A dinghy is a small, lightweight boat, typically propelled by oars, sails, or a motor. Dinghies are usually used for recreation, racing, or as a tender to a larger vessel.
There are four main types of dinghy sailing:
These dinghies are designed for speed and maneuverability. They are typically lightweight and have large sails to maximize their speed potential. Common racing dinghies include the Laser, Hobie Cat, and Optimist.
2. Cruising
These dinghies are designed for comfort and stability. They are typically larger and heavier than racing dinghies and have smaller sails to make them easier to handle. Common cruising dinghies include the Sunfish, Catboat, and Daysailor.
What is a fishing boat ? Well, it’s a boat which have designed for catching fish from the sea and fishing dinghies are designed for stability and storage. They are typically wider and have more storage space than other types of dinghies. Common fishing dinghies include the Bass boat, Jon Boat, and Pontoon boat.
Utility dinghies are designed for a variety of purposes. They are typically the largest and most versatile type of dinghy. Common utility dinghies include the RIB, Inflatable, and Tender.
What Is Sail Boat Sailing?
Sailboat sailing is the act of moving a sailboat using only the power of the wind. Sailboat sailors use a variety of techniques to harness the wind and propel their boats forward.
The most important piece of equipment for sailboat sailing is the sail. Sailboats have one or more sails that has mounted on masts. The sails have made of a variety of materials, including cloth, canvas, and Kevlar.
Sailboats also have a variety of other sails that used for different purposes, such as spinnakers and jibs. Sailboat sailors use the wind to their advantage to move their boats forward.
They use a variety of techniques to do this, including tacking and jibing. Tacking is when the sailor turns the bow of the boat into the wind. This causes the wind to push against the sails and move the boat forward. If you are a beginner sailor , you should have idea about sailing.
Types of Sail Boat Sailing
There are four main types of sailboat sailing: traditional sailing, and kite sailing.
1. Traditional
Traditional sailing is the most common type of sailboat sailing. It involves using the wind to power the vessel forward by filling the sails with air.
Kite sailing is a newer form of sailboat sailing. It involves using a kite to power the vessel forward. The kite also attaches to the sailboat by a tether, and the vessel controls by a rudder. Kite sailing uses for recreation and travel.
Dinghy Sailing vs Sailboat Sailing
Eight key differences between dinghy sailing and sailboat sailing:
A dinghy is a type of small boat, often carried or towed for use as a lifeboat by a larger vessel. Dinghies usually range in length from about 2 to 6 m (6.6 to 19.7 ft.) and can carry from 1 to 8 people.
Sailboats are much larger than dinghies, typically ranging in length from about 20 to 50 feet (6 to 15 meters). They can carry 8 to 10 people or more.
Dinghies are small, lightweight boats, and they propel by wind power alone. This means that they are extremely maneuverable, but they can also be quite difficult to control in high winds.
Sailboats, on the other hand, are much larger and heavier. They have attached to engines, which give them more power and make them much easier to control.
Dinghies also have a shallower draft than sailboats, which means they can sail in shallower waters. And because they’re lighter, they’re less stable than sailboats and can be more difficult to control in high winds.
Sailboats, on the other hand, have designed for longer voyages and can accommodate more people. They’re also heavier and have a deeper draft, which allows them to sail in deeper waters.
And because they’re more stable, they’re easier to control in high winds.
Sailboats typically have much larger and more luxurious cabins than dinghies, and they often equipped with full kitchens, bathrooms, and bedrooms.
This makes them ideal for longer sailing trips or for live-aboard sailors. Dinghies, on the other hand, usually have small, simple cabins or none at all. This makes them better suited for day sails or racing.
Sailboats typically have more storage space below deck than dinghies. This is because sailboats are larger overall and have more room for storage. Sailboats also usually have a dedicated storage area for sails, while dinghies typically do not.
This is because sails take up a lot of space and need to store in a way that protects them from the elements. Finally, sailboats typically have more onboard amenities than dinghies, which means they require more storage for things like food, towels, and dishes.
There are a few key differences between dinghy sailing and sailboat sailing, and the most notable is the size of the vessel and the number of crew required.
Dinghies are much smaller than sailboats and usually only require one or two people to operate, whereas sailboats are larger and typically require a crew of four or more.
7. Maneuverability
Dinghies are much lighter and easier to maneuver than sailboats. This is because they have a smaller hull and less weight overall.
Dinghies have a shorter keel, which makes them more maneuverable than sailboats. This is because the keel provides stability and resistance to wind forces. Third, dinghies have a higher center of gravity than sailboats.
Dinghies are small, light, and sleek, which makes them much faster than your average sailboat. They also don’t have all the extra gear and equipment that a sailboat carries, which further adds to their speed advantage.
Dinghies have sailed with the wind behind them, while sailboats have sailed with the wind in front of them. This means that dinghies can tack much closer to the wind than sailboats, giving them an even bigger speed advantage.
Hopefully, you’ve got your answer about dinghy vs sailboat sailing, and we’ve inspired you to consider a dinghy sailing experience sometime soon. If so, good for you! Dinghies are truly fascinating boats, and they can offer plenty of thrills when you learn to sail them.
The next time the weather is nice, I recommend that you look into renting or borrowing one!
Saiful Emon is the founder and editor of Sun Sea Skis , a sailing blog for adventure seekers. He loves sailing, traveling, and sharing his experiences with others. He also writes about fitness, wellness, business, and marketing in his spare time!
What Is the Difference Between Sailing Ship and Steamship?
Sailboard vs. paddle board: what are the differences.

The Definitive Guide to Different Types of Dinghies

If you’ve ever gone out sailing or are just starting out, you’ve probably had the opportunity to get onto a dinghy to scoot yourself around. Dinghies can be extremely useful and fun at the same time whether you’re on a sailing dinghy or a power dinghy. The first time I ever got on a dinghy was a two person sailing dinghy, which is exactly when I started learning how to sail.
So what are the different types of dinghies? The different types of dinghies include sailing dinghies and power dinghies. Sailing dinghies have sails and do not have any type of motor attached to them and power dinghies have no sails and rely on motor power to move through the water.
When it comes to a dinghy, don’t let the size fool you. These little vessels can catch some serious speed and are central to many boating competitions around the world.
However, sailing dinghies and power dinghies usually serve different purposes, so let’s dive into the different types of dinghies to get a better understanding.
Sailing Dinghies
Sailing around on a dinghy is one of the more overlooked styles of sailing since everyone seems to want to get on a bigger yacht.
While there’s no arguing against the feeling of sailing on a larger vessel, dinghy sailing is a lot of fun which requires a good understanding of sailing fundamentals and an eye for precision.
High-Performance Dinghies
A high-performance sailing dinghy is as the name suggests; high-performance.
Its design is optimized to produce a fast and powerful sailing dinghy that can perform well in many environments and is often found in top regattas around the world. As you’ll soon realize, most sailing dinghies are constructed using fiberglass.
High-performance sailing dinghies usually have a spinnaker that can be attached to the sailboat so as to improve the speed of the boat under the right conditions.
Along with that, these sailing dinghies have what’s called a trapeze which is a wire that’s attached to the top of the mast and comes all the way down to the sailor’ harness.
This allows you to balance the force of the wind against the sail when the weather really kicks in.
Racing Dinghies
As you might have assumed already from the name, racing sailing dinghies are used primarily in racing environments.
While not too dissimilar to a high-performance sailing dinghy, there are some differences in terms of size, weight, and shape of the hull.
The design of a racing sailing dinghy is very important, but the skills of the crew on-board are usually what matters the most. Again, these types of sailing dinghies are made out of fiberglass.
The tactics implemented by the crew on a racing sailing dinghy are incredibly important. A racing sailing dinghy allows for crews to take advantage of the dinghy’s design so that they can tack and jibe much faster and more fluid than other dinghies.
On top of that, the hull of a racing sailing dinghy is quite flat which allows it to plane much easier resulting in a reduction of hull surface area touching the water.
Cruising Dinghies
If you’re not looking to compete with a racing or high-performance sailing dinghy, then you’re more likely to be sailing around in a cruising sailing dinghy. As the name suggests, they are made to cruise around the water and comfortably at that.
Designed for stability and safety in mind, cruising sailing dinghies are one of the most leisurely dinghies to take out on the water. Cruising dinghies are almost always made out of fiberglass.
As opposed to the previous sailing dinghies, cruising sailing dinghies generally have smaller sails and a more round hull .
As you might have guessed, the smaller the sails the less potential energy (and thus speed) your dinghy has.
The smaller sail also makes it easier to handle while cruising along. When it comes to the hull, a rounder hull also brings stability to the sailing dinghy as well as a very low chance of planing since there’s more contact between the hull and the water.
Cruiser-Racer Dinghies
If you have an inkling for racing but want to just cruise around comfortably from time to time, using a cruiser-racer sailing dinghy is an excellent choice.
These sailing dinghies are perfect for many different sailing environments and are my preferred type of sailing dinghy. It’s extremely common to find cruiser-racer dinghies made out of fiberglass.
Just like a cruising dinghy, the experience of being on a cruiser-racer dinghy is comfortable and provides good stability when out on the water.
However, if you want to turn up the notch and get it moving quickly, you can do just that since they have flatter hulls and generally larger sails. In the end, a cruiser-racer dinghy is right smack dab between a racing and cruising dinghy.
Classic Dinghies
If you’re looking for a classic experience on a sailing dinghy, then why not try out a… classic!
Classic dinghies can be found more often than you might think and can be fun to learn on when just starting out.
While you definitely won’t get the same performance as the other types of sailing dinghies, they’re quite comfortable and easy to use.
As opposed to most sailing dinghies, classic dinghies can be found to be made out of wood but usually they’re made from fiberglass.
Classic dinghies are unique in the sense that they have a cat sail and mast configuration . A cat, or “catboat”, has a single sail connected to a mast positioned at the bow of the sailboat.
Again, this makes them very easy to use and can be a great way to start learning how to sail. Also, I think they look rather nice, so beauty definitely plays a bit of a role in using a classic dinghy.
Power Dinghies
Before setting sail and exploring the beautiful waters of the world, you’ll want to make sure you know what kind of dinghy you have on-board.
As opposed to sailing dinghies, larger sailboats often times will have a power dinghy on-board in case you and your crew need to scoot around the local area quickly and easily.
Also, if you ever plan on anchoring out anywhere, it’s helpful to have a power dinghy to get to and from shore or to simply explore the surroundings.
The main differentiating factor between one power dinghy and another is the type of motor. More often than not, you’ll find dinghies with outboard motors, but that doesn’t encompass ever power dinghy out there.
Outboard Motor
As I just mentioned, the most common type of motor you’ll find on a power dinghy is an outboard motor.
Simply put, an outboard motor is attached on the backside of the power dinghy by means of a stern bracket and clamps or by bolts and nuts. Most outboard motor are powered by gasoline/petrol, however I’ve been on plenty of electrically powered dinghies when out fishing.
Outboard motors are popular because they’re relatively easy to maintain and can be replaced quickly if they crap out.
They also can be tilted up while still propelling your power dinghy forward, which allows you to cruise around shallow water without having your motor’s propellers hit the ground.
Your outboard motor can be either 2-stroke or 4-stroke. A 2-stroke motor requires mixing the gasoline/petrol with oil (most of the times this is automatic) and are generally less expensive to purchase.
A 4-stroke motor doesn’t require an oil-gasoline/petrol mix and is usually quieter, smoother, and more environmentally friendly, however more expensive to buy.
Inboard Motor
It’s not common that you’ll find a power dinghy with an inboard motor. However, you might see them if you’re on a power dinghy that holds 10 or more passengers and if the power dinghy is heavier in weight.
An inboard motor is fitted inside the power dinghy, so working on it or replacing it is a much larger hassle compared to an outboard motor.
Since power dinghies with inboard motors are quite heavy, you won’t find them on most sailboats. You will see them on shores where people are being taxied around as well as on-board much larger water vessels like megayachts.
Jet Drive Motor
Another type of dinghy motor is the jet drive motor, which, like the inboard motor, isn’t the most common type of motor to see on a power dinghy.
Similar to an inboard motor, a jet drive motor is generally built into the power dinghy making it more difficult to maintain and replace.
However, having a jet drive motor has its advantages and disadvantages. One advantage is one of safety being that, similar to a jet ski, a power dinghy with a jet drive motor doesn’t have propellers meaning nearby swimmers are much safer.
A major disadvantage to jet drive motor is that they can easily get items stuck inside of them, like plastic bags, jellyfish, and more, resulting in the motor shutting down.
Dinghy Materials
Apart from a power dinghies motor, another major differentiating factor when it comes to power dinghies is the material it’s made out of.
While the most common types of power dinghy you’ll find nowadays are inflatable, there are still plenty of solid material power dinghies out there.
If you’re on a power dinghy, there’s a good chance that it’s an inflatable power dinghy. There are several advantages of using an inflatable power dinghy especially that they’re easy to stow and less likely to damage vessels when they coming alongside.
A major disadvantage to using an inflatable power dinghy is that, unlike solid materials, they’re easier to puncture by reefs, sticks, and other sharp debris.
Fiberglass and Metal
Power dinghies that are made out of solid materials are often made out of either fiberglass or metal. While these types of materials aren’t as common nowadays for a power dinghy onboard a sailboat to have, they certainly aren’t rare.
The main advantage of having a power dinghy made out of fiberglass or metal is that it’s highly unlikely to be punctured compared to an inflatable power dinghy.
Some disadvantages include the fact that they can be heavy and they can scratch a sailboat’s hull when coming alongside.
Unless you’re a collector of classic dinghies, whether power or sailing, you won’t find many dinghies made out of wood nowadays.
Certainly, they exist but on much rarer occasions. The main advantage of a wood power dinghy is that it can look classy and antique-like while also not easily puncturable.
However, the downsides include those of the fiberglass/metal power dinghies as well as it being susceptible to leaks and having a greater maintenance cost compared to other power dinghies.
Get the very best sailing stuff straight to your inbox
Nomadic sailing.
At Nomadic Sailing, we're all about helping the community learn all there is to know about sailing. From learning how to sail to popular and lesser-known destinations to essential sailing gear and more.
Quick Links
Business address.
1200 Fourth Street #1141 Key West, FL 33040 United States
Copyright © 2024 Nomadic Sailing. All rights reserved. Nomadic Sailing is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Yacht Cruising Lifestyle
Everything fun you can do from your yacht
Choosing the Best Dinghy for Your Boat
January 7, 2021 by Travis Turgeon 5 Comments
At anchor, a dinghy boat serves as your lifeline to everything from leisurely excursions to provisioning trips. Every captain or crew will use their dinghy differently, so it’s essential to consider what features and functions are important to you.
Do you plan to explore remote areas away from anchor? Do you plan to fish, snorkel, or dive from the dinghy? How many people will you need to carry at once? Every aspect should play into your decision.
Below, we cover the following to help you choose a dinghy that’s right for your boat:
- Key Factors to Consider
- Types of Dinghies
- Outboard Motors
General Information and Tips
What should i consider before buying a dinghy for my boat.
Make the following considerations before purchasing a dinghy for your boat:
- DInghy Storage
- Carrying Capacity
- Use of the Vessel
Dinghy Storage
Storage should be a defining factor when purchasing a dinghy for your boat. There are several common ways to store a dinghy, but not all storage is suitable for every vessel. A rigid dinghy will need enough space to be tied on the deck or at the back of the boat, while you can stow an inflatable dinghy in lockers or lazarettes.
Regardless of where you choose to keep your dinghy on the boat, it should be in a location that does not reduce drag, restrict access to important areas, or prevent easy access for storage and use.
The most common options are:
- Dinghy Davits
- On-Deck
- Locker
Davits: Permanently installed at the stern of the boat, davits are used to store, deploy, and retrieve your dinghy from the water. Davit storage is standard for any dinghy that’s too heavy to manually lift in and out of the water. Although storage on dinghy davits is convenient, it poses a risk when sailing through heavy seas. Large waves and wind can cause the dinghy to flood while in transit, and the weight can damage the stern of the boat or the davits.
On-Deck: Some people choose to tie the dinghy upside-down at the bow, stern, or side of the boat. For this to be an option, you need sufficient unused space on the deck, and you need to be sure that the dinghy is not interfering with any important pathway or area on the boat.
Swim-Step: Boats with an elevated swim-step can accommodate a dinghy at the boat’s stern as long as it’s elevated far enough out of the water. Keep the dinghy tied aerodynamically and tilted so that it doesn’t fill with water.
Locker: Roll-up inflatable dinghies are easily deployed and retrieved from the water by hand, and they can be deflated and stored in a locker anywhere onboard.
Towed: For nearshore journeys in calm conditions, you can easily pull the dinghy behind your boat. Be careful, though, as high speeds and choppy seas can cause a dinghy to flip in the water.
Dinghy Carrying Capacity
If you’re sailing with multiple crew or passengers, you will want a dinghy that can carry the same amount of people. Making numerous trips from ship to shore will not only cost you time, but it will also run up fuel costs. Further, you’ll want extra room for luggage, provisions, recreational gear, and anything else that may find its way onto your boat.
The handling in your dinghy can become problematic when loaded beyond capacity, so use caution – especially in rough seas. Safety should always be a top priority, so the goal is to aim for the biggest dinghy you can get without sacrificing too much storage space.
Dinghy Material
Rigid dinghies are most commonly made of fiberglass or aluminum, but you can opt for a more classic wooden design as well. The material will partially dictate where the dinghy can be stored and the need for equipment such as dinghy davits. While fiberglass hulls are cheaper than aluminum, they also come with the burden of a heavier weight. Alternatively, aluminum hulls will outlast their fiberglass counterparts, but for a higher price. Overall, rigid dinghies can withstand wear-and-tear better than inflatables, although routine maintenance is required.
Inflatable dinghies are kept afloat using tubes surrounding the boat’s hull, commonly made of either PVC or CSE. CSE, or “Hypalon,” is a synthetic rubber material that is highly resistant to chemicals, UV light, extreme temperatures, and abrasion. CSE is a lot like PVC, but it’s lighter and has more UV and water-resistant properties. It’s also more abrasion resistant, making it ideal for taking to shore. CSE offers a longer service life and a more extended warranty, although again at a higher cost. The most common complaint you’ll hear about CSE is the rate at which the air escapes from the tubes. On average, CSE tubes lose about 15% of their air within 24 hours, while PVC loses under 7%.
PVC is an excellent alternative to the more durable CSE, as the material still offers a reasonable service life at a lower cost. PVC is also much lighter, more convenient to fold, and easier to clean than CSE. The biggest potential problem with PVC is simple neglect and lack of maintenance. If cared for properly, modern PVC materials can last long enough to justify not paying the higher costs for CSE.
For some excellent tips on maintaining your inflatable dinghy, check out Sail Magazine’s Tender Choices article , here.
How You’ll Use The Dinghy
The last factor to consider is how you intend to use the vessel. Will you be traveling long distances from anchor? Exploring remote locations? How many people do you need to transport? Do you need special features to accommodate scuba diving and fishing? You should do as much research as you can to ensure that you’re buying a tender that suits your needs while staying within your budget. Below, we discuss the difference between each type of dinghy – and who each is best suited for.
Types of Dinghies
Choosing the right type of dinghy for you and your boat will require some careful thought. Your dinghy is your primary source of transportation between journeys, and you’ll want to make sure that your purchase is fitting for your immediate and future needs.
The three most common types of dinghies are:
Rigid Boats
Inflatable boats, rigid inflatable boats (rib).
Hard-body (rigid) dinghies are among the simplest styles of tender, and they come in a variety of shapes, sizes, and materials. Rigid dinghies are sufficient for those who don’t need to travel long distances or through rough conditions. However, more and more people are moving to inflatables or semi-inflatables for their wide range of abilities when needed.
When considering if a rigid dinghy is right for you, think hard about the material each is built with. For the hull specifically, the materials will affect the price, durability, and cosmetics of the vessel, as well as the weight and ability to transport. Most rigid dinghies are constructed with fiberglass, aluminum, or wood and have a lower carrying capacity than inflatables. They also have less stability when entering, exiting, and moving through the water.
Advantages:
- Easily Propelled
- Puncture Resistant
- Outboard Compatible
- Low-Cost Option
- UV Resistant
Disadvantages:
- Easily Scratched and Blemished
- Adequate Storage Space Required
More popular than rigid dinghies and less popular than RIB’s, inflatables offer a good middle ground for those looking to compromise between cost and functionality. The large PVC or Polyurethane tubes in the front and sides of the boat are more stable than rigid vessels and allow for a higher carrying capacity due to their buoyancy. Compare those benefits with the low costs of materials, and it’s easy to see why inflatables are so popular.
There are numerous variations of Inflatable dinghies, with the most common being:
- Soft Bottom Roll-Up
- Rigid Floor with Soft Bottom
- Soft Bottom with Rigid Transom
Dinghies with soft bottom have the widest variance in configuration. Some have rigid transoms where an outboard motor can be mounted. Some have rigid, removable floors, and some have an inflatable keel that increases the vessel’s stability and planing abilities. Other than the lower-end inflatables, though, almost all will have stable floors and a captain’s seat. Rowing is difficult in rough conditions, so inflatables are most commonly used with a 5-10 horsepower outboard.
Roll-up inflatables are easily stored, don’t take up much space, and are the lightest of all inflatable options. They also have the least to offer in functionality, and since most don’t have a rigid transom, they must be rowed by hand. Unless you only plan to use the vessel in calm conditions, you should consider dinghies with hard floors and transoms.
Soft bottom dinghies with rigid floors and transoms are more ideal, as they can be used efficiently in a wider variety of situations. The ability to mount an outboard allows you to use the vessel in harsher conditions and travel greater distances. The rigid floors allow you to use the vessel for fishing, diving, provisioning, and more without sacrificing stability and comfort.
- Lightest Option
- Easily Compacted and Stored
- Easily Damaged and Punctured
- Consistent Maintenance Required
- Low Efficiency
The RIB design is a cross between a soft bottom and rigid hull and gives you the most bang for your buck in the water. The hard-bodied hull makes for a stable and damage-resistant body, while the inflatable tubes add optimal stability. The RIB design is so efficient that it’s even used by the US Military and Coast Guard. The tradeoff you make with a RIB is portability and storage, as the hull can not be taken apart or broken down. However, this can be overlooked by carefully choosing a RIB that’s right for your boat. If you’re looking to outfit your boat for scuba diving , a RIB should be pretty much your only consideration for a tender.
Rigid Inflatable Dinghies are the most popular type of dinghy for cruising sailors, and it’s easy to see why. RIBs used as dinghies are commonly between 10 and 15-feet long, with anything larger being reserved for massive yachts with dinghy garages or excess storage space. RIBs are typically stored on davits or lashed upside down somewhere on the deck of the boat. For shorter trips near shore and in calm conditions, you can tow the RIB behind the boat.
Typically, RIBs are available with either aluminum or fiberglass hulls. Aluminum is lighter and stronger than fiberglass, although you should expect to see a price tag that matches those benefits.
- Optimal Speed, Handling, and Stability Rugged
- Limited Storage Options
Outboard Dinghy Motors
After choosing the dinghy that’s right for you and your vessel, you’ll need to select an outboard to fit. You’ll want something powerful enough to make the dinghy plane at full capacity but also light enough to transfer to and from the dinghy‘s transom. Before making a decision, check with the manufacturer to determine the recommended power output for your intended use.
Generally speaking, fully inflatable dinghies that measure around 10-feet in length support a 5-8 horsepower outboard, which is sufficient for the basics. For a more capable inflatable, look for a 10-25 horsepower outboard. Just be cautious, as too much power can flip a lightweight dinghy.
Similarly, a 10-foot RIB will support a heavier engine, such as a 10-15 horsepower outboard that provides enough power for the boat to plane while carrying more than one passenger. For more capability, look for an outboard in the 20-50 horsepower range.
Either way, you’ll need to decide your dinghy’s primary purpose and buy an outboard to support it.
If it’s simply used for trips to shore in calm conditions, a lower-powered outboard will likely be sufficient. The more power you can apply, the more capable your dinghy will become. Further, the maximum power output of the engine should always exceed the recommendations for operating the dinghy at full capacity. If you have a powerful outboard, you won’t have to worry as much about overworking the engine when the boat is full.
When determining which motor is right for you, keep in mind the storage and transportation options you have. If you need to lift the dinghy and outboard out of the water manually, it might be safe to say that the lighter the outboard’s weight, the better. If your back can handle the extra weight, though, the 4-stroke engines are far better suited for things like water sports and rough surface conditions.
Dinghy Excursion Checklist
- Check inflation levels and make sure there is no water inside the boat. If there is, look for leaks or damage.
- Ensure the boat is free of all loose lines, flags, or anything that could get caught in the boat propeller.
- Check to make sure the outboard is appropriately and securely mounted to the transom.
- Quickly test both the forward and reverse gears to make sure everything is working as it should.
- Test the lights on the dinghy, even if it’s still light out.
- Check for paddles, lifejackets, first-aid kits, and dinghy repair kits.
Operating the Dinghy
- When operating the dinghy alone, clip the emergency motor stop to your clothing. If you fall overboard, your motor will stop.
- Be cautious when using a powerful outboard. Too much power can cause a lightweight inflatable to flip or overturn.
- Bring the dinghy upwind when returning to your boat for a more controlled approach.
- Always use both front and rear-facing lights when operating the dinghy after dark.
- When towing the dinghy behind your boat, experiment with the length of the tow rope to find the smoothest pull.
- If there is any surf present, do not attempt to beach your dinghy.
- Use a dinghy anchor if there are large tide changes, waves, or swells present.
- Keep a dinghy repair kit on board at all times in case of small punctures or tears.
- Dinghy covers reduce UV light exposure and prolong the life of the dinghy by up to five years.
- Cosmetically, CSE doesn’t wear down for about 10 years. PVC begins to look rough after only a few.
- Consider where you intend to use your dinghy. Will it be in locations with high swells, rocky shores, and cold water? If so, consider a more rugged and damage-resistant material.
- Before purchasing a dinghy, visit a few boat shows, and read user reviews. You want to be comfortable making a purchase, and having first-hand resources to chat with is the best way to feel confident about your decision.
- Keep your dinghy insured separately in case of incidents that happen away from your yacht.
- Dinghies and their outboard motors are common targets of theft, so be sure to lock up both whenever possible.
When choosing a dinghy for your cruising lifestyle, it’s important to know exactly how to buy a new or used boat and what considerations should be prioritized.
Join the #BoatLife community and contribute to our new forum! Get a new conversation started, or use your experience to address existing posts.
If you found this article helpful, please leave a comment below, share it on social media, and subscribe to our email list.
For direct questions and comments, shoot me an email at [email protected]
Sharing is caring!
Reader Interactions
July 3, 2021 at 10:26 am
I have one for my canoe, my dinghy, and my power boat So, the next time you see a 5 year old boat in Seabridge marina in Ventura California, that looks brand new, it’s my boat.
July 30, 2021 at 8:17 am
It is a great article and quite intresting to read too thanks for sharing such good information with us.
August 1, 2021 at 4:15 pm
Thanks for reading, Cassey. We’re always here to help – don’t hesitate to reach out with any questions or comments!
December 14, 2021 at 2:08 pm
Travis – My name is Mark and I am a member of the Great Lakes Cruising Club. We’ve been around since 1934, we have 2,500 US & Canadian members and we are a volunteer driven organization. For the last twelve years we have operated an on-line school, the GLCCSchool.com. Annually we present 35-40 webinars and have an attendance of around 900 people. We really liked your article on dinghies and are wondering if you would consider turning that into a presentation for our school. If you have the slightest interest please check us out and send me an email so we can explore this further. Thanks.
January 23, 2022 at 2:27 pm
Thank you for all of the applicable information. I appreciate how the differences of each type of boat were well defined. This article was extremely helpful.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
MB #20512 PO BOX 480 Sevenoaks Kent TN13 9JY
Tel: +44 56 0386 9163
Keep In Touch
Thank you for reading.
Join our online crew and find more about the #boatlife

What is The Best Sailing Dinghy for Cruising?
Whether you are a seasoned sailor or completely new to sailing, choosing the right dinghy for your escapades is crucially important. If you begin to look at all of the available sailing dinghies on the market, you will likely be overwhelmed with all the options and unsure which one is truly the best. Let’s take an in-depth look and answer the question: What is the best sailing dinghy for cruising?
One of the best sailing dinghies for both beginners and experts alike, the Wayfarer is perfect for day cruising and multi-day adventures. Wayfarers are also versatile due to their streamlined and stable design. There are also other great options, including Gull and Enterprise dinghies.
In the next few sections, I’ll take a look at some of the most popular and best sailing dinghies so that you can get an idea of what is out there. Let’s get right into it!
Looking for a Sailing Dinghy for Cruising?
If you are looking to purchase a dinghy, there are a lot of options available to you. A few dinghies rise above the rest in terms of maneuverability, quality, design, functionality, and a thousand other factors; however, it is nearly impossible to pick out a single dinghy as the best due to the varying opinions and needs of individual people.
So, while there isn’t a single “best” dinghy that I can recommend to everyone, the ones listed below are absolutely amazing and will work for various crew sizes, needs, and situations.
Now, let’s take a closer look at these five great sailing dinghies and address each one’s pros and cons.
Wayfarer Sailing Dinghy
The Wayfarer is a widely loved dinghy that has quite a reputation as a good and reliable boat. There are many different versions of the Wayfarer, with slight adjustments and design changes throughout the years. While all of the Wayfarers are considered excellent boats, ones closer to the original Mark I design are ideal for sailing due to their extra storage capacity and added stability.
Pros of Cruising in a Wayfarer Sailing Dinghy
Wayfarers are overall great dinghies for a variety of situations and people. They are incredibly versatile, maneuverable, and very enjoyable to sail.
Whether you are entirely new to sailing and just looking into getting your first dinghy, or you have been around the block a few times, a Wayfarer is an excellent choice for many people. Due to its extreme versatility, you can take your Wayfarer out on both day trips and multi-day excursions, and they are even great racing dinghies as well!
Cons of Cruising in a Wayfarer Sailing Dinghy
When considering the cons of owning a Wayfarer, they are relatively few and far between. One thing to keep in mind is you will usually want a crew of at least two people to sail a Wayfarer. Unless you are very competent and know how to sail solo well, a Wayfarer will most likely be too large and heavy to sail and beach if you are alone.
It is also important to note that the newer versions of the Wayfarer are more prone to turtling while sailing than earlier models. If you are just getting into sailing, I would highly suggest that you get a Wayfarer similar to the Mark 1 designed by Ian Proctor.
Gull Sailing Dinghy
First designed by Ian Proctor in 1956, the Gull is a reliable and versatile dinghy that is well-loved by many people. The first iteration of the Gull was made of plywood, as most boats of the time were, and since then has gone through many more versions and is now made of GRP (Glass Reinforced Plastic).
Pros of Cruising in a Gull Sailing Dinghy
Much like the Wayfarer mentioned above, the Gull is a very versatile and excellent dinghy. While the Gull makes a fantastic sailing dinghy, it is a versatile craft that you can fit with an outboard engine or rowlocks for alternate propelling methods.
Another significant aspect of the Gull is its sleek and small design. While you lose some onboard space, the Gull’s smaller hull allows this two-person dinghy to be easily sailed solo if you have a little experience and wish to do so. Overall, the Gull is a very sturdy and reliable dinghy bound to meet all of most sailors’ needs.
Cons of Cruising in a Gull Sailing Dinghy
Gulls are very sturdy dinghies that don’t have too many downsides to them. The only real offputting aspect of the Gull for many sailors is its small size that sometimes doesn’t have as much room as you might like on a multi-day excursion on a dinghy.
The Gull has a pretty small hull, which gives it a lot of maneuverability, but it also results in less space for yourself, crew, passengers, and supplies. The lack of space on the Gull isn’t too big of an issue if you pack lightly, go on excursions that last a few days at a maximum, and have minimal people on board.
Enterprise Sailing Dinghy
Designed in 1956 by Jack Holt, the Enterprise is one of the oldest dinghy classes, yet remains wildly popular to this day due to its appealing design and beginner-friendly handling. Enterprise dinghies are extremely popular and versatile worldwide, being used for sailing, racing, and nearly everything in between.
Pros of Cruising in an Enterprise Sailing Dinghy
The Enterprise is seemingly the perfect blend of size, design, power, and weight. This near-perfect combination of elements has been the primary thing that has made this dinghy class have such a strong following and be so popular for many decades.
While it may take some adjustments and time, Enterprise dinghies are also relatively easy to sail singlehandedly, even though they are meant to be sailed two-up. Overall, Enterprise dinghies are excellent and reliable boats that are great for sailing adventures, whether you have a friend with you or not.
Cons of Cruising in an Enterprise Sailing Dinghy
Enterprise dinghies are considered one of the best options out of the vast array of sailing dinghies out there. However, there is one major thing that can be quite offputting to many sailors about them.
This one flaw of Enterprise dinghies is their stability.
While it isn’t too much for an experienced sailor to handle, Enterprise dinghies do have a noticeable lack of stability when out on the water when compared to similar sailboats. By no means is this a fatal flaw of the design, but rather a characteristic unfamiliar to this type of dingy and usually seen on dinghies meant for racing.
Wanderer Sailing Dinghy
Another design by Ian Proctor that has made this list, the Wanderer is a very light and agile dinghy that is quite popular among new and experienced sailors alike. The Wanderer began as a lighter version of the previously mentioned Wayfarer, but its design has diverged quite a bit and has become unique in its own right since then.
Pros of Cruising in an Wanderer Sailing Dinghy
One of the Wanderer’s greatest strengths is its weight. It is actually relatively light, with a hull weight of 291 pounds, making it pretty easy to launch and maneuver. Additionally, the Wanderer’s weight, or lack thereof, does not significantly impact its stability because it is quite a stable boat that is not prone to turtling.
Overall, the Wanderer is a top-rated and fabulous boat that, while on the lighter side of things, is very stable and reliable.
Cons of Cruising in an Wanderer Sailing Dinghy
While the Wanderer is a great boat for sailing, a potential downside to this dinghy is the need to have multiple crew onboard. While sailing a Wanderer can undoubtedly be done solo, for most sailors, having some extra hands on deck will make sailing the 2-3 person Wanderer dinghy much more pleasant.
Of course, there is absolutely nothing wrong with having a multi-person sailing dinghy – for many it’s the perfect choice – but it does eliminate the possibility of solo sailing, which can be quite relaxing and fun once you are competent and experienced.
James Gerard
Hi, I'm James! I started sailing at a very early age here in the UK, and have enjoyed so many opportunities to sail all over the world. I created this website to share the many sailing tips I've leaned over the years, so that you can also discover the joy of sailing with safety and confidence.
Recent Posts
How to Predict Wind Direction & Speed from a Surface Pressure Chart
Learning how to read a surface pressure chart will allow you to predict the wind speed and direction based on the weather chart. This will help you in planning your next sailing trip.
What Does a Black & Yellow Buoy Mean? (Cardinal Marks Explained)
If you see a black and yellow buoy while you're sailing, don't ignore it. Cardinal Marks are there to help you avoid hidden hazards in the water. This helpful article will help you to identify a...
- AROUND THE SAILING WORLD
- BOAT OF THE YEAR
- Email Newsletters
- America’s Cup
- St. Petersburg
- Caribbean Championship
- Boating Safety
- Ultimate Boating Giveaway

Boat of the Year 2020 Best Dinghy: Tiwal 2
- By Dave Reed
- Updated: December 10, 2019
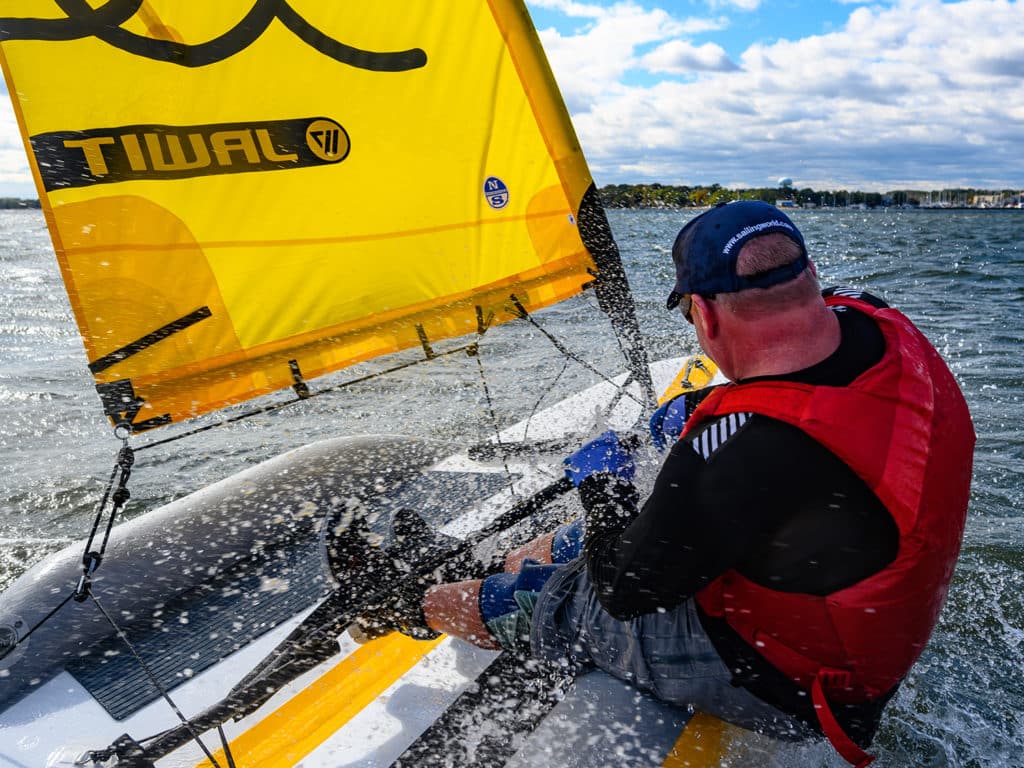

At A Glance
Price As Sailed: $4,800
Design Purpose: Freestyle sailing
Crew List: One or two
Allen and Stewart are like two oversize kids duking it out on the playground. Stewart, weighing in at a smidge over 200 pounds, is stretched out across the Tiwal 2’s nonskid decking, his feet dangling off the starboard float; his head pillowed by the port float. Allen is contorted over the top of the centerboard trunk, trying to get his Tiwal’s transom to break from the glassy surface. On starboard, he targets Stewart, who is trying to shake him in the prestart of the first-ever impromptu Tiwal 2 North American Challenge.
“Starboard!” Allen hollers.
“Hold your course!” Stewart retorts as he starts to bear away.
Allen can’t resist, and he too bears away as the two converge, plowing right into Stewart’s lap. The rubber boats simply bounce off each other and carry on up the course on opposite tacks.
“It’s Tiwal racing!” shouts its designer and energetic young visionary, Marion Excoffon, who is observing the comical two-boat slugfest from our Highfield RIB. “There are no rules. Only to have fun!”
Fun sailing is the way of the Tiwal tribe, an almost cult-like sailing community in Europe where hundreds of owners of these high-pressure, inflatable sailboats gather on lakes and Mediterranean beaches to play together.
Yes, they are “toy” boats, Excoffon says, but even as playthings, racing is irresistible whenever there’s more than one. It is also designed as a toy for a cruising boat that “allows you to sail and have an amazing moment around your boat while at anchor,” Excoffon says.

The Tiwal 2 is not to be confused with the larger Tiwal 3, a Boat of the Year finalist of the past, which has aluminum-bar racks for hiking. Customers asked for a smaller version that was also kinder to the gelcoat of their cruising boats and superyachts. The 9-foot, PVC-built Tiwal 2 weighs only 20 pounds. Add its marine-grade, coated plywood rudder and centerboard, ropes, hardware, five-piece carbon mast and bulletproof sail from North, and the whole enchilada is still only 60 pounds.
Portability is what has earned the Tiwal line of boats numerous innovation awards in Europe. When broken down to its bits, the entire craft fits into two duffle bags that are small enough to stuff into a lazarette or into the trunk of a Mini Cooper. Tiwal inflatables are standard equipment now in the toy boxes of superyachts, which Excoffon says is 20 percent of their market, where there can never be enough water toys.
“We’ve sold about 80 of them since this summer,” she says. “For less than $5,000, this boat is good for the whole family to share nice moments with your child, or to go have fun and play in good breeze. The boat is adaptable to different people, and adaptable to the wind.”
The judges agree with that much. They sail it first in glassy, drifting conditions, goof off and laugh their way to sunset. (Racing is ultimately abandoned, so there is no clear winner of the Tiwal Challenge.) With a gale in the forecast, however, they request a resail later in the week.
Allen takes the first spin, into frothy whitecaps whipped up by an opposing tide and wind at the entrance to the Severn River: “Downwind, in the 20-knot puffs and bigger waves, it was a little squirrelly, but once I got into flatter water and went power-reaching along, the thing was ripping and planing easily. Then I started playing with moving my weight and using my feet to push it around like a surfboard in the waves. It was so much fun. The rudder is nice and responsive; it turned on a dime.”
In one “angry puff of 30 knots” that comes along, he lets the sail luff, waits in “hang mode” and lets it pass. “The boat is quite buoyant, which is a nice safety element if a kid got caught out in too much breeze,” he says.

Tacking and jibing are easy, Allen adds, because of the buoyancy; and by vang sheeting and hardening the cunningham, he motors upwind. “I was surprised the bow wasn’t flexing all over the place, so whatever air pressure and stiffness they have going on there, it really works,” he says. “It was by far one of the most fun boats of the week. I’m a Tiwal fan—you can quote me on that.”
Stewart is a fan as well, but also claims to be 2 knots faster than Allen upwind because he’s heavier and able to use more of the sail. “I had a great time,” he says. “It’s one of those boats where we knew we were going to get wet and have fun. And amazingly, we didn’t break it.”
Not for lack of trying, though. Once, or maybe twice, Stewart ungracefully pearled in the photo boat’s wake and pirouetted into the brown bay waters.
He’s a big guy, but he easily hauled himself back into the boat, up forward on the wing deck. “I could easily grab the bar that is part of the mast structure and pull myself right in,” he reports. “There are also handles on the tubes to grab hold of if you need to.”
Powlison, meanwhile, boasts of sailing it in the most breeze: “It was nuking.” He thoroughly enjoys hiking hard off the supple tubes beneath his hamstrings. The wing, he says, is a nice comfortable platform, although maybe a little slippery toward the back: “A couple of times, I almost slid right off.”
His jibes are the smoothest of the team, and his suggestion in strong breeze is to simply “do it quickly.”
“It’s sensitive to steering,” he says. “I could throw it around in the jibe, and it would spin right around the centerboard. It’s a cool little boat that’s well engineered, and as we showed, it can handle the big stuff. We sailed it at both ends of the wind range, and the light-air part was fun too.”
See All Winners
Other Winners:
- 2020 Boat of the Year
- Best Crossover
- Best Multihull
- Best Foiler
- Best Dinghy
- More: BOTY , boty 2020 , Dinghy , Sailboats
- More Sailboats

Sporty and Simple is the ClubSwan 28

Nautor Swan Has A New Pocket Rocket

Pogo Launches its Latest Coastal Rocket

A Deeper Dive Into the Storm 18

Mistakes And Misfires On the Final Day of Cup’s Preliminary Regatta

Emirates Team New Zealand Remain the Bullies of Barcelona

Start-Box Sparring in Barcelona on Day 2 of Preliminary Regatta

Real-time Wind Overlay Feature Added to Cup Broadcast

- Digital Edition
- Customer Service
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Cruising World
- Sailing World
- Salt Water Sportsman
- Sport Fishing
- Wakeboarding
Tender vs Dinghy: Understanding the Key Differences
by Emma Sullivan | Aug 18, 2023 | Sailboat Gear and Equipment

Short answer: Tender vs Dinghy
A tender is a small boat used primarily for transport between a larger vessel and the shore, whereas a dinghy is a small boat typically used for recreational purposes or as a lifeboat. Tenders are usually designed with greater stability and carrying capacity for passengers and supplies, while dinghies prioritize maneuverability and ease of use.
Understanding the Tender vs Dinghy: A Comprehensive Comparison
When it comes to boating or yachting, having a vessel that allows for easy transportation between the shore and your main boat is essential. This is where the tender and dinghy come into play. Both serve as vessels used to transport people, supplies, or equipment from one point to another, but they each have their own unique characteristics and purposes. In this comprehensive comparison, we dive deep into understanding the differences between a tender and a dinghy.
1. Definition and Purpose: A tender refers to a small boat used to ferry passengers or goods from a larger vessel, such as a yacht, to land or vice versa. It is designed with comfort in mind, often equipped with plush seating and amenities that mirror those on the main boat. Tenders are primarily used for transporting people in style while maintaining an element of luxury.
On the other hand, a dinghy is typically known as a small utility boat that serves several purposes beyond passenger transportation. While it can certainly act as transport between larger boats and land, it is also commonly used for water sports activities like sailing, rowing, or fishing due to its lightweight construction and maneuverability.
2. Size Matters:
In terms of size, tenders are generally larger than dinghies because their purpose revolves around providing comfortable transfers for both passengers and crew members. They often range from 8 feet up to 40 feet in length (or even bigger), depending on the size of the main vessel they accompany.
Dinghies, on the other hand, tend to be smaller in size since their primary role is centered around utility rather than luxury. Ranging from 6 to 16 feet long (sometimes more), they are compact enough to be easily transported alongside a larger vessel without causing inconvenience.
3. Construction:
Tenders often feature a rigid hull made of materials like fiberglass or aluminum which provides stability during transportation. Some higher-end tenders may even have inflatable collars to enhance buoyancy and shock absorption.
Dinghies, conversely, come in two main types: rigid-hulled and inflatable. Rigid-hulled dinghies (RIBs) consist of a solid material like fiberglass or aluminum for the hull with inflatable tubes providing added buoyancy. Inflatable dinghies, as the name suggests, are entirely inflatable and can be easily folded or deflated for convenient storage.
4. Propulsion:
Tenders typically employ more powerful engines since they may need to transport larger groups of people or heavier equipment. These engines could range from inboard motors to outboard motors, ensuring smooth and efficient transfers regardless of weather conditions.
Dinghies traditionally use smaller engines due to their lightweight nature and versatility in water sports activities. Their propulsion systems often consist of outboard motors attached to the transom for easy maneuverability and quick acceleration.
5. Pricing:
As expected with their added luxury features, tenders usually come at a higher price point compared to dinghies. The cost is influenced by factors such as size, materials used, engine power, and additional amenities provided onboard.
Dinghies score economically here as their primary purpose revolves around utility rather than opulence. The price tags on these compact vessels are generally lower compared to tenders but can still vary depending on features such as hull materials, propulsion systems, and any added accessories.
In conclusion, understanding the tender vs dinghy comparison is crucial when deciding which vessel best suits your boating needs. If you prioritize comfort, style, and seamless transportation between your main boat and land destinations with an extra touch of luxury; a tender would undoubtedly be your ideal choice. However, if you seek versatility for water sports activities along with basic transport capabilities – accompanied by a more budget-friendly option – then a dinghy should definitely be on your radar!
How to Differentiate Between a Tender and a Dinghy: Step-by-Step Guide
When it comes to boating, there are many terms that can often be confusing – especially if you’re new to the scene. One question that frequently pops up is: What is the difference between a tender and a dinghy? Well, fear not! We’re here to provide you with a step-by-step guide on how to differentiate between these two nautical terms.
First things first, let’s clarify what each term actually means. A tender refers to a small boat used for transportation between a larger vessel and the shore or other boats. On the other hand, a dinghy is simply a small open boat that is often used as either a recreational craft or as transport for short distances.
Now that we’ve got some basic definitions under our belt, let’s dive deeper into distinguishing features:
1. Size Matters: One of the most fundamental differences between tenders and dinghies lies in their size. Tenders generally tend to be larger than dinghies and are specifically designed to accommodate multiple people comfortably, along with additional equipment such as oars or an outboard motor . Dinghies, on the contrary, are usually smaller in size and generally intended for solo use or carrying only one or two passengers.
2. Construction: While both tenders and dinghies can be made from various materials like fiberglass or aluminum, traditional dinghies often have inflatable tubes (known as pontoons) enabling them to float even when filled with water. This design feature makes them incredibly stable in choppy waters compared to non-inflatable tenders.
3. Purpose: Another key factor separating these two vessels is their intended purpose. Tenders primarily serve as auxiliary boats for larger vessels – think of them as floating shuttles that ferry people, supplies, or even equipment back and forth from land or other boats anchored nearby. Dinghies, however, are more focused on recreational activities such as fishing trips, exploring shallow waters, or simply joyriding. They are not exclusively tied to a parent vessel and can be used independently.
4. Seating and Accessories: When comparing tenders to dinghies, it’s essential to consider the available seating options and additional accessories they offer. Tenders usually come equipped with multiple seats, often padded for better comfort during longer journeys. Additionally, they may feature storage compartments for stowing gear or even built-in fixtures like oar locks or towing rings for easy maneuvering. Dinghies typically have less seating space since they are designed to accommodate fewer passengers and generally lack additional features found in larger tenders.
5. Nomenclature: Interestingly enough, sometimes the difference between a tender and a dinghy could simply be a matter of semantics within certain boating circles. Some people might use both terms interchangeably depending on their specific context or personal preference – so always remember that context matters!
In conclusion, differentiating between tenders and dinghies boils down to various factors such as size, construction, purpose, seating arrangements, and individual definitions employed by boaters themselves. By considering these elements carefully, you’ll be able to navigate the sometimes murky waters of boat terminology with ease.
So there you have it – our step-by-step guide on how to differentiate between a tender and a dinghy! Armed with this knowledge, you’ll impress your fellow boaters with your newfound ability to identify each vessel correctly. Now go forth (or should we say float forth?) confidently into the world of boats !
Tender vs Dinghy: Unveiling the Key Differences and Similarities
When it comes to boating, choosing the right vessel is crucial. Whether you’re a seasoned sailor or a novice on the water, understanding the differences and similarities between tenders and dinghies is essential. In this blog post, we will dive deep into these two types of boats, unraveling their key distinctions and highlighting their commonalities.
Firstly, let’s address what precisely tender and dinghy mean in the context of boating terminology . A tender is a smaller boat employed primarily to transport people or goods between a larger vessel (such as a yacht) and shore. On the other hand, a dinghy is an open boat typically used for recreational purposes like rowing or sailing.
One of the primary differences between tenders and dinghies lies in their intended purpose. While both vessels serve as means of transportation in some form or another, tenders are specifically designed to cater to larger boats . Tenders enable passengers or necessities to shuttle back and forth from the main vessel to land. They often feature more advanced features like comfortable seating arrangements and weather protection measures.
In contrast, dinghies are primarily focused on individual enjoyment rather than practicality for larger vessels. Dinghies are commonly found in sizes ranging from 6ft up to around 14ft long. They can be rowed, sailed with minimal equipment (such as a small sail), or powered by an outboard engine. These agile little boats offer riders an exciting experience exploring waterways close to shorelines.
Another significant distinction lies in their build characteristics . Tenders are usually sturdier than dinghies due to their typical use on open waters away from land for longer durations. Their construction materials may include durable components such as fiberglass hulls that withstand rough conditions encountered while transporting passengers or items.
Dinghies come in various forms depending on their intended purpose; however, many are built using lighter materials like aluminum or inflatable tubes. Choosing the right material for a dinghy largely depends on factors such as portability, ease of storage, and recreational activities planned.
Despite these key differences, there are also noteworthy similarities between tenders and dinghies. One common aspect is their versatility. Both can adapt to different water situations, whether it’s calm lakes or more challenging sea conditions . This adaptability allows users to explore various waterscapes with confidence.
Moreover, both tenders and dinghies possess excellent maneuverability capabilities. Whether you’re using oars to row a dinghy or utilizing an outboard engine on a tender, navigating through tight spaces or congested harbors becomes hassle-free with these agile boats.
Finally, both vessels offer ample opportunities for customization and personalization . From adding comfortable seating options to equipping them with navigation systems or even fishing accessories, boat owners have the freedom to tailor their tender or dinghy to suit their individual needs and preferences.
In conclusion, understanding the distinctions between tenders and dinghies helps boating enthusiasts make informed decisions when embarking on water adventures. Tenders serve as practical transportation solutions for larger vessels while offering enhanced features for passenger comfort. On the other hand, dinghies provide individual enjoyment through rowing or sailing experiences closer to shorelines. Despite their differences, both boats exhibit versatility, maneuverability, and customizability that add value to any boating experience. Choose wisely and set sail with confidence!
Your Burning Questions Answered: FAQs about Tender vs Dinghy
Welcome to our blog series where we aim to address your burning questions about various boating topics. In this edition, we delve into the frequently asked questions regarding a tender versus a dinghy, two common vessels used for different purposes. So let’s dive straight in and satisfy your curiosity with detailed, professional yet witty and clever explanations.
1. What is the difference between a tender and a dinghy? – A tender refers to a vessel primarily used for transportation between a larger boat or yacht and the shore. It often has a more refined appearance, resembling its parent vessel in design and style. On the other hand, a dinghy is typically an open small boat that can be used independently from the main vessel for various activities such as fishing, exploring shallow waters or water sports.
2. Why would I need a tender? – Ahoy! Having a tender provides great convenience when you want to go ashore from your larger boat without having to maneuver it through potentially tricky waters or crowded marinas. It grants you access to shoreside amenities, restaurants, and attractions with ease.
3. Can’t I just use my dinghy as a tender? – While you could technically use your dinghy as a means of getting ashore, using it solely for that purpose might limit its potential uses. Dinghies are versatile boats that can accommodate several recreational activities like fishing or frolicking around in shallow coves independently without relying on your main vessel.
4. Are tenders only for luxurious yachts ? – Not at all! Though commonly associated with high-end yachts due to their matching appearance and style, tenders come in various sizes suitable for different types of boats and budgets. Even if you have a modest-sized sailboat or motor cruiser , investing in an appropriately sized tender can greatly enhance your boating experience.
5. Are dinghies inferior to tenders ? – Absolutely not! Both tenders and dinghies serve different purposes, and neither is superior to the other. Dinghies excel in their versatility and independence, making them perfect for adventurers seeking a range of recreational activities. Tenders, on the other hand, prioritize comfort and convenience when moving between the large vessel and shore.
6. Can I customize my tender or dinghy? – Certainly! One of the great joys of owning either type of boat is that you can personalize it to your heart’s content. Whether you want to add plush seating and elegant finishes to your tender or outfit your dinghy with fishing accessories or water sports equipment, there are endless possibilities for customization.
7. How do I choose between a tender and a dinghy? – The choice ultimately depends on your boating preferences and needs. Consider factors such as intended use, budget, storage space on your main vessel, number of passengers you intend to transport, and desired level of comfort versus versatility. Assessing these aspects will help guide you towards selecting the ideal boat for your specific requirements .
We hope these answers have shed some light on the frequently asked questions regarding tenders versus dinghies. Remember, both vessels offer unique advantages based on their individual strengths. So whether you’re cruising in luxury aboard a yacht or embarking on thrilling adventures with a smaller boat by your side, happy boating!
Exploring the Purpose and Usage of Tenders and Dinghies: What Sets Them Apart?
When it comes to boats, most people tend to think of grand vessels cruising through the open waters. However, not every boating experience requires such extravagance. Sometimes, a smaller and more versatile option is needed for various purposes. This is where tenders and dinghies come into play.
Tenders and dinghies are both small boats that serve different purposes on the water. While they may share some similarities in appearance, it’s important to understand their distinctions in order to make an informed choice for your boating adventures . So, let’s dive in and explore the purpose and usage of tenders and dinghies while unraveling what truly sets them apart.
Firstly, let’s take a closer look at tenders. These are specially designed inflatable or rigid-hulled boats that act as a companion boat to larger vessels like yachts or superyachts. Tenders function as transportation between the shore and the main vessel when anchoring offshore or when navigating shallow waters inaccessible by larger crafts. They typically have ample space for passengers, equipment, supplies, or even water sports activities like wakeboarding or snorkeling gear.
Tenders are incredibly versatile due to their ability to be easily stowed on board larger vessels without taking up much space. Their inflatable nature allows them to be deflated when not in use, making them compact enough for storage in lockers or other dedicated spaces on a yacht. Additionally, their maneuverability enables easy access to confined spaces, giving owners the freedom to explore secluded coves or access marinas with limited docking facilities.
On the other hand, dinghies differ from tenders primarily in terms of functionality and usage. Dinghies are small rowing boats that can either be powered by oars alone or equipped with small outboard engines for added convenience. Unlike tenders that are specifically designed as companions for larger vessels, dinghies often serve as stand-alone craft suitable for various leisure activities.
Dinghies are commonly used for fishing, recreational rowing, or simply as a means of transportation when anchored close to shore. They offer an affordable and easily transportable option for those who wish to explore nearby waters independently. Their lightweight and compact nature make them ideal for individuals or small groups looking for an intimate boating experience without the need for additional amenities or accommodations.
Although tenders and dinghies have their distinctive uses, there may be some overlap in functionality depending on individual preferences and the specific design of each boat. Some larger tenders may incorporate rowing capabilities similar to dinghies, while certain dinghies may provide space for limited equipment like coolers or small outboard engines. It’s essential to consider your intended purpose before making a decision.
To sum it up, tenders and dinghies play vital roles in the boating world by offering versatile options that suit various needs. While tenders are primarily companions to larger vessels, providing transportation and access to remote locations, dinghies serve as stand-alone craft for leisure activities such as fishing or exploration of nearby waters . Owning either one can enhance your boating experience significantly by expanding your opportunities on the water.
So whether you’re cruising through coastal destinations aboard a luxurious yacht or prefer a more independent adventure closer to shore with a trusty dinghy, both tenders and dinghies have their unique advantages that set them apart in their purpose and usage – giving all boaters the perfect vessel tailored to their specific preferences.
Choosing Between Tender or Dinghy: Factors to Consider for Boating Enthusiasts
When it comes to boating, having the right vessel is crucial. Whether you are a seasoned sailor or a novice boater, one important decision you will have to make is choosing between a tender and a dinghy. While both options serve as auxiliary boats, each has its own set of factors that should be carefully considered before making a decision.
Firstly, let’s clarify what exactly a tender and a dinghy are. A tender is typically larger in size and is designed to transport people or supplies from shore to a larger boat (like a yacht). On the other hand, a dinghy is smaller and more versatile, often used for recreational purposes such as fishing or exploring shallow waters .
Size Matters: One of the key factors to consider when choosing between these two options is the size of your main vessel. If you have a larger boat that requires transportation for numerous people or heavy equipment, a tender would be the practical choice due to its increased carrying capacity. However, if your main boat is smaller and space efficiency is important, then opting for a compact dinghy would be more suitable.
Versatility vs. Practicality: Another aspect worth contemplating is how you plan on using your auxiliary boat. If your primary goal involves leisurely activities like fishing or cruising around secluded coves, then a dinghy might just fulfill all your dreams. They are nimbler in nature and can navigate through tight spaces with ease while providing an intimate and adventurous experience.
On the contrary, if you envision using your secondary vessel solely for transportation purposes or frequently traveling long distances from shore to your main ship – practicality takes precedence over versatility. This makes the tender an ideal choice as its spaciousness allows for comfortable seating arrangements while still accommodating essential supplies needed during longer journeys.
Power Preferences: It’s vital not to overlook power requirements when debating between these two vessel types. Tenders generally offer more horsepower options thanks to their bigger engines which can deliver greater speed and carry substantial loads. If you have a need for speed or venture into choppy waters, then the tender’s power advantage might be hard to resist.
However, if fuel efficiency and ease of maintenance are important factors for you, opting for a dinghy with a smaller motor might be the prudent decision. Their lightweight construction allows them to glide gracefully across calm waters while being more economically friendly.
Storage and Transport: As any experienced boater knows, storage space is valuable real estate onboard. When contemplating between a tender or dinghy, you must consider how much space you are willing to sacrifice when stowing it away on your main vessel. Tenders often require designated davits or cranes for secure lifting and storage due to their larger size. If you have limited storage capacity available, this could prove challenging.
On the other hand, dinghies shine in terms of compactness and portability. Many can be easily deflated and rolled up into small packages that can fit snugly into lockers or even carried ashore if necessary. Their lightweight design makes it hassle-free to transport them from land to sea without requiring additional equipment.
Overall Aesthetics: Lastly but significantly, aesthetics play an important role in boating as well. The choice between a tender and dinghy can greatly impact the overall aesthetic appeal of your boat setup. Tenders tend to have sleeker designs with luxurious finishes that seamlessly match larger vessels’ profiles – enhancing the overall visual appeal.
In contrast, dinghies may come in more varied designs suited towards specific activities such as fishing or water sports enthusiasts . They offer the opportunity to add some personal flair through customization options like vibrant colors or artwork – reflecting your own unique style on the open waters .
In conclusion, choosing between a tender or a dinghy boils down to carefully considering several factors including size compatibility with your main vessel, intended usage (versatility versus practicality), preferred power requirements, storage limitations, and desired aesthetics. Weighing these aspects against your personal boating preferences and needs will allow you to make an informed decision that ensures years of enjoyable experiences out on the water.
Recent Posts

- Sailboat Gear and Equipment
- Sailboat Lifestyle
- Sailboat Maintenance
- Sailboat Racing
- Sailboat Tips and Tricks
- Sailboat Types
- Sailing Adventures
- Sailing Destinations
- Sailing Safety
- Sailing Techniques
- New Sailboats
- Sailboats 21-30ft
- Sailboats 31-35ft
- Sailboats 36-40ft
- Sailboats Over 40ft
- Sailboats Under 21feet
- used_sailboats
- Apps and Computer Programs
- Communications
- Fishfinders
- Handheld Electronics
- Plotters MFDS Rradar
- Wind, Speed & Depth Instruments
- Anchoring Mooring
- Running Rigging
- Sails Canvas
- Standing Rigging
- Diesel Engines
- Off Grid Energy
- Cleaning Waxing
- DIY Projects
- Repair, Tools & Materials
- Spare Parts
- Tools & Gadgets
- Cabin Comfort
- Ventilation
- Footwear Apparel
- Foul Weather Gear
- Mailport & PS Advisor
- Inside Practical Sailor Blog
- Activate My Web Access
- Reset Password
- Customer Service

- Free Newsletter

Blue Jacket 40 Used Boat Review

Catalina 270 vs. The Beneteau First 265 Used Boat Match-Up

Ericson 41 Used Boat Review

Mason 33 Used Boat Review

How to Create a Bullet-Proof VHF/SSB Backup
Tips From A First “Sail” on the ICW

Tillerpilot Tips and Safety Cautions

Best Crimpers and Strippers for Fixing Marine Electrical Connectors

Polyester vs. Nylon Rode

Getting the Most Out of Older Sails

How (Not) to Tie Your Boat to a Dock

Stopping Mainsheet Twist

Fuel Lift Pump: Easy DIY Diesel Fuel System Diagnostic and Repair

Ensuring Safe Shorepower

Sinking? Check Your Stuffing Box

What Do You Do With Old Fiberglass Boats?

Boat Repairs for the Technically Illiterate

Boat Maintenance for the Technically Illiterate

Whats the Best Way to Restore Clear Plastic Windows?

Stopping Holding-tank Odors

Giving Bugs the Big Goodbye

Galley Gadgets for the Cruising Sailor

The Rain Catcher’s Guide

Sailing Gear for Kids

What’s the Best Sunscreen?

UV Clothing: Is It Worth the Hype?

Preparing Yourself for Solo Sailing

R. Tucker Thompson Tall Ship Youth Voyage

On Watch: This 60-Year-Old Hinckley Pilot 35 is Also a Working…

On Watch: America’s Cup

On Watch: All Eyes on Europe Sail Racing

Dear Readers
Walker bay dinghies, 8 and 10, these volksdinghies are the favorite of the marine store chains, at least partially because they nest tightly together and are easy to deliver and stock. what's tops in the chains ends up being 'popular' by default. but is there more to these ubiquitous little boats than sales and marketing momentum as a matter of fact, there is..

It took a moment to decide whether to make this article a boat review or a Chandlery piece—but only a moment. Walker Bay dinghies are unabashedly placed, by both manufacturer and ship’s store, as items to be picked up along with paint and sandpaper. They lean against the outside walls of the store. They rest in the aisles, filled with season specials like PFDs and bottom paint. They’re front and center. You can just nab one at the counter on the way out.

The prices aren’t shocking; in fact for such big physical items, and such necessary ones, they’re cheap. If you’re used to going into West Marine or BoatU.S. and dropping a few hundred dollars on a piece of navigation gear or some good-sized ground tackle, you could just as easily leave with a Walker Bay boat on your car. And many, many people do.
Walker Bay was kind enough to loan Practical Sailor the sailing versions of both an 8-footer and a 10-footer for a couple of weeks this summer. We rowed, towed, and sailed both boats. We trailered them and cartopped them. We pulled them on their stern wheels over hill and dale. (Actually we left Dale outof it.)
The essential fact about these boats is that they’re very, very plastic. This is both their weak point, in that they have none of the warmth of wood, and their strong point, in that they’re effective, no-maintenance, and virtually indestructible.
We learned quickly to suppress our Bristol Fashion Sense, assuming that those with lovely wooden boats—character boats—will generally prefer to be seen in the company of character dinghies like peapods or Whitehalls or even Dyers. Then we went on with our evaluations.
Background Founded in South Africa in 1997, Walker Bay is now based in Union Gap, Washington, with offices in Vancouver and Paris. The stated aim of the company is to bring its boats to the masses, worldwide. It’s off to a good start, with sales recorded now in 50 countries.
The Walker Bay 8 was first out of the molds in 1998; the 10-footer was introduced this spring. Both dinghies were designed by Paolo Rista, described by the company as a “water-sports professional and artist.”
There’s a lot involved in the design of dinghy hull forms, just as with any boat. There are issues of entry, rocker, freeboard, deadrise, transom width, weight and balance—and there are always scads of small-boat builders eager to debate the details. The debates will always go on because, in a dinghy, when you move something, everything changes.
Mr. Rista deserves credit not only for using a good, versatile form, but, presumably, for specifying the ersatz lapstrake construction that gives the injection-molded hulls some rigidity fore and aft. By this we mean that if you removed the thwarts you could possibly fold the boats from gunwale to gunwale, but not from bow to transom. After the thwarts are secured, the Walker Bay boats are well-supported in all directions, except, perhaps, in the 10-footer between the middle thwart and the bow. More on that later.
On both boats there’s a full-length molded skeg (or keel, if you prefer) from transom to bow. This too, adds stiffness and helps the boats track straight when rowed or towed. It also houses the handy rolling wheel aft.
Solid vs. Inflatable In a water world increasingly populated by inflatable tenders, there are still plenty of good arguments for solid dinghies, as long as they’re relatively light and manageable, which these are. Solid dinghies don’t have to be blown up or deflated. They can be stowed upside-down on the decks of larger boats and lowered or tossed overboard easily. They usually tow better than inflatables, and they always row better, especially in a headwind. Size for size, they have more carrying capacity, although again, any advantage depends on the distribution of weight and the efficiency of the form when loaded.

Most importantly, some hard dinghies, like these, can be sailed, and there’s nothing more fun than poking around a far-flung harbor at sunset in a sailing dinghy.
Walker Bay would of course like to see their sailing rigs used in more and more junior and community programs.
A new JY Trainer costs about $1,850. A new Optimist costs around $2,325. The Walker Bay 8, with performance sailing rig, costs $920. One-design fleets? They could happen.
Construction Both the 8 and the 10 are made of polypropylene resin, which is injected into a steel mold and pressed at 5,000 tons. With a slick mold and such high pressure, the boats emerge smooth and detailed, including molded spaces on the underside of one set of strakes to retain stainless hex nuts for the thwarts. The basic hull is born in about five minutes. Take that, Noah.
At the chandlery or at home, the solid, foam-filled thwarts are then set in place and bolted through the strakes. That’s about it for construction.
Performance It would have been most efficient to test all performance aspects of both boats at the same time. Of course, that’s not how we were able to do it. Instead, over the course of two weeks we had to move them around quite a bit, on and off trailers and cartops, across yards, and up and down dock ramps. This process, while not at all convenient, allowed us to get to know the boats well. We found them easy to wrestle (usually by one person, the editorial “we”) and very tough when being dragged, dropped, and tossed about. Just as importantly, they were meek neighbors when alongside other boats. They don’t scrape and bang, and they don’t leave traces of themselves on people’s topsides. They’re not much of a worry in any respect.
We sailed the 8-footer in a light harbor breeze of about 6 knots and found it surprisingly nimble and fun. It tacked and jibed easily and quickly, without being tender, and it was fairly comfortable to sit on either the center thwart or in the boat bottom.
A few days later we sailed the 10-footer in a stronger offshore breeze of about 12 knots with puffs up to 14. The breeze later faded to about 6 knots.
In the heavier air the 10 was not ideally balanced with one person in what would be considered a reasonable steering position; the boat sailed slightly down by the stern, and dragged water. This would probably have been helped by the addition of a five-year old child or a loaded cooler forward. Unfortunately we had neither of those things handy, and it wasn’t possible to balance the boat correctly without leaning well forward on the middle thwart. Sitting on the thwart while sailing doesn’t work, because the sheet is led down from the boom through a block in a clamshell-like device that clamps to the aft edge of the seat.
Moving through light chop in the heavier air, the boat’s bottom oilcanned some forward of the middle thwart. This is one area where too much may be expected of thin polypropylene stretched over an unsupported area. It’s not really a structural problem because the stuff is so resilient—you could probably leap into the boat with hobnail boots without hurting it, but oilcanning is not good for speed.
Despite the stern-down attitude and consequent sluggish steering, the 10 went well—4.8 knots on a reach.

The sailing characteristics we experienced in the 10-footer slightly undercut some very thoughtful design and manufacture work on the part of Walker Bay: The sail kit and fittings are first-rate: a well-cut sail of 3-oz. Dacron with a big window, a tensionable shaping batten near the head of the sail, nicely shaped daggerboard and rudder, and an excellent rudder-mounting system. The clam clamp for the sheet block is also smart, but we’d prefer to have the sheet simply come down from the boom the way it does on the 8-footer.It’s perfectly possible to have it that way—just unmount that clamp.
Both boats rowed very well. Walker Bay sent along an outstanding pair of 7-1/2′ wooden oars with rubber collars that set neatly in round plastic oarlocks. The oarlocks are placed fore and aft in the gunwale sockets, and as they’re turned outboard they lock in.
This is good, except that you have to remember to unship your oars early when coming alongside someone.
We rowed the boats with differently sized people and batches of gear in various places, and found that we could put our backs into it without fear of breaking or deforming any of the plastic parts. Most gratifyingly, the boats were balanced well enough that increased labor yielded increased speed. Nothing is more frustrating than finishing a stroke in a badly balanced dink and finding that all you’ve done is turn the bow into a plow. These are not pulling boats by any stretch of the imagination, but they do well enough.
Finally, we towed both boats at varying speeds behind a motorboat on long and short tethers, making arbitrary turns. Here again, both the 8 and the 10 were well-behaved, tracking straight on their skegs and planing high on the water without skittering or swerving. We weren’t able to tow them in rough water, and can’t speak for what they might be like in a seaway. (Some hard dinghies will follow a mother ship obediently through hell and high water, and some quickly become swamped drogues.) If we had to guess, we’d say they’d do well.
Once the boats were planing, we hand-tested the tethers for tension. In flat water behind the towboat, the 8-footer tugged back at about 15 lbs. The 10-footer pulled at roughly 20.
Conclusions These Walker Bay boats are already a juggernaut, thanks to a firm initial concept, good design, excellent plastic engineering and manufacturing, and the goodwill of retailers. Far be it from Practical Sailor to stand in the way: We like these boats just fine. They do the several things they’re supposed to do very well, and more besides, all at a price that has to be one of the best values in sailing.
The 10-footer clearly has greater cargo-carrying capacity, and will be able to stay out in rougher water longer. It’s a good choice for those who need to do more serious transport than harbor touring.
Our favorite, though, is the 8, not because we enjoyed sailing it more than the 10, but because it’s so easy to manage: You can sling it on your back like a turtle shell and walk far with it. You can whip it up on the roof-rack. You can throw it around, leave it alone—it doesn’t mind a thing.
Also With This Article Click here to view Walker Bay 8 and Walker Bay 10 specs .
Contact- Walker Bay Boats, 607 West Ahtanum Rd., Union Gap, WA 98903. 888/449-2553, www.walkerbay.com .
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR

Sharing the Cost of Boat Ownership

Mailport: Mainsail; Furl Fan; Keel Boats

What’s Involved in Setting Up a Lithium Battery System?
Excellent review that confirmed what I experienced with the 8 foot model. What’s not to love about the little dinghy that could and just keeps going after 20 years
Very reasonable dinghies but cheap for a reason–parts and accessories are astronically priced.
I have an 8 foot model and the centre board is extremely stiff to lower and retract which would make use less than ideal for anyone not of great strength and balance. One needs to stand to pull it up when approaching shallows. The sail being sleeved over the mast before stepping makes getting underway into an onshore breeze difficult and this is exacerbated by the centre board stiffness. The sail/ mast would benefit greatly from a more normal and expensive sail attachment system. The rudder attachment pins look frail but have so far held up but be warned and do as I do, to take your oars with you when sailing to avoid an embarrassing Bismarck moment. Can’t expect much for the price I suppose and even with its shortcomings I am having great fun with it every time I get onto the water. Oh and a pulley block it’s can clear makes the world of difference to arm fatigue by removing the need to continually hold the main sheet.
My previous post shows in the third last line that my proof reading needs some work. It should read ‘…a pulley block with cam cleat….’.
Thank you for this excellent and amusing review; I was waffling between the 8 foot that I can “sling on top of my car and carry like a turtle shell” (as I am very strong and am frequently alone during my excursions), I do believe it would be most advantages for me to simply get the 8 foot that is so manageable and does not need a freaking trailer versus the 10 foot that is more boat than I can manage by myself. HOWEVER..I am also planing on using a nice quite trolling motor on my boat as well. Did you get to try the dinghy using a trolling motor? I am wondering about battery placement/storage. Thanks
We are looking for a dinghy/skiff type boat to cross the bay over to a large sand spit in Morro Bay, CA. We happened to see a Walker 8 and loved the look. What is the weight capacity? Also, can a trolling motor work with it? Lastly, I read somewhere that they are no longer being produced – is that true? If not, we are very interested in buying one. Thank you.
The Walker Bay is now being produced in Mexico and without wishing to impugn the quality of Mexican products in general, the quality control is slipshod. I bought an 8 and sail kit last year and the holes to install the drainplug were mis-drilled requiring me to re-drill them. Worse, the rivets holding the plastic plugs in the top and bottom of the daggerboard had not been made flush. Fortunately, I found this out using the short plug instead, because it took two full grown adults using a screwdriver and a 2×4 as a lever to remove the plug. Had it been the actual daggerboard, I would not have been able to remove it without taking out the thwart. Having realized that the 8 was too small for me (I’m not as limber as I used to be) I ordered a 10. The boat arrived missing a number of bolts for the thwarts. The dealer I ordered through was told that the sail kit was missing pieces. Walker Bay refused to send the sail kit without the pieces and also refused to say what pieces were missing. For over two months both the dealer and I were constantly assured that the pieces were on their way when in fact they were not. After an incredible amount of foot dragging, the sail kit was finally sent sans the missing piece which turned out to be the daggerboard. On setting up I discovered that the clam cleat which is supposed to hold the clew outhaul was mounted backwards. It took another month for Walker Bay to send the missing daggerboard which, like the first, required me to flatten the rivet heads so it wouldn’t get stuck. Throughout this ordeal, the representatives at Walker Bay flat out lied to both the dealer and myself, and resolutely refused to make any sort of amends for their mis-dealings. The 8 and 10 are both fine boats, but I suggest buying one used rather than trying to go through obtaining one from Walker Bay.
Looking to by parts for an old Walker 8ft need tthe dagger board, sail and rudder could not afford a new one got the boat and hope to find parts. Thanks
I have had my 8′ West Marine PRU 3 roll up dinghy as my ship to shore boat for my Cal 25 sailboat in Mission Bay San Diego and it’s a used 2018 and it can leak a bit and it can be a challenge to get it up on the foredeck. I see a 2015 8′ Walker on Craigslist with a sail and orrs for $499 and I think I can buy this Walker and sell my inflatable and have a better boat to bring my wife a gear ship to shore. What do you experts think?
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Log in to leave a comment
Latest Videos

Cabo Rico 34 Boat Review

Super Shallow Draft Sailboat: The Leeboard Sharpie

Hans Christian 41T – Boat Review

Seven dead after superyacht sinks off Sicily. Was the crew at...
Latest sailboat review.

- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell My Personal Information
- Online Account Activation
- Privacy Manager

- Log in/Log out (Opens in new window)
- All content
- Rural Alaska
- Crime & Courts
- Alaska Legislature
- ADN Politics Podcast
- National Opinions
- Letters to the Editor
- Nation/World
- Film and TV
- Outdoors/Adventure
- High School Sports
- UAA Athletics
- National Sports
- Food and Drink
- Visual Stories
- Alaska Journal of Commerce (Opens in new window)
- The Arctic Sounder
- The Bristol Bay Times
- Today's Paper (Opens in new window)
- Legal Notices (Opens in new window)
- Peak 2 Peak Events (Opens in new window)
- Educator of the Year (Opens in new window)
- Celebrating Nurses (Opens in new window)
- Top 40 Under 40 (Opens in new window)
- Alaska Spelling Bee (Opens in new window)
- Alaska Craft Brew Festival
- Best of Alaska
- Spring Career Fair (Opens in new window)
- Achievement in Business
- Youth Summit Awards
- Oktoberfest Ticket Giveaway
- 311 Ticket Giveaway
- Teacher of the Month
- 2024 Alaska Summer Camps Guide (Opens in new window)
- Holiday Bazaar Guide (Opens in new window)
- 2024 Back to School (Opens in new window)
- Alaska Visitors Guide 2024 (Opens in new window)
- Bear Paw Festival 2024 (Opens in new window)
- 2023 Best of Alaska (Opens in new window)
- Alaska Health Care (Opens in new window)
- On the Move AK (Opens in new window)
- Senior Living in Alaska (Opens in new window)
- Youth Summit Awards (Opens in new window)
- Alaska Visitors Guide
- ADN Store (Opens in new window)
- Classifieds (Opens in new window)
- Jobs (Opens in new window)
- Place an Ad (Opens in new window)
- Customer Service
- Sponsored Content
Haines man dies after jet boat capsizes on Chilkat River
An 83-year-old man died last week after the boat he was on capsized on the Chilkat River near Haines, Alaska State Troopers said.
The jet boat lost power Thursday with two men aboard and was pushed into woody debris and became stuck, said troopers spokesman Justin Freeman. One of the men swam to shore, and Ronald Martin spent the night on the boat, Freeman said.
“The next morning, the water level rose and pushed the boat from the sweeper and Martin went into the water at that time,” Freeman wrote in an email.
Troopers were notified by an SOS activation on a wireless device just after 6:30 p.m. Friday that the jet boat capsized less than 50 feet from the riverbank, Freeman said. The man who swam to shore was picked up by friends, but Martin was missing, troopers said .
The U.S. Coast Guard responded and searched by air Friday night and early Saturday, Freeman said. Alaska Wildlife Troopers and volunteers in three boats began searching for Martin around 6 a.m. Saturday. His body was found about 90 minutes later, troopers said.
The two men had been preparing for the moose hunting season opener on Sunday, Freeman said.
- Electric Cars
- Electric Bikes
- Electric Boats
- EV Conversions
- Electric Flight
- Electric Transport
- Hydrogen Fuel Cell
- Readers’ Questions

Electric Candela hydrofoil boat sets world record by crossing Baltic Sea
- September 16, 2024
- 2 minute read
- Joshua S. Hill

An all-electric hydrofoiling boat from Swedish company Candela has set two new world records by travelling between Stockholm and the Finnish autonomous region of Åland, marking the first time an electric boat has crossed the Baltic Sea.
Candela, which has developed a range of electric hydrofoil boats and ships, wanted to demonstrate that “that zero-emission sea travel is not only possible today, but that foiling electric ships and boats are so much cheaper to operate than fossil-fuelled vessels.”
The record-breaking journey was undertaken in the Candela C-8, a €330,000 ($A544,500) leisure craft, equipped with a battery from technology partner Polestar.
The journey covered 150 nautical miles from the port of Frihamn in Stockholm, Sweden, to Mariehamn, the capital and largest town of the Åland Islands, an autonomous region of Finland, with a charging stop in Kapellskär.
While charging along the trip was made mostly with existing charging infrastructure, a 40kW Kempower Movable Charger was needed in Kapellskär.
Leaving from Frihamn at 6am, the Candela C-8 made it to Mariehamn by lunchtime, and returned to Frihamn the same day.
YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6hFoRF_Q0CA
“The disadvantage of electric boats has been their short range, due to traditional boat hulls consuming so much energy,” said Gustav Hasselskog , the company’s CEO and founder.
“With our hydrofoil technology, we combine high speed and range, but you get so many other benefits. Flying over the Åland Sea in total silence and without slamming was absolutely magical.”
A gasoline-powered chase boat of similar size accompanied the Candela C-8 on the journey and had to be refuelled for a cost of €750, or around $A1,230. For comparison, the Candela C-8 consumed 213 kWh of electricity, at a cost of about €40-50 (around $A66-83).
“We actually had range anxiety, but not for the Candela,” said Gustav Hasselskog.
“The irony is that the photographer’s gasoline-powered chase boat had to refuel six times during the trip, while we only charged three times.
“We’re talking about 95% lower operating costs,” concluded Hasselskog. “This is a revolution that makes waterborne transöport competitive with land transport in terms of costs, which we will now demonstrate in public transport in Stockholm.”
Joshua S. Hill is a Melbourne-based journalist who has been writing about climate change, clean technology, and electric vehicles for over 15 years. He has been reporting on electric vehicles and clean technologies for Renew Economy and The Driven since 2012. His preferred mode of transport is his feet.
We are definitely in an age of disruption, as much as the bashers, critics and cynics like to deny it. Amazing, 1/25th the cost of their ICE partner boat! And quieter, cleaner and calmer too boot!
Google informs me a litre of diesel is € 1.668, so that trip would have used ~450 litres of diesel, or 4,500 kWh. That’s shockingly inefficient.
I’m all for cheaper and cleaner water transöport!
Input your search keywords and press Enter.

- SUBSCRIBE TO EMAIL
- Weather
Search location by ZIP code
Vacationing couple rescued from water in south carolina after following gps, driving off boat dock.
- Copy Link Copy {copyShortcut} to copy Link copied!

GET NATIONAL BREAKING NEWS ALERTS
The latest breaking updates, delivered straight to your email inbox.
A couple in their 60s is safe after a near disaster in Isle of Palms, South Carolina, thanks to the quick actions of strangers.
The vacationing couple accidentally drove their vehicle off a marina boat dock and into the water below due to GPS confusion, leading to a dramatic rescue.
Christopher Sollom, general manager of the Islander 71 restaurant, described the scene.
"One of our bartenders, Johnny, a former lifeguard down in Myrtle Beach, didn't even hesitate; he jumped right in and was able to pull two people out of the car before it submerged into the water," Sollom told WCIV-TV .
Another employee, known as "Cash," joined Johnny in the water while other staff members sprang into action.
"By the time that I got down here, it was completely submerged," Sollom said. "So, that was a matter of 60 seconds from when someone got me upstairs to when I ran downstairs."

After the initial rescue, Sollom helped the woman to safety.
"The lady was very frantic; you could tell she was trying to gather everything to get out, so that’s where we assisted her from there," he added.
Fortunately, the couple had left their windows open, making the rescue easier.
The couple is doing well and plans to thank their rescuers.
On Sunday, a dive team from the Charleston County Sheriff’s Office helped retrieve the submerged vehicle.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Dinghy sailing helps improve your understanding of a wide variety of skills, whether you are just starting out or a seasoned keelboat sailor, sailing a dinghy is a hugely rewarding pastime. TAGS ...
5) Sailing Dinghy. The sailing dinghy is the quintessential starter sailboat. These tiny, lightweight, popular, and highly affordable little craft is easy to operate and relatively difficult to capsize. The popular Optimist Sailing Dinghy, while designed for children up to the age of about 15, can be used (sometimes hilariously) by adults as well.
Dinghy Cons: Difficult for larger people who may not be able to fit comfortably in certain boats. Can cause soreness and injury because of athleticism required, and can be difficult for older or less active people. Less mid-level sailing available for adults. Fun, noncompetitive sailing and high level regattas are most common.
For decades, the boat has been the single-handed sailors choice among junior sailing programs, and with the addition of the Radial, 4.7 and M rigs, smaller competitors have also found the boat to be a great sailing platform. Today, theres some lawyer saber-rattling over the sale of the design rights, but the boat remains more popular than ever.
The Laser is the best choice for a single-hander sailboat dinghy. This boat is ideal for cruising or competitive racing, and they hold their resale value. Laser. You get options for three rig sizes, the 4.7, Standard, and the Radial model. These boats feature fiberglass design and low hulls for easy navigation through shallow waters.
Dinghy sailboats are small, single-person boats with a sail to add power. Dinghies can be rowed or sailed, but if you're new to the sport of dinghy sailing, it's best to find a boat that has both options. Most dinghies have a rudder for steering and are made of lightweight materials like aluminum or fiberglass. The design of dinghies makes ...
Dinghy sailboats are the most traditional and widely used type of dinghies. They come in various designs and materials, such as fiberglass, wood, or aluminum. Dinghy sailboats use the wind as their primary means of propulsion, with a main sail and, in some cases, a jib. These boats offer an excellent opportunity for learning to sail due to ...
Tie the boat securely on the trolley. Put the detachable items inside the Dinghy. Fit the boat cover over the top and make sure that it is fastened firmly. Secure it under the Hull, Bow, as well as the sidedecks. To prevent your Dinghy from being blown over, tie the Sailboat down to securing points on the ground.
A crew of two can manage with a much smaller dinghy than a family of six. As well, four adults require a bigger boat than two adults and two small children. Knowing the total number and maximum weight of your crew is important information for choosing a dinghy that will be comfortable and safe. 2.
Sailing World Magazine's Best Dinghy of 2024 is the RS Toura, a 15-foot rotomolded plastic dinghy designed for sailing schools and community boating, yacht clubs and adult and junior sailing ...
The decision tree is a circle. The decision to go to a RIB was a simple one. The hard, slightly V'd bottom planes easier, runs faster and turns better than an air floor. The RIB tows better and is far less likely to flip when under tow. The bottom is better suited for beaching without worrying about sharp objects.
Each one has product ranges covering almost all the inflatable types mentioned above, though not everyone makes a soft tail. Achilles LT Series - Soft tail dinghy with oars and an engine mount for up to 3Hp. Check it here. Zodiac Cadet - Soft bottom hull with several options for rolling or rigid floor. Check it here.
Dinghy Sailing vs Sailboat Sailing. Eight key differences between dinghy sailing and sailboat sailing: 1. Size. A dinghy is a type of small boat, often carried or towed for use as a lifeboat by a larger vessel. Dinghies usually range in length from about 2 to 6 m (6.6 to 19.7 ft.) and can carry from 1 to 8 people.
The different types of dinghies include sailing dinghies and power dinghies. Sailing dinghies have sails and do not have any type of motor attached to them and power dinghies have no sails and rely on motor power to move through the water. When it comes to a dinghy, don't let the size fool you. These little vessels can catch some serious ...
Above: A 2022 Polycraft 300 Tuffy tender boat for sale on Boat Trader by Nautical Ventures in Sarasota, FL. This lightweight plastic hull tender (made of polyethylene, a thermoplastic polymer) is strong, durable and easy to maintain, clean and repair. Photo via Nautical Ventures. Hard dinghies also vary in size, weight and design and are made ...
Generally speaking, fully inflatable dinghies that measure around 10-feet in length support a 5-8 horsepower outboard, which is sufficient for the basics. For a more capable inflatable, look for a 10-25 horsepower outboard. Just be cautious, as too much power can flip a lightweight dinghy.
Sailing schools, clubs and training centres use a variety of boats with beginners, including singlehanders such as the Pico, Hartley 10 and the RS Quba, the latter having three rigs catering from entry level to more experienced sailors. There's also a range of larger training dinghies from builders such as RS, Topper, Laser and Hartley Boats.
Cons of Cruising in an Wanderer Sailing Dinghy. While the Wanderer is a great boat for sailing, a potential downside to this dinghy is the need to have multiple crew onboard. While sailing a Wanderer can undoubtedly be done solo, for most sailors, having some extra hands on deck will make sailing the 2-3 person Wanderer dinghy much more pleasant.
Boat of the Year dinghy expert Chuck Allen puts the 9-foot Tiwal 2 inflatable dinghy to the stress test in 20 to 30 knots of breeze. It was plenty quick, he says, and the bow was rigid enough to ...
A hard dinghy is virtually indestructible compared to an inflatable or RIB. Its economical, and its always ready to deploy. There are almost just as many reasons why hard dinghies are the wrong solution. They are harder to stow, hard on topside paint, relatively unstable, and require more patience when getting from here to there.
Short answer: Tender vs Dinghy. A tender is a small boat used primarily for transport between a larger vessel and the shore, whereas a dinghy is a small boat typically used for recreational purposes or as a lifeboat. Tenders are usually designed with greater stability and carrying capacity for passengers and supplies, while dinghies prioritize ...
Before choosing a boat for all your watercraft adventures, deciding which boat will be the best option for your needs is important. Today, we look at the differences between the two boats we just mentioned — center consoles vs. bay boats — and how to determine if one of these boats is the best one for your needs. Center Consoles
Understanding trade-offs is the key to selecting the right dinghy. Each type of dinghy has both strong points and limitations. Charter companies love the durability and ease of repairs that comes with fiberglass dinghies. From the main boat they are easy to get in and out of. In addition, they carry loads easily and stand up well to the wear ...
Most importantly, some hard dinghies, like these, can be sailed, and there's nothing more fun than poking around a far-flung harbor at sunset in a sailing dinghy. Walker Bay would of course like to see their sailing rigs used in more and more junior and community programs. A new JY Trainer costs about $1,850. A new Optimist costs around $2,325.
The Candela C-8 electric boat reduces energy consumption 80%. And, it just broke a distance record. LeeAnne Lowry. More Videos. Boeing Starliner: Astronauts reveal mission's affect on families.
Troopers were notified by an SOS activation on a wireless device just after 6:30 p.m. Friday that the jet boat capsized less than 50 feet from the riverbank, Freeman said.
Sailing schools, clubs and training centers use a variety of boats with beginners, including singlehanders such as the Pico, Hartley 10 and the RS Quba, the latter having three rigs catering from entry level to more experienced sailors. There's also a range of larger training dinghies from builders such as RS, Topper, Laser and Hartley Boats.
An all-electric hydrofoiling boat from Swedish company Candela has set two new world records by travelling between Stockholm and the Finnish autonomous region of Åland, marking the first time an electric boat has crossed the Baltic Sea. Candela, which has developed a range of electric hydrofoil ...
Prosecutors in Italy are seeking a six-year jail term for deputy prime minister Matteo Salvini over a decision in August 2019 to stop a migrant boat from docking. The ship, operated by the Open ...
The Isle of Palms police sa's confusion with the couple's gps led them off the marina's boat dock into the water. By the time I got down here, the car was completely submerged underwater. So that ...