Types of Sailboats: Essential Guide for Every Sailor
Sailboats have been an essential part of human history, contributing to exploration, trade, and leisure. With a myriad of designs and sizes, these versatile vessels cater to various purposes and preferences. The defining characteristics of sailboats come from their rigging, sails, and hull design.

The basics of sailboat design play a significant role in the classification and function of these vessels. Hull shapes, keel types, and construction materials contribute to the speed, stability, and maneuverability of sailboats. Additionally, rigging and sails come in various shapes and sizes, which influence sailing performance and handling.

Key Takeaways
- Sailboats are classified by hull design, rigging, and sails that serve specific purposes.
- Designs and materials have a direct impact on the performance and handling of sailboats.
- A wide range of sailboat types exists, which cater to different needs and preferences.
Basics of Sailboat Design
Sailboats come in various shapes and sizes, designed for different purposes and sailing conditions. One can classify sailboats based on hull types, keel types, and mast configurations. This section will briefly discuss these basic components of sailboat design.
There are mainly two types of hulls: monohull and multihull.
- Monohull : This is the traditional and most common type of sailboat hull. It consists of a single hull, providing stability through the use of a keel or centerboard. Monohulls come in various shapes and sizes, suitable for various sailing conditions.
- Catamaran : Catamarans have two parallel hulls of equal size, offering increased stability and speed compared to monohulls. They are commonly used for cruising and racing.
- Trimaran : Trimarans have three hulls, with a larger central hull and two smaller outrigger hulls. This design offers even more stability and speed than catamarans.
The keel is an essential component in sailboat design, helping with stability and performance. There are various keel types, including:
- Full keel : This traditional design features a long and wide keel that extends along the boat's bottom. It offers good tracking and stability but sacrifices speed and maneuverability.
- Fin keel : Fin keels are shorter and deeper than full keels, providing a better combination of stability and maneuverability. These are common in modern monohull sailboats.
- Bulb keel : A bulb keel features a fin keel with a heavy bulb at the bottom, which concentrates the boat's weight, increasing stability and performance in rough conditions.
- Swing keel or centerboard : Swing keels and centerboards can be raised or lowered, allowing the boat to adapt to different water depths and sailing conditions. They are common in smaller boats and racing sailboats.

Mast Configuration
The mast configuration affects the sail plan and overall performance of a sailboat. Some common mast configurations include:
- Sloop : This is the most popular mast configuration and features a single mast with a mainsail and a headsail. The simple design makes it easy to handle and suitable for various sailing conditions.
- Cutter : Similar to the sloop, the cutter also has a single mast but carries two headsails, providing more sail area and better performance in heavy weather.
- Ketch : A ketch configuration has two masts: a taller main mast and a shorter mizzen mast. This design offers more flexibility in sail combinations and better balance in different sailing conditions.
- Yawl : Similar to a ketch, a yawl also features two masts but the mizzen is located further aft and is smaller. This design provides better balance and control, particularly in downwind sailing scenarios.
In conclusion, the basics of sailboat design involve selecting the appropriate hull type, keel type, and mast configuration for the desired sailing performance and conditions. Understanding these concepts can help sailors make informed decisions when choosing a sailboat or planning their sailing adventures.
Rigging and Sails
When it comes to sailboats, the rigging and sails play a crucial role in the boat's overall performance and capabilities. This section will briefly cover popular rig types and sail types seen on different sailboats.
There are several types of rigs commonly found on sailboats:
- Sloop : Sloops are the most common type of rig found on modern sailboats. They have a single mast with a mainsail and a single headsail, typically a genoa or jib.
- Ketch : Ketches have two masts, with the main mast taller than the mizzen mast situated aft. They carry a mainsail on the main mast and a mizzen sail on the mizzen mast. Ketches benefit from easier handling and reduced sail area under strong winds.
- Yawl : Similar to ketches, yawls have two masts, but the mizzen mast is smaller and sits further aft, behind the rudder post. Yawls are often chosen for their graceful appearance and improved balance.
- Schooner : Schooners have two or more masts, with the aft mast(s) typically taller than the forward mast(s). Schooners can handle more sails, offering increased sail area for better performance, especially downwind.
- Catboat : Catboats are single-masted sailboats with a single, large mainsail and no headsails. They have a wide beam, which provides stability and ample space for passengers.
- Cutter : Cutters are similar to sloops but carry two headsails, usually a jib and staysail. Cutters may have multiple headsails for increased versatility in various wind conditions.
In addition to the types of rigs, there are also several types of sails used on sailboats, including:
- Mainsail : The primary sail attached to the back of the main mast. It is typically raised on a track or luff groove and managed by a combination of halyard, sheet, and boom vang.
- Genoa : A large triangular sail that overlaps the mainsail, typically used in light winds to provide additional surface area for better performance.
- Jib : A smaller, non-overlapping triangular sail attached to the forestay. Jibs are easier to manage than genoas and are used in a variety of wind conditions.
- Spinnaker : A large, lightweight sail used primarily for downwind sailing . Spinnakers are often brightly colored and shaped like a parachute to catch wind efficiently.
- Staysail : A smaller sail typically used in cutter rigs, positioned between the main mast and the forestay. Staysails provide additional sail area and versatility in varied wind conditions.
Understanding the relationship between sail and rigging can help sailors optimize the performance of their sailboats. With various options for rig types and sail types, each sailboat can be configured to meet the unique needs of its skipper and crew.

Classes and Types of Sailboats
Monohulls are the most common type of sailboats, consisting of a single hull that provides stability and balance. They come in various sizes and designs, depending on their intended use. Some popular monohull sailboats include the Optimist , Finn, and Sunfish, which are frequently used for racing and recreational sailing. Monohulls tend to have a deeper draft, requiring more water depth than their multi-hull counterparts.
Multihulls, also known as multi-hull sailboats, are a more modern innovation in sailing. They feature two or more hulls connected by a frame or bridgedeck. This design offers increased stability and speed over monohulls. Some common types of multihulls are catamarans (with two hulls) and trimarans (with three hulls). Due to their wider beam and shallower draft, multihulls are particularly suitable for cruising in shallow waters and provide more living space on board.
One-Design Sailboats
One-Design sailboats are a specific class of racing sailboats in which all boats are built to the same design specifications, ensuring that the competition focuses on the skill of the sailor rather than the design of the boat. These boats must adhere to strict rules and standards, with minimal variations allowed in terms of hull shape, sail area, and rigging. Some popular one-design sailboats include the Enterprise and the aforementioned Optimist and Finn sailboats.
Dinghies and Skiffs
Dinghies and skiffs are small, lightweight sailboats that are often used for sailing classes, short-distance racing, or as tenders to larger boats. Dinghies usually have a single mast with a mainsail and sometimes a small jib. Some popular types of sailing dinghies include the Optimist, which is specifically designed for children, and the versatile Sunfish sailboat. Skiffs, on the other hand, are high-performance sailboats primarily used for racing. They have a larger sail area relative to their size and typically include features such as trapezes and planing hulls, which allow for faster speeds and greater maneuverability.
In conclusion, there are various classes and types of sailboats, each with its own unique features and characteristics. From the simplicity of monohulls to the stability and speed of multihulls, and from the fair competition of one-design sailboats to the excitement of dinghies and skiffs, there is a sailboat to satisfy every sailor's preferences.
Sailboat Size and Use
When exploring the world of sailboats, it's important to understand their different sizes and purposes. Sailboats can be categorized into three main types, each with unique characteristics and uses: Day Sailers , Racing Sailboats, and Cruising Sailboats .
Day Sailers
Day Sailers are small sailboats typically ranging from 10 to 24 feet in length. These boats are perfect for short sailing trips and are easy to maneuver for beginners. They have limited accommodations on board, providing just enough seats for a small group of people. Some popular day sailer models include the Laser, Sunfish, and Flying Scot. Lightweight and agile, Day Sailers are often used for:
- Recreation: casual sailing or exploring nearby waters with family and friends
- Training: beginner sailing lessons or practicing sailing techniques
- Competition: local club races or interclub regattas
Racing Sailboats
Racing Sailboats are designed to provide maximum speed, maneuverability, and efficiency on the water. Sizes may vary greatly, from small dinghies to large yachts. Key features of racing sailboats include a sleek hull shape, high-performance sails, and minimalistic interiors to reduce weight.
Career racers and sailing enthusiasts alike participate in various types of racing events , such as:
- One-design racing: all boats have identical specifications, emphasizing crew skill
- Handicap racing: boats of different sizes and designs compete with time adjustments
- Offshore racing: long-distance racing from one point to another, often around islands or across oceans
Cruising Sailboats
Cruising Sailboats are designed for longer journeys and extended stays on the water. They typically range from 25 to 70 feet in length and provide comfortable accommodations such as sleeping cabins, a galley, and storage spaces for supplies and equipment. Sailing cruisers prioritize stability, comfort, and durability for their voyage.
Here are some common types of cruising sailboats:
- Cruiser-racers: These boats combine the speed of a racing sailboat with the comfort and amenities of a cruising sailboat. They are ideal for families or sailors who enjoy participating in racing events while still having the option for leisurely cruises.
- Bluewater cruisers: Designed for handling the world's most demanding ocean conditions, bluewater cruisers are built with a focus on sturdy, self-reliant sailboats that can withstand long-distance voyages and challenging weather conditions.
- Multihulls: Catamarans and trimarans are gaining popularity in the cruising world for their typically more spacious interiors and level sailing characteristics. With two or three hulls, multihulls offer high levels of stability and speed for a comfortable cruising experience.
Understanding the differences between various sailboat types will help potential sailors select the perfect vessel for their sailing goals, skills, and preferences. Day Sailers, Racing Sailboats, and Cruising Sailboats each have their unique features, catering to distinct uses and sailing experiences.
Advanced Sailboat Features
Sailboats have evolved over time, and many advanced features have been developed to enhance performance and safety. In this section, we will discuss some of the key advanced features in modern sailboats, focusing on performance enhancements and safety/navigation.
Performance Enhancements
One critical component that impacts a sailboat's performance is the type of keel it has, which affects stability, resistance, and maneuverability . There are several kinds of keels such as fin keel , wing keel , and bulb keel . Fin keels offer low drag and high efficiency, making them suitable for racing sailboats. On the other hand, wing keels provide better stability at low speeds, while bulb keels provide a lower center of gravity to enhance overall stability and comfort during long voyages.
Another feature that contributes to a sailboat's performance is its sails and rigging. The jib is a triangular sail at the front of the boat, which helps improve its upwind performance. More advanced sailboats use a combination of shrouds , which are the supporting cables running along the sides of the boat, and stays , the cables that help hold the mast in place, to create a stable and efficient rigging system.
A sailboat's performance can also be influenced by the presence of a centerboard or daggerboard , which can be adjusted to optimize stability, maneuverability, and speed. When racing or navigating in shallow waters, retractable centerboards and daggerboards are particularly useful as they provide better performance and versatility.
Safety and Navigation
Safety and navigation onboard a sailboat relies on a combination of advanced gear and equipment. A modern sailboat is usually equipped with:
- GPS and chartplotters to assist with navigation and planning routes
- VHF radios for communication with other vessels and authorities
- Radar to detect obstacles, weather systems, and other vessels
- AIS (Automatic Identification System) which helps monitor nearby vessel traffic
The design of a sailboat's hull, rigging, sails, and hardware also contribute to its safety. The boom , the horizontal pole that extends the sail, should be properly secured and designed to avoid accidents while sailing. The keel , whether it's a fin, wing, or bulb keel, plays a vital role in the overall stability and safety of the sailboat. The choice of keel should be based on the intended use of the sailboat and the prevailing sailing conditions.
In summary, advanced sailboat features significantly improve the performance, safety, and navigation capabilities of modern sailboats. Innovations in keel design, rigging systems, and onboard navigational equipment have undoubtedly contributed to the overall enjoyment and safety of sailing.
Sailboat Ownership
Buying Considerations
When considering buying a sailboat , it is important to understand the different types of sailboats available and the purpose each serves. Sailboats can be broadly categorized into three types:
- Racing sailboats: Designed for speed and performance, with minimalistic interiors and advanced sail systems.
- Cruising sailboats: Built for comfort and longer trips, featuring more spacious interiors and amenities.
- Daysailers: Smaller, easy-to-handle boats that are often used for short trips and recreational sailing.
Prospective boat owners should consider factors such as boat size, type, budget, and intended use (solo vs. family sailing, charter operations, etc.). It's also essential to evaluate the availability of necessary gear and the level of experience required to handle the chosen sailboat.
Maintenance and Upkeep
Sailboat ownership involves maintenance and upkeep to ensure the boat remains functional, safe, and holds its value. Some common maintenance tasks include:
- Hull cleaning and inspection: Regularly inspect the hull for damages and clean off any growth to maintain performance and fuel efficiency.
- Antifouling paint: Apply antifouling paint to prevent marine organisms from attaching to the hull, which can negatively impact the boat's performance.
- Engine maintenance: Check and replace engine oil, inspect cooling and fuel systems, and clean or replace air filters.
In addition to regular maintenance, sailboat owners should also be prepared to replace or repair critical systems and components, such as:
- Sails: Monitor the condition of your sails and replace them as needed to maintain performance and safety.
- Rigging: Regularly inspect and maintain the standing and running rigging, and replace worn or compromised parts.
- Electronics and instruments: Ensure navigation systems, radios, and other electronic equipment are functioning properly.
Taking proper care of a sailboat can be time-consuming, and some owners may choose to charter their boats when not in use as a way to offset ownership costs. Others may opt for hiring professionals to manage routine maintenance, particularly when sailing solo or with limited sailing experience.
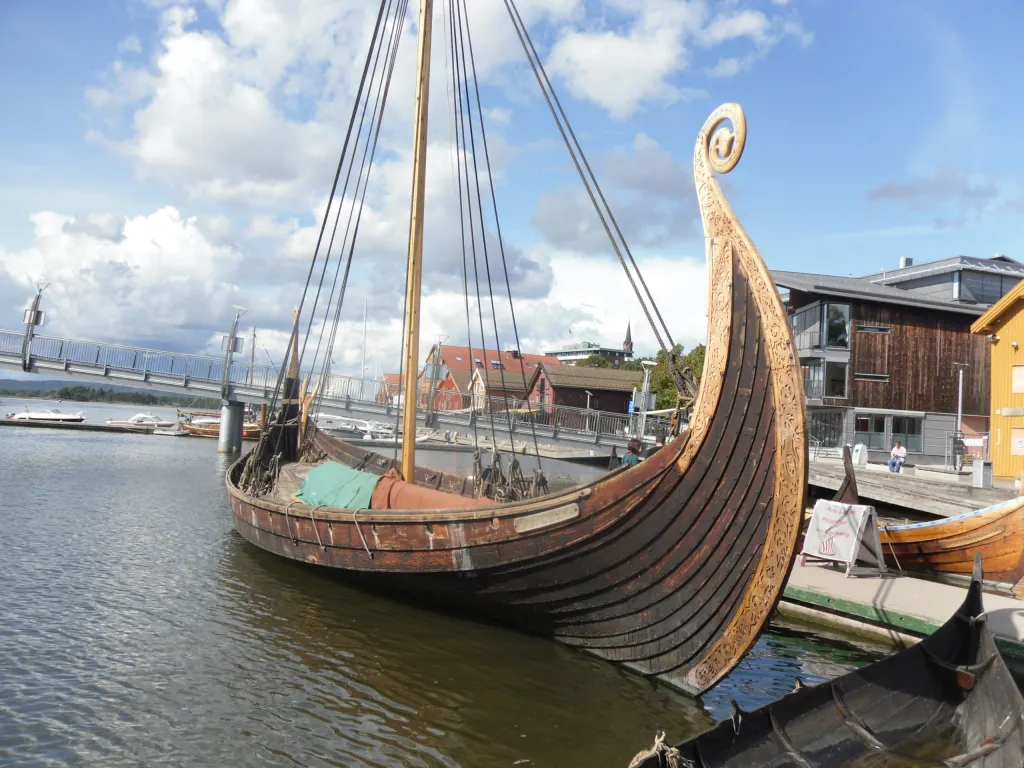

Historical and Special Sailboats
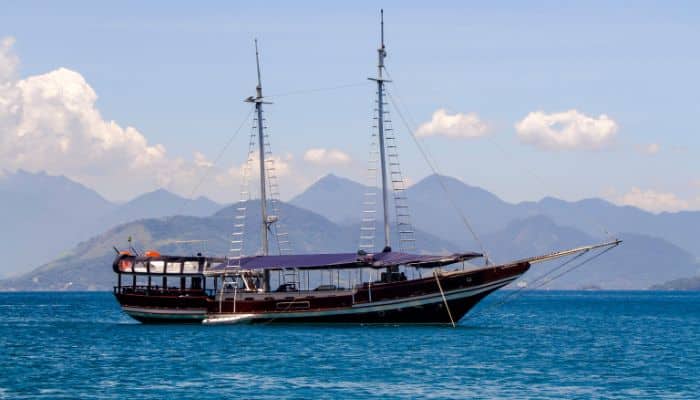
Tall ships and gaffers.
Tall Ships are large, traditionally rigged sailing vessels with multiple masts, typically square-rigged on at least one of their masts. Some examples of these ships include the clipper, brig, and square-rigged vessels. The clipper is a fast sailing ship known for its sleek hull and large sail area, while the brig features two square-rigged masts. Square-rigged ships were known for their impressive sail area and could cover large distances quickly.
Gaffers are a subset of historical sailing vessels with a gaff mainsail as their primary sail type. This gaff-rig is characterized by a spar (pole) that extends the top edge of the mainsail, giving it a quadrilateral shape to optimize wind coverage. Gaff mainsails were commonly used in England and influenced the development of other sailing vessels.
Classic and Antique Sailboats
Classic and antique sailboats refer to older, traditionally designed sailing vessels that have been preserved or restored. They often feature wooden construction and showcase a variety of rigging types, including gaff rigs and square rigs. These historical sailboats have unique designs, materials, and techniques that have since evolved or become rare.
Here are some examples of antique and classic sailboats:
- Sloop : A single-masted sailboat with a Bermuda rig and foresail
- Cutter : A single-masted vessel with a similar rig to the sloop, but with additional headsails for increased maneuverability
- Ketch : A two-masted sailboat with a smaller mizzen mast aft of the main mast
In summary, historical and special sailboats encompass a wide range of vessel types, from large, multi-masted tall ships to smaller, single-masted gaffers and classic sailboats. These vessels reflect the rich maritime history and the evolution of sailing techniques and designs over time.
Sailboat Culture and Lifestyle
Sailboat culture and lifestyle encompass a variety of aspects including racing events, leisurely cruising, and exploring new destinations. The main types of sailboats include racing yachts, cruising sailboats, and motorsailers, each offering a unique experience for sailors.
Regattas and Racing Circuits
A popular aspect of sailboat culture involves participating in regattas and racing circuits . These events create a competitive atmosphere and develop camaraderie among sailors. Racing sailboats are specifically designed for speed and agility , and sailors often team up to compete in prestigious races such as the Rolex Sydney Hobart Yacht Race or the America's Cup. Yacht clubs play an essential role in cultivating this competitive sailing environment.
Sailboat Charter and Tourism
Another facet of sailing culture is the sailboat charter and tourism industry, which allows people to experience the cruising lifestyle without owning a sailboat. Charters are offered for various types of sailboats, from family-sized cruising vessels to luxurious superyachts . Yacht sailing provides tourists with a unique travel experience, as they can explore diverse destinations, immerse themselves in local cultures, or simply relax on the open water.
Cruising sailboats are designed to provide comfortable living spaces and amenities, making them perfect for longer journeys or exploring remote destinations. Motorsailers, on the other hand, are equipped with both sails and engines, offering versatility and convenience for sailors.
Some popular sailing destinations include the Caribbean, Mediterranean Sea, and the South Pacific. These regions offer beautiful scenery, rich cultural experiences, and ideal sailing conditions.
The sailboat culture and lifestyle attract individuals who enjoy adventure, exploration, and camaraderie. From competitive racing events to leisurely cruising vacations, sailing offers diverse experiences that cater to a wide range of interests.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the distinguishing features of different sailboat classes?
There are various sailboat classes, each with its own distinguishing features. Monohulls, for example, are the most common type of sailboat and have a single hull. Multihulls, such as catamarans and trimarans, have two or three hulls, respectively. These differences in hull design often affect the boat's stability, speed, and maneuverability.
Which sailboat types are best for novice sailors?
Novice sailors often benefit from starting with smaller, more manageable boats. Sailing dinghies and daysailers are popular choices due to their simple rigging and ease of handling. These boats typically have a single mast and a limited number of sails, making them ideal for beginners to learn sailing basics.
What are common types of small sailboats ideal for day sailing?
For day sailing, small sailboats such as sailing dinghies, day sailers, and pocket cruisers are ideal options. These boats usually range between 12 and 25 feet in length and offer simplicity, ease of handling, and portability. Examples of common day sailing boats include the Sunfish, Laser, and O'Day Mariner.
How do the purposes of various sailboat types vary?
Sailboats serve different purposes based on their design, size, and features. Daysailers and dinghies are ideal for short trips, sailing lessons, and casual outings. Racing sailboats, with their lighter weight and streamlined design, are built for speed and competition. Cruising sailboats, on the other hand, are designed for longer voyages and often include living quarters and additional amenities for comfortable onboard living.
What is considered the most popular class of sailboat for recreational use?
The most popular class of sailboat for recreational use often varies depending on individual preferences and local conditions. However, monohulls are commonly preferred due to their widespread availability, versatility, and affordability. Within the monohull class, boats like the Sunfish, Laser, and Catalina 22 are popular choices for their ease of use and adaptability to various sailing conditions.
Could you describe a sailing dinghy designed for two people?
A two-person sailing dinghy typically has a simple rig with a single mast and one or more sails, making it easy to handle for both experienced and novice sailors. The RS Venture , for example, is a popular choice for two-person sailing. It features a spacious cockpit, durable construction, and simplicity in its rigging and control systems. These characteristics make it an excellent option for recreational sailing, training, and even racing.
Related Articles

Top 5 Boat Dealers Kentucky: Best Places to Buy or Lease a Boat

Beneteau Gran Turismo 50 Sportfly: A Comprehensive Review

Sunworld Watersports Sarasota: Your Guide to Exciting Aquatic Adventures

How Do You Know When You Are Operating Your Vessel at a Safe Speed? Essential Tips and Guidelines

John Pennekamp State Park: A Gateway to Florida's Underwater Wilderness

Jet Boat Essentials: A Comprehensive Guide for Enthusiasts

Shipping Companies: Complete List & Guide to Efficient Global Transport

Safe Harbor - Ultimate Marina Guide: Essential Tips and Insights
- Types of Sailboats
- Parts of a Sailboat
- Cruising Boats
- Small Sailboats
- Design Basics
- Sailboats under 30'
- Sailboats 30'-35
- Sailboats 35'-40'
- Sailboats 40'-45'
- Sailboats 45'-50'
- Sailboats 50'-55'
- Sailboats over 55'
- Masts & Spars
- Knots, Bends & Hitches
- The 12v Energy Equation
- Electronics & Instrumentation
- Build Your Own Boat
- Buying a Used Boat
- Choosing Accessories
- Living on a Boat
- Cruising Offshore
- Sailing in the Caribbean
- Anchoring Skills
- Sailing Authors & Their Writings
- Mary's Journal
- Nautical Terms
- Cruising Sailboats for Sale
- List your Boat for Sale Here!
- Used Sailing Equipment for Sale
- Sell Your Unwanted Gear
- Sailing eBooks: Download them here!
- Your Sailboats
- Your Sailing Stories
- Your Fishing Stories
- Advertising
- What's New?
- Chartering a Sailboat
The Different Types of Sailboats
If you’re a sailboat fanatic like me, all types of sailboats will attract your attention. Some more so than others admittedly, but all will have something about them that catches your eye.
If you’re not a fanatic (not yet, that is) but just an interested observer, then the first thing you’ll notice about a sailboat will be how many masts it has and the configuration of its sails - in other words, its 'rig'.
This observation alone will enable you to identify the five main types of sailboats — sloops, cutters, ketches, yawls and schooners - all of which are described here.
But apart from the various rig types, you can describe types of sailboats from a different viewpoint - sailing dinghies, dayboats, motorsailors, monohulls, catamarans and trimarans.
Let's make a start with the various rig types...
A single-masted sailboat with just two sails — a foresail (aka headsail or jib) and a mainsail — is a sloop, the purest type of sailboat.
The sloop rig can also be described as a Bermuda rig, Bermudian rig or Marconi rig.
Read more about sloops...
Examples of Sloops

If a sloop has an additional sail between the headsail and the mainsail, then it's no longer a sloop - it's a cutter.
Some cutters - like the one shown here - have the foresail set forward on a bowsprit, with the inner forestay permanently rigged to the stemhead where the foresail otherwise would be, or to a central chainplate further aft on the foredeck.
Read more about cutters...
Examples of Cutters

The following boats may look like cutters with their double headsails, but they're not cutters at all...

To find out why, click here...
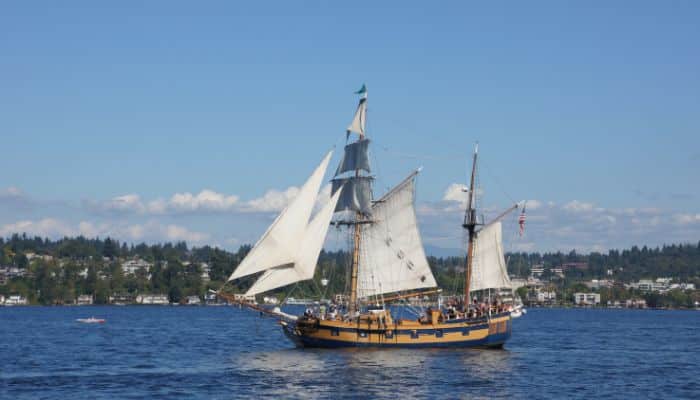
A ketch is a two-masted sailboat, a main mast forward and a shorter mizzen mast aft.
But not all two-masted sailboats are ketches — they might be yawls (see below).
A ketch may also sport a staysail, with or without a bowsprit, in which case it would be known as a cutter-rigged or staysail ketch.
Read more about ketches...
Examples of Ketches

Note that the Ocean 71 and the Irwin 52 are cutter-rigged, and are traditionally referred to as Staysail Ketches .
Cat Ketches
Cat-ketches are recognised by the lack of any standing rigging to support their pair of unstayed masts.
And yes, if the after mast is taller than the foremast then it's called a cat- schooner sailboat.
Read more about cat-ketches...

Yawls have their origins as old-time sail fishing boats, where the small mizzen sail was trimmed to keep the vessel steady when hauling the nets.
Much like a ketch, the difference being that the yawl has the mizzen mast positioned aft of the rudder post whereas the ketch has its mizzen mast ahead of the rudder post.
You’ll not be surprised to learn that a yawl with a staysail is known as cutter-rigged yawl.

A schooner is a two-or-more masted sailboat, in which the aft-most mast - the mainmast - is the same height or taller than the foremast.
The one shown here is gaff cutter rigged, with a topsail set on the mainmast.
Many sailors agree that of all the different types of sailboats, a schooner under full sail is one of the most beautiful sights afloat.

Gaffed-rigged sailboats, or 'gaffers', have their mainsail supported by a spar - the 'gaff' - which is hauled up mast by a separate halyard.
Often these types of sailboats are rigged with a topsail, as shown here and in the gaff schooner above, which really adds some grunt in light airs.
All this comes at a price of course, both in terms of material cost and weight aloft, which is why very few modern yachts are fitted with gaff rigs these days.
All artwork on this page is by Andrew Simpson

Examples of the Various Types of Sailboats...

Other Types of Sailboats
The seven sailboat rig variations shown here are the most popular types of modern cruising boat rigs, but there are other rig versions which were once found on commercial, fishing, and naval sailing vessels.
They include:
- Full square-rigged sailing vessels
- Barkentines
- Brigantines
And you can see examples of them here ...
In this article I've said that ketches, yawls and schooners with two headsails can be called cutter rigged. This is a commonly used description but strictly speaking, there's only one rig that can accurately be called a cutter - and that's a single-masted sailboat with two headsails. My thanks to 'Old Salt' for drawing my attention to this!
Recent Articles
The CSY 44 Mid-Cockpit Sailboat
Sep 15, 24 08:18 AM
Hallberg-Rassy 41 Specs & Key Performance Indicators
Sep 14, 24 03:41 AM
Amel Kirk 36 Sailboat Specs & Key Performance Indicators
Sep 07, 24 03:38 PM
Here's where to:
- Find Used Sailboats for Sale...
- Find Used Sailing Gear for Sale...
- List your Sailboat for Sale...
- List your Used Sailing Gear...
Our eBooks...

A few of our Most Popular Pages...

Copyright © 2024 Dick McClary Sailboat-Cruising.com

All You Need to Know: Explaining the Different Types of Sailboats
Sailboats are a type of watercraft that are powered by the wind. They come in a variety of shapes and sizes, each with its unique characteristics and features. Understanding the different types of sailboats and their uses can be helpful for those who are interested in sailing or looking to purchase a sailboat.
Several factors determine the types of sailboats, including the hull type , keel type , mast configuration, and sails and rigging . The hull is the boat’s body and can be either a monohull, catamaran , or trimaran .
The keel is the underwater part of the hull that provides stability and can be either a fin keel, wing keel, bilge keel, daggerboard, or centerboard. The mast configuration and sails determine how the boat is powered, and can be a sloop, fractional rig sloop, ketch, schooner, yawl, cutter, or cat.
Types of Sailboats
Sailboats come in many different shapes and sizes, each designed for a specific purpose. Here are the most common types of sailboats:
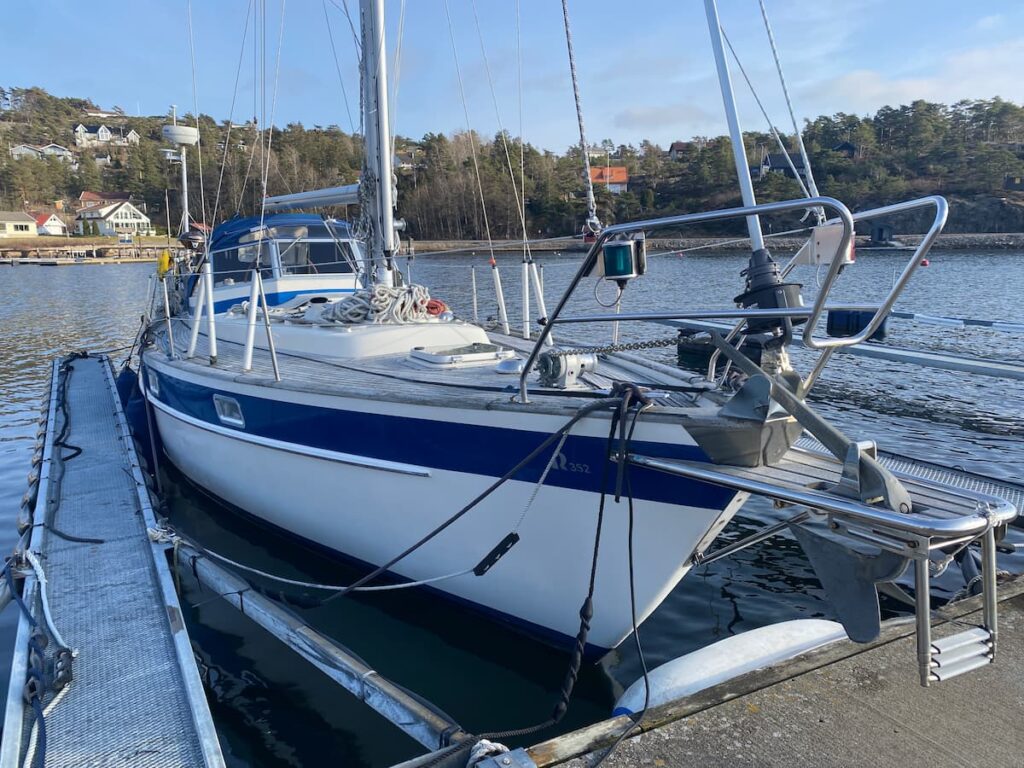

Cruising Sailboats
Cruising sailboats are designed for long-distance sailing and living aboard. They typically have a spacious interior with a galley, head, and sleeping quarters. They also have a large fuel and water capacity to allow for extended time at sea. Cruising sailboats come in many different sizes, from small pocket cruisers to large bluewater yachts.
Racing Sailboats
Racing sailboats are designed for speed and agility. They typically have a lightweight hull and a tall mast with a large sail area. Racing sailboats come in many classes , from dinghies to large offshore racing yachts. They are designed to be sailed by a skilled crew and require a high level of skill and experience to handle.
Daysailers are designed for short trips and day sailing. They typically have a simple interior with minimal accommodations. Daysailers come in many different sizes, from small dinghies to larger keelboats. They are easy to handle and are a great choice for beginners or for those who want to enjoy a day on the water without the hassle of a larger boat.
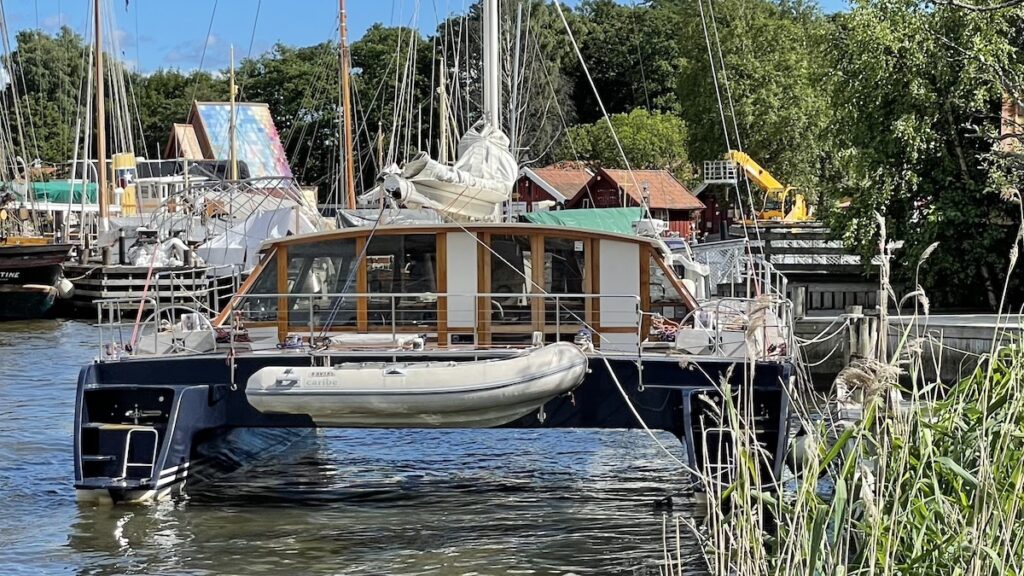

Catamarans are sailboats with two hulls. They are designed for stability and speed and are often used for cruising or racing. Catamarans have a spacious interior and a large deck area, making them a popular choice for those who want to live aboard or entertain guests. They are also popular for chartering and can be found in many popular sailing destinations around the world.
Trimarans are sailboats with three hulls. They are designed for speed and stability and are often used for racing or long-distance cruising. Trimarans have a narrow hull and a large sail area, making them incredibly fast and agile on the water. They are also popular for their spacious interior and large deck area, making them a great choice for those who want to live aboard or entertain guests.
Sailboat Hull Types
When it comes to sailboats, there are two main categories of hull types: monohull and multihull. Each has its unique characteristics and advantages.
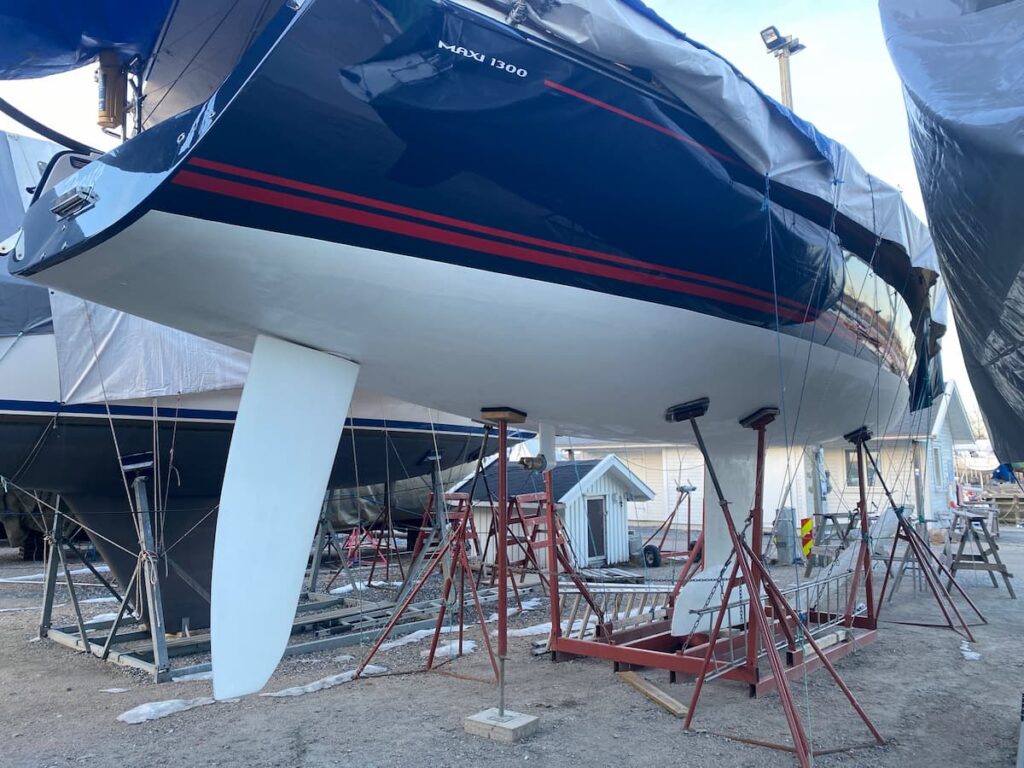

Monohull Sailboats
Monohull sailboats are the most common type of sailboat. They have a single hull, and the hull is typically long and narrow, which makes them more efficient when sailing upwind. Monohulls come in a variety of styles, including:
- Flat-bottom vessels
- Fin-keel racers
- Bulb and bilge keel cruisers
- Heavy semi-displacement sailboats
- Dense full-keel displacement cruisers
Each of these styles has its advantages and disadvantages. For example, flat-bottom vessels are the most stable, but they don’t work well in deep waters. Fin-keel racers are designed for speed and performance but may not be as comfortable for long-term cruising.
Multihull Sailboats
Multihull sailboats have two or more hulls. The most common types of multihulls are catamarans and trimarans. Multihulls have several advantages over monohulls, including:
- More stability
- Better performance in light winds
Catamarans have two hulls, which are connected by a deck. They are known for their stability and spaciousness. Trimarans have three hulls, which make them even more stable and faster than catamarans. However, they are not as spacious as catamarans.
Sailboat Rigging Types
When it comes to sailboat rigging types, there are several options to choose from. Each type of rig has its advantages and disadvantages, and choosing the right one will depend on a variety of factors, including the type of sailing you plan to do and the size of your boat . Some of the most common sailboat rigging types include:
The sloop rig is one of the most popular sailboat rigging types and is commonly used on boats ranging in size from small dinghies to large cruisers. It consists of a single mast with a mainsail and a jib or genoa. The mainsail is typically a triangular shape, while the jib or genoa is a smaller sail that is used to control the boat’s direction.
The cutter rig is similar to the sloop rig but with an additional headsail. This makes it a popular choice for sailors who want more control over their boat’s speed and direction. The mainsail is still triangular, but the headsail is typically smaller than the jib or genoa used in a sloop rig.
The ketch rig is a two-masted sailboat rigging type that is commonly used on larger boats. It consists of a main mast and a smaller mizzen mast located aft of the cockpit. The mainsail is typically triangular, while the mizzen sail is smaller and located behind the cockpit. The ketch rig is known for its versatility and is often used for long-distance cruising.
The yawl rig is similar to the ketch rig but with a smaller mizzen mast located further aft. This makes it a popular choice for sailors who want more control over their boat’s direction, especially in heavy winds. The yawl rig is also known for its ability to sail close to the wind, making it a popular choice for racing sailors.
Sailboat Sails
Several types of sails are commonly used on sailboats . Each sail has a specific purpose and is designed to work in different wind conditions. The main types of sails include mainsails, jibs, genoas, and spinnakers.
The mainsail is the largest sail on a sailboat and is typically located behind the mast. It is attached to the mast and boom and is used to capture the wind and propel the boat forward. The mainsail is the most important sail on the boat and is used in a wide range of wind conditions.
The mainsail can be adjusted in several ways to optimize its performance. The sail can be reefed, or reduced in size, to reduce the amount of sail exposed to the wind in high winds. The sail can also be twisted to adjust the shape of the sail and improve its performance in different wind conditions.
The jib is a smaller sail that is located in front of the mast. It is attached to the mast and forestay and is used to help balance the boat and improve its performance in light wind conditions. The jib is typically used in conjunction with the mainsail and can be adjusted to optimize its performance.
There are several types of jibs, including the working jib, the genoa jib, and the storm jib. The working jib is the most common type of jib and is used in moderate wind conditions. The genoa jib is a larger jib that is used in light wind conditions, while the storm jib is a smaller jib that is used in high wind conditions.
The genoa is a large jib that is used in light wind conditions. It is similar to the jib but is larger and overlaps the mainsail. The Genoa is attached to the mast and forestay and is used to capture as much wind as possible to propel the boat forward.
The Genoa is typically used in conjunction with the mainsail and can be adjusted to optimize its performance. It can be furled, or rolled up when not in use to reduce wind resistance and improve the boat’s performance.
The spinnaker is a large, balloon-shaped sail that is used for downwind sailing. It is typically used in light wind conditions and is attached to a spinnaker pole to keep it away from the boat’s mast and sails.
The spinnaker is used to capture as much wind as possible and propel the boat forward. It is typically used in conjunction with the mainsail and jib and can be adjusted to optimize its performance.

What factors determine the types of sailboats?
The factors that determine the types of sailboats include hull type, keel type, mast configuration, and sails and rigging.
What are the two main categories of sailboat hull types?
The two main categories of sailboat hull types are monohull and multihull.
What are some common sailboat rigging types?
Common sailboat rigging types include sloop rig, cutter rig, ketch rig, and yawl rig.
What are the main types of sails used on sailboats?
The main types of sails used on sailboats include mainsails, jibs, genoas, and spinnakers.
What are the differences between a catamaran and a trimaran?
A catamaran has two hulls connected by a deck, while a trimaran has three hulls. Trimarans are generally more stable and faster than catamarans, but they are not as spacious.
- Recent Posts
- Responsibilities of a Fourth Engineer on Cargo Ships – September 10, 2024
- The Role of Cargo Ships in Global Trade – August 22, 2024
- Report: Yang Ming’s YM Mobility Explosion at Ningbo-Zhoushan Port – August 9, 2024
About the author
I worked as an officer in the deck department on various types of vessels, including oil and chemical tankers, LPG carriers, and even reefer and TSHD in the early years. Currently employed as Marine Surveyor carrying cargo, draft, bunker, and warranty survey.
Latest posts

Is Maritime Security Necessary on Modern Ships?
It’s vital for ships to stay vigilant. Isolation from land means having no backup or protection for miles, making them vulnerable to attacks and other threats. Equip modern ships using modern maritime security methods.

Responsibilities of a Fourth Engineer on Cargo Ships
A Fourth Engineer on cargo ships oversees engine room operations, machinery maintenance, and ensures compliance with regulations like MARPOL.

The Quality Control Process in Marine Manufacturing
Companies in the marine manufacturing space must have tight and effective quality control processes. What steps should an effective quality control process include?
- Articles and Guides
Types of Sailboats: Dive into the World of Sailboats
29th oct 2023 by samantha wilson.

Sailing is a wonderful hobby that can bring a lifetime of relaxation, adventure, and fun. It offers the chance to learn new skills, spend quality time with the whole family, to explore new destinations and take part in a whole host of different activities. There are many types of sailboats for sale, so before you venture down the road of buying your first sailboat , it’s important to understand the different types of sailboats and which one will be best for you and your family. With everything from tiny dinghies up to enormous superyachts , the range is huge.
Here we’ll explore the different sailboat types and uses, look at their pros and cons, and how to choose the right one.
Different Types of Sailing Boat by Hull
With so many different sailboat variations, sailboat uses and styles of sailboat, there are different ways we can identify them, and one way is by hull type. There are three categories; monohulls (with one hull), catamarans (with two hulls) and trimarans (with three hulls).
Monohull sailboats
Monohulls are the most common type of sailboat and are designed with a single hull, and have a long, narrow shape which makes them fast and easy to maneuver. Monohulls are typically designed for recreational sailing, and are great for long-distance cruising, coastal sailing, and racing. As they can be relatively inexpensive to buy and easy to maintain, monohulls are often one of the most popular types of sailing boats for beginners. As the broadest range of sailboats, monohulls come in all shapes and sizes, but can also have vastly different keel types. See our comparison between monohull and catamaran sailboats .

Examples of monohull keels include:
Full keel consists of heavy ballast which runs along the bottom of the hull and keeps the boat centered in the water
Cutaway keel
Cutway keep works in the same way as a full keel but has a section cut away to allow for better maneuverability in shallow waters
Fin keel or wing keel
These are often bolted on to the hull and can have a heavy bulb or wing at the bottom for additional stability
Swing keel, lifting keel, daggerboard or centerboard
All of these are identified by their ability to be retracted into the hull, allowing for access to shallow water and additional speeds
Shallow planing hull:
Usually found on types of small sailing boats and dinghies, it allows them to surf on waves and enter shallower water.
Catamaran sailboats
Catamarans are two-hulled sailboats with a deck or trampoline in between that are typically wider and more stable than monohulls. They also provide more space and storage, and are great for sailing in shallow waters. Popular choices for those wanting to go fishing , cruising and racing, catamarans are gaining in popularity particularly because of their increased stability which is less likely to cause seasickness. Because of their lack of deep, heavy keels (not necessary because of their two-hulled stability) catamarans are known for their speeds and make for popular daysailers and charter boats.

Trimaran sailboats
Trimarans are three-hulled sailboats that are usually faster and more stable than monohulls. They have a long, narrow shape, and they provide a good amount of space and storage. Trimarans are great for racing and long-distance cruising, and they are often used for fishing and recreational sailing. With a higher purchase price and less availability on the market, they are still fairly uncommon compared to monohulls and catamarans although larger trimaran yachts are gaining popularity thanks to their stability and speed. See our comparison guide between trimarans and catamarans .

Different Types of Sailing Boats
There are many ways to categorize sailboats, from their rigging to their mast configuration, their rudder type, hull type or by the different classes of sailboat.
Another way to identify or categorize sailboat types is by their rigging. This refers to the configuration of the mast (or masts) and sail (or sails) and there are several types depending on what they’re used for.
These are some of the most common sailing yacht types:
Sloop are the most common type of sailboat on the water, and are characterized by a single-mast rig which frequently has a triangular mainsail and a headsail. They make for one of the most popular types of sailing boats for beginners as well as seasoned pros as they are easy to learn to control and maneuver, fun to sail and can be used for all types of sailing in different conditions. Sloops can get to great speeds with their rig configuration and offer good windward performance and as such they are popular racing boats as well as the perfect multi-purpose, easy maintenance leisure yacht. On the downside, sloops can be easier to capsize than some other sailboats and they require a tall mast to accommodate the two sails.
While it might seem as though a cutter and sloop are barely distinguishable, a closer look shows that in fact the rigging is quite noticeably different. Yes, both types have a single mast, but a cutter has a two headsails, the additional one known as a staysail. This additional sail offers better control and more stability than a sloop and its singular jib sail, as well as being better at performing in adverse weather. The other difference worth noting is that many cutters have a spar extending from the bow, known as a bowsprit which increases the amount of sail area. The downsides to a cutter for some people is the rigging is more complex than that on a sloop.
Schooners are probably the most easily identifiable type of sailboat to grace our seas. For centuries these multi-masted sailing yachts have transported sailors, soldiers, goods and passengers around the world, their multiple sails offering excellent offshore handling and the ability to withstand powerful sea conditions. They have a minimum of two masts, but can have many more, with two almost identical sized sails in the foresail and mainsail. Better suited to experienced sailors with a crew, they have a complex rigging with multiple sail options allowing for precise control offshore.
Ketch and Yawl
Similar in appearance and handling, the ketch and yawl are characterized by their two masts, with the mainmast being taller than the mizzen mast. The two differ in that the ketch has the mizzen mast is forward of the rudder post, while the yawl has its mizzen aft of it. In general, ketch and yawl sailboats have shorter masts and smaller sails, making them slower than a sloop or cutter but more able to withstand rough sea conditions. Check our guide: Ketch vs Yawl
Daysailer and Dinghy
At the smaller end of the sailboat classification list are daysailers and dinghies. A dinghy tends to be under 28 feet in length and usually dual powered with a small outboard engine. Perfect for short cruises in protected water s they are great beginner yachts and easy to handle and rig. While usually slightly larger than a dinghy, the daysailer is, as the name suggests, perfect for short coastal cruising, have a single mast and can be either monohull or multihull. Both are a broad categorizations based on usage and size rather than shape or rigging.

Racing Sailboats
The sport of racing sailboats dates back centuries and is today as popular as ever. There is no one type of racing sailboat, and the term in fact covers a broad spectrum of yachts, from one-man dinghies all the way to 100-foot yachts. In fact, any sailing yacht can be raced and there are many classes of sailboats and competitions around the world. Keel boats such as sloops and cutters are popular for racing, as they can sail quite close to the wind, but you’ll also find multihulls and the ultra-fast foiling hull boats which rise out of the water onto a narrow foil and can reach speeds well in excess of 50mph.
Motorsailer Vs Sailboat
While many sailboats also have engines, the motorsailer is a different and easily identifiable style of yacht. It uses a combination of wind power and engine power, and in some cases resembles a motorboat in style more than a classic yacht shape. The motorsailer offers great opportunities for varying types of cruising such as coastal voyages, as well as living onboard, and is a reliable and easy-to-handle yacht popular with families. On the downside, a motorsailer does tend to come with a higher price tag than sailboats of the same size and they aren’t usually as fast or efficient as a either a full powerboat or sailboat.
Best Types of Sailboat by Activity
With so many variations, styles and types of sailboat on the market, it makes sense that they are designed for different activities and uses. Whether you want to sail around the world , enjoy a spot of day sailing or want something easy to handle, then you need to find the right kind of boat for your needs.
Best sailboat for stability
When it comes to stability, the answer to which sailboat is best isn’t as clear cut as it might at first seem. The multihulls are the clear winners in temperate conditions, the trimaran taking first place thanks to its wide beam and triple hull configuration. A close second is the catamaran, also known for its lack of rolling, which is gaining popularity with those prone to seasickness who are looking for a yacht for day sailing or coastal cruising.
However multihulls tend to be less stable when it comes to rougher sea conditions, and it’s impossible to right a capsized catamaran or trimaran. Monohulls with deep displacement hulls are by far the best choice in these instances, their design allowing them to keel far over in rough weather without capsizing.
Best sailboat for Offshore Cruising
When adventure is calling and you want to head further offshore or embark on blue water cruises , then you need a yacht that is up to the challenge . The most important aspect of offshore cruising is experience and preparation, and there are many boats out there that can cross oceans if they’re properly equipped and handled. The simple rigged sloop, cutter or ketch are popular options. With easy handling qualities and good windward performance, a simple sloop is a good choice, while the cutter (similar in many ways) has even better rough weather performance qualities thanks to its additional headsail. The ketch, although slower, can be more stable in rough weather and has shorter and therefore stronger masts.
While it’s not a beginner’s sailboat, a classic schooner is probably the best sailboat for offshore cruising as it allows for precise handling even in big seas, as well as being fast and powerful. They have a deep displacement keel, which means they are more stable in rough weather too.
Best sailboat for a day
More simple rigged sailboats tend to be the most popular day sailers, with the sloop, ketch, yawl and cutter top of the list. The idea of a simple rig makes using them coastally or in inland waters fun and fuss-free, and they make for great beginner boats . Likewise, on very protected waters such as lakes or coastal areas, smaller dinghies can great day boats too.
Best budget sailboat
When it comes to budget, dinghies top the list of the cheapest sailboats. With or without an engine, they tend to be small and simple, without cabins, heads, instruments or other luxuries to add to the cost. Sloops, ketches and cutters too can be found on a budget, especially on the second hand market. But it’s important to look at more than the purchase price when buying a second hand boat, and consider the condition, repairs and maintenance that might need doing. Check out our guide Buying a Cheap Boat: Is it a Good Idea?
If you’re considering buying a sailboat then Rightboat.com has one of the biggest collections of new and used boats for sale in the world. From dinghies to sailing superyachts and everything in between we work with the best brokers in the business as well as private sellers offering you the biggest choice.
Written By: Samantha Wilson
Samantha Wilson has spent her entire life on and around boats, from tiny sailing dinghies all the way up to superyachts. She writes for many boating and yachting publications, top charter agencies, and some of the largest travel businesses in the industry, combining her knowledge and passion of boating, travel and writing to create topical, useful and engaging content.

More from: Samantha Wilson
Related Articles and Guides

6th Sep 2024
The Best Mini Yacht Brands for Cruising and Luxury

16th Aug 2024
Best Luxury Pontoon Boat Brands Have it All: Glamor, Speed, Fishing, Waterslides...

10th Aug 2024
Deck Boat vs. Bowrider: Which Runabout is Best?

19th Jul 2024
The World’s Best Yacht Brands

- Explore Rightboat
- Boats for Sale
- Boating Articles
- Buyers Guide
- About RightBoat
- Sell Your Boat
- Boat Selling Advice
- All manufacturers
- All categories
- Are you a broker/dealer?
- Learn more about the Rightboat:HUB
Enter your email to keep up to date with the latest news
Join for free
Sign up now for free and discover how easy it is to keep up to date with THE latest boats for sale. Find your right boat, and tailor your voyage to finding your next boat.
Benefits of becoming a member:
- Set up tailored alerts
- Personalise your experience
- Download full specifications and broker details
- Keep tabs on your favourite boats
Are you a broker? Join as a Broker
Rightboat - join for free.
Do you have an account already? Login
Save this search
Save your search and receive new boats in your email..
You can unsubscribe from your alerts whenever you like. By pressing the button you accept the Legal Terms and conditions

U.S Navy Commissions USS New Jersey, First Ever Submarine For A Mixed Gender Crew

World’s Largest Hotel-Branded Superyacht Sets Sail For Maiden Voyage

India Establishes Its First Maritime Arbitration Center

Yanmar Unveils Its First Electric Propulsion Product For Emission-Free Sailing

Types of Sailboats – A Comprehensive Classification
Traditionally, sailboats were made of marine wood and other materials however; modern ones use premium marine lumber products. Sailboats are divided into subclasses, and one such is the catamaran which is made of fiberglass, which makes it more durable and low maintenance.
Sailboats are propelled by wind captured through their sails, masts and rigging lines. Some are equipped with generators, wind makers and other technologies to generate more power, hence providing more speed. They are considered a separate class of vessels independent of motor-powered crafts since their hydrodynamic characteristics differ.
They can vary in occupancy from single-seater crafts for competitions or adventure sailing to recreational vessels spanning hundreds of metres that can host up to thirty individuals. The luxury yachts are ideal to experience sailing in comfort and style. These vessels are known for their remarkable craftsmanship and innovative design.
The most common type of sailboat is the racing sailboat, used in sailing competitions around the world. Several international events intended to raise awareness about sailing allow a wide range of craft types to participate, including catamarans and racer-cruiser.
For most sailing vessels, sail plans are often drawn up before the vessel leaves port. These plans indicate sail positions for various weather conditions.
In this article, we will go through the different types of sailboats and their key features.
Hull-Based Classification Of Sailboats
Sailboats can be classified into three distinct types based on their primary hull type.
These include
- catamarans, and
- multi-hull crafts.
Traditionally, monohulls are the most common design for sailboats since they provide storage in addition to a certain level of stability.
However, with the advent of sailing competitions and an increased focus on performance and stability features, there has been a general shift towards catamarans and trimarans.
Monohulls are single-hulled structures, much like conventional vessels , that have a large hull beam (breadth) which provides stability while sailing. The advantage of having a single large hull is that the longer beam allows for improved onboard systems and amenities. It has a cabin, a cockpit, a galley, a v-berth and a saloon as well.

Catamarans refer to twin-hulled structures that are attached by specialized members to provide strength. The term originates from the South Indian phrase for “tied pieces of wood”, as this was the manner in which traditional sailboats were built in the subcontinent.

Twin hulls offer an increased level of stability. In addition, if designed properly the vessel will have a much higher speed than conventional crafts owing to lower wetted-surface resistance forces.
On the other hand, extensive care must be taken in designing the vessel, or else the resistive forces can exceed the values found in monohulls.
Multi-hull crafts, or simply multihulls, include vessels with anywhere between three to five hulls, although the three-hull variation is the most common. Such crafts are known as trimarans and are considered to be extremely stable owing to their large beam and lower centre of gravity.

Four and five-hulled vessels are more difficult to manufacture and hence are rarely used commercially. An advanced form of the catamaran design is the SWATH version.
SWATH is an acronym for Small Waterplane Area Twin Hull, and it achieves unprecedented levels of speed owing to a considerably small waterplane area. To reduce this area, the hull has a reduced beam above the surface of the water, while underwater buoyant structures ensure that the vessel has the necessary weight balance.

Common Monohull Designs
Monohulls are relatively easier to manufacture compared to multi-hull structures. Thus, there has been a wider range of innovations for this type of hull over the last thousand years.
The common classes of monohull crafts are – sailing dinghies, cutters, sloops, catboats, ketch and schooners.
A dinghy is a relatively common sailboat owing to its short overall length and ease of manoeuvring. They are used in competitions and in the port industry.

Generally, dinghies are used to transport people or small cargo to and from a larger vessel such as a cruise ship that is anchored away from the shore.
Such vessels may not be able to enter a port due to size and tonnage regulations. Hence, dinghies serve as the best mode of transporting essential goods between the port and the vessel.
Dinghies can have sails, such as the three-sailed variant consisting of the mainsail, jib and spinnaker. However, motor-powered dinghies are also commonly used especially as lifeboats onboard ships.
Cutters are another class of sailboats that are medium-sized and generally have three sails. The mainmast on which the sails are mounted is located near the stern of the ship to allow for larger sails to be used.

Cutters were commonly used in competitions as their design favours speed and agility. A different combination of the sails also allows cutters to be used for cruises and other recreational sailboats.
Sloops are similar to cutters and are the most commonly found sailboats. They are the standard in sail designs, with a two-sail configuration used for added manoeuvrability. They have a mainsail and a headsail called jib or genoa.

In addition to the generic sloop sail configuration, there is also a fractionally-rigged sloop in which one of the sails lies below the top of the mast.
This design allows the crews of smaller sloops to handle the craft while improving performance. Catboats are sailboats equipped with only a single sail. They are aimed at capacity rather than speed and have the mainsail mounted on a single mast.
For increased speeds, sails can be added to the rigging such that wind force is better optimized by the vessel.
The ketch is a sailboat that has two main masts- the main mast located around the midship, and the mizzen mast at the aft. The mizzen mast is generally smaller than the main mast and serves to add speed to the craft. The word ketch is derived from the word catch, denoting the manner in which the sails “catch” the wind as they move.

Schooners are a class of sailboats that can have more than two sails supported on masts known as the main mast and foremast. The foremast is located near the fore of the vessel and is slightly shorter than the main mast. In variations where additional masts are added to support more sails, they are positioned such that they remain shorter than the main mast depending on their sizes.

Keel Based Classification
The keel is the base of a vessel that provides a central backbone for the design of the entire structure. The boat keel is structurally relevant since it often has to carry the weight of the vessel.
In the case of sailboats, the keel is often what the entire craft rests on during transport by road or rail. Thus, keels need to have integral strength and be able to withstand a variety of forces.
Similarly, while sailing, the keel is the lowermost point of the vessel at which resistive forces act. As a result, many modifications are often made to the keel so that hydrodynamic features can be incorporated to reduce drag. Sailboats often sit high in the water owing to their design and shape.
However, for competition and performance crafts, it is essential that they try to sit as close to the surface of the water as possible without capsizing. Thus, the keel often plays the role of a central ballast, by integrating heavy iron or steel components so that the vessel draft increases.
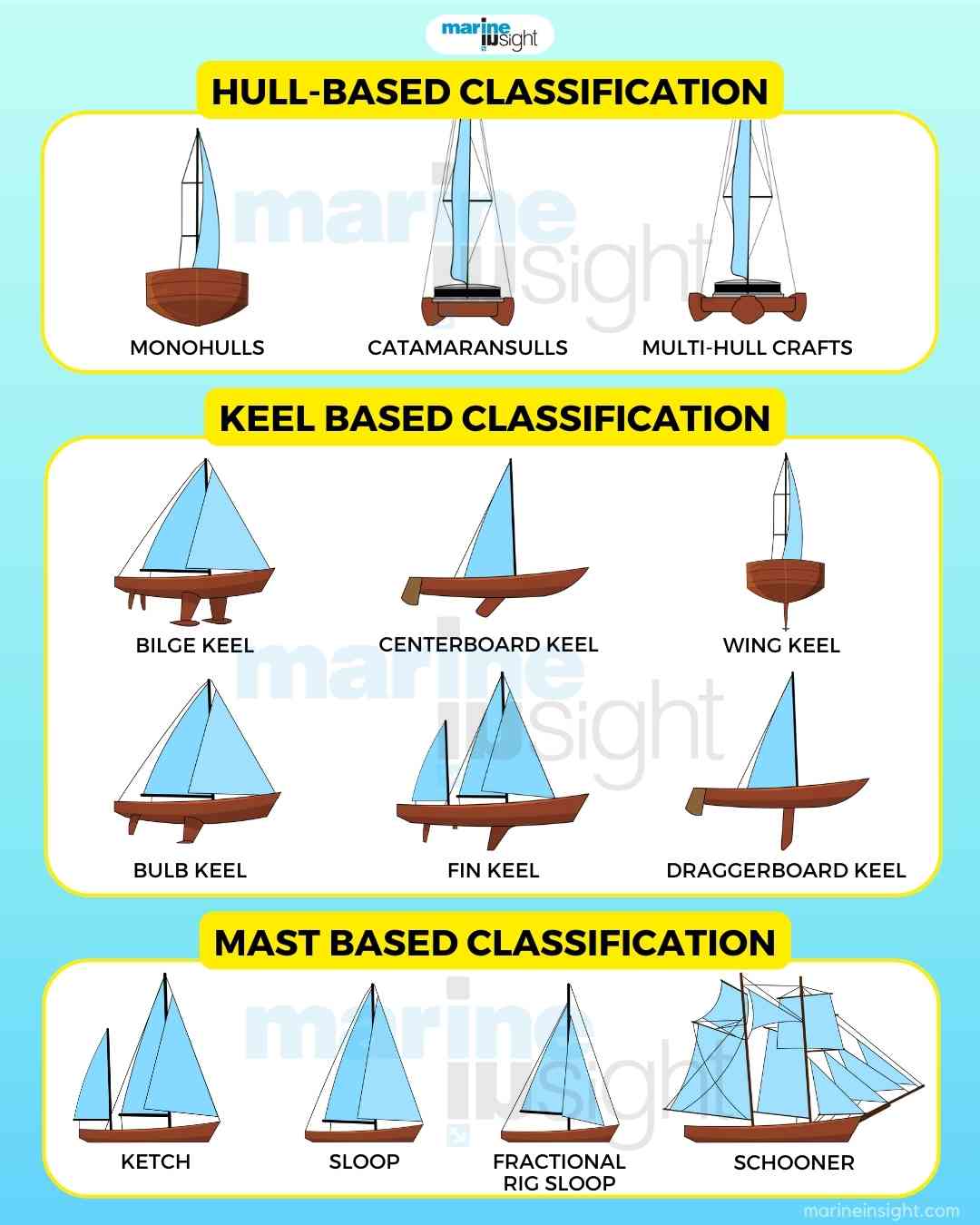
Based on keel type, there are several sailing boat variants found in the market. These generally have modified keels for improving performance and speed by integrating hydrodynamic features such as hydrofoils .
The types of keels commonly associated with sailboats are as follows: full-length keel, fin keel, centreboard keel, bilge keel, bulb keel and wing keel.
As the name suggests, full-length keels have keels that extend in the form of a long fin below the main structure of the ship. The fin runs along the length of the ship and often has an integrated rudder system attached at the stern.
The advantage of this type of keel is that it is easy to manufacture, with little cost in terms of development. Also, the ballast effect is provided by the extra weight of the full-length keel.
Since it can be difficult to enter certain ports or quays owing to the large draft that comes with this type of keel, manufacturers attempt to reduce fin depth and instead increase its length.
Fin keels , on the other hand, run only along certain regions of the sailboat. Located on the underside of the craft, it sticks out similar to the fin of a fish giving rise to this nomenclature. Since this type of keel must perform the same functions as the full-length keel without having a large length, the fin is deeper.

Owing to this large draft, it may be difficult to dock at certain ports due to depth restrictions. A key feature of this type of keel is that the rudder and manoeuvring systems remain independent of the fin keel, and are located at the extreme aft of the vessel. Centreboard keels are a common feature of high-performance crafts that take part in competitions. They are not restricted to monohull structures and are often found in catamarans and trimarans.
The centreboard keel employs a type of fin that is pivoted about a point on the keel of the vessel. By having a pivot, the natural flow of the vessel and surrounding water varies the depth at which the keel sits below the vessel. Similar to the fin keel, it only runs along a certain length of the vessel.
However, it is distinguished by being able to vary the angle of tilt with respect to the baseline of the craft. In some variations, the crew are able to manually change the angle of tilt, to change performance features during certain events and competitions.
Another variation of the centreboard keel is the daggerboard keel , which allows the fin to completely integrate into the underside of the vessel.

By providing a bay at the underside, the fin can be raised or lowered from the slot. In this type of keel, the raised configuration allows for higher speeds and reduced resistive forces. However, when lowered into the water, the vessel gains added stability and makes up for the loss in speed by improving hydrodynamic features.
Bilge keels refer to protrusions on the sides of the hull of the vessel, commonly called the bilges. These protrusions run along the length of the vessel while tapering into the hull panels at both ends.
The primary purpose of bilge keels is to improve the rolling stability of the craft. The fins stick out perpendicular to the hull and can vary in length depending on the purpose. For instance, sailboats require larger anti-roll stability and hence have long tapering bilge keels.

The bilge keels must be symmetrically placed on both the port and starboard sides, so as to ensure even hydrodynamic characters.
A bulb keel is a protrusion sticking vertically below the craft and terminating in an oblong-shaped hydrodynamic device called the bulb. The bulb acts as a 3D hydrofoil that improves the stability and handling of the vessel. Due to the increased wetted surface area, there is a slight drop in the speed, but it can be made up through superior handling capabilities.

For smaller crafts, longer bulb keels are required, and as this length increases, the chance of accidental grounding of the vessel increases.
The last commonly found type of keel is the wing keel . The wing keel is similar to the bulb keel, except that instead of a bulb terminating a vertical protrusion, there are horizontal hydrofoils extending from the central shaft.
The primary purpose of the wings underneath the ship is to improve handling and stability. In addition, they slightly lift the craft above the surface of the water. As a result, the total wetted surface area remains constant and may even decrease. Thus, speed remains constant and may improve as the craft picks up velocity.
Mast Based Classifications
The mast of the vessel refers to a vertical shaft extending out of the deck which supports the sails and rigging. Older models of sailboats and ancient ships had masts constructed out of wood, while modern speed-oriented versions use galvanized steel or aluminium.
Aluminium has the benefit of being extremely light while still retaining its strength, which is important during harsh weather conditions.
The various mast-based classification includes – sloop, fractional-rig sloop, cutter, ketch, schooner and catboat.
The sloop is the most common mast type, where a single mast supports two sails called the headsail (or foresail) and the mainsail.

The headsail also goes by different names depending on the purpose and configuration of the sails.
In a fractional rig sloop , the forestay cable that is used to hoist the headsail is actually placed below the top of the mast. This configuration is particularly useful when it comes to performance, as the tip of the mast can be hauled towards the aft using stiff cables, and the sails can be collapsed.

This is useful on days when wind power can be used to propel the sailboat, without the sails having to be fully extended.
Another useful feature of being able to trim or flatten the sails is that during particularly strong squalls of wind, the sails will not be punctured or ruptured due to the high wind pressure. The next type of mast configuration is the cutter. This involves a single mast supporting three sails- one mainsail, and two headsails known as the staysail hauled by the inner stay cable, and the jib hauled by the headstay cable.
The mast is located more towards the aft compared to the sloop, to allow for an easily manoeuvrable configuration. In addition, a wide range of sail arrangements makes it favourable for cruise operators and for competition purposes.
The ketc h has a two-mast configuration, with the aft mast known as the mizzen mast. The mizzen mast is located fore of the rudder post, and aft of the main mast.

The mizzen sail rests on the mizzen mast. In general, the mizzen mast is slightly shorter than the main mast.

The main mast supports two sails known as the mainsail and the headsail.
The schooner is another configuration similar to the ketch, but where the aft mast is taller than the foremast.

Schooners can have multiple masts and are not restricted to commercial small and medium sailboats. The images of ancient ships that were used for trade and military purposes were often schooners having between four to six masts with an average of over ten sails each.
In addition, the sails of the schooner tend to lie along the length of the vessel, rather than along the beam. This is to prevent sail rupture during violent storms or during heavy winds. The catboat is one of the simplest configurations where only a single sail and mast arrangement are used.
The mast can be located either aft or fore of midships, with varying advantages to each configuration. The ease of design and construction makes it a favourable sailboat for beginners and trainees. However, the disadvantage behind the catboat is that the sail cannot be used to move against the direction of the wind, unlike other sail variations.
Apart from recreation purposes, sailboats are one of the most common types of vessels used in recreational purposes and competitions. They can vary in the hull, keel and sail configurations based on the primary purpose that they are intended to be used for.
For over five thousand years, sailboats have been in use, whether it has been for transportation in Ancient Egypt, or for sailing events in modern times. Technological advancements have turned the sailboat into a sleek, agile and fast vessel capable of reaching extremely high speeds by harnessing the power of the wind.
Whether it be for cruises or for racing events, sailboats and other such crafts continue to be a favourite choice for sailors.
Frequently Asked Questions About Sailboats
1. how many different kinds of sailboats are there.
There are many types based on their hull type- monohulls, catamarans and trimarans; keel type- fin keel, wing keel, daggerboard, centreboard; mast configuration and sails- sloop, fractional rig sloop, schooner, ketch, yawl, cutters and catch.
2. What is the most common type of sailboat?
The sloop is the most common sailboat. It has a mast, two sails, commonly a Bermuda rigged main and a headsail. They include a gaff rig, a mix of gaff and square rig or a Bermuda rig.
3. What is a four-masted sailboat called?
It is called a schooner. Traditional schooners have a gaff-rig, which means that they have a square topsail on the front of the mast. They were mainly constructed for carrying cargo, passengers and for fishing.
4. How many masts does a ketch have?
Ketch has two masts whose main mast is taller than the mizzen mast. It is similar to a yawl and has a triangular mizzen sail and a triangular or square headsail. Due to their smaller sails, they are easily manageable and preferred by sailors.
5. What is the most beautiful sailboat?
Some of the most beautiful sailboats in the world include Pelagic Australis, Thomas W Lawson, Royal Clipper, Barque Sedov and Amerigo Vespucci.
6. What are some popular sailboat brands?
Beneteau, Sparkman and Stephens, Oyster Yachts, Amel Yachts and Nautor’s Swan are some popular sailboat brands that sell the most number of sailboats yearly.
You Might also like to read
- Real Life Accident: Officer Of The Watch Ignores Lookout’s Warning, Ship Collides with Sailboat
- Introduction To Different Types Of Yachts
- 12 Sailing Books For Beginners
- The Ultimate Guide to Different Types of Boats – Top 20
- Main Types of Catamarans Used in the Shipping World
- What are Tug Boats – Types And Uses
Disclaimer : The information contained in this website is for general information purposes only. While we endeavour to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the website for any purpose. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk.
In no event will we be liable for any loss or damage including without limitation, indirect or consequential loss or damage, or any loss or damage whatsoever arising from loss of data or profits arising out of, or in connection with, the use of this website.

About Author
Ajay Menon is a graduate of the Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur, with an integrated major in Ocean Engineering and Naval Architecture. Besides writing, he balances chess and works out tunes on his keyboard during his free time.
Read More Articles By This Author >

Do you have info to share with us ? Suggest a correction
Daily Maritime News, Straight To Your Inbox
Sign Up To Get Daily Newsletters
Join over 60k+ people who read our daily newsletters
By subscribing, you agree to our Privacy Policy and may receive occasional deal communications; you can unsubscribe anytime.

BE THE FIRST TO COMMENT
Leave a reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Subscribe to Marine Insight Daily Newsletter
" * " indicates required fields
Marine Engineering
Marine Engine Air Compressor Marine Boiler Oily Water Separator Marine Electrical Ship Generator Ship Stabilizer
Nautical Science
Mooring Bridge Watchkeeping Ship Manoeuvring Nautical Charts Anchoring Nautical Equipment Shipboard Guidelines
Explore
Free Maritime eBooks Premium Maritime eBooks Marine Safety Financial Planning Marine Careers Maritime Law Ship Dry Dock
Shipping News Maritime Reports Videos Maritime Piracy Offshore Safety Of Life At Sea (SOLAS) MARPOL
WAIT! Did You Download 13 FREE Maritime eBooks?
Sign-up and download instantly!
We respect your privacy and take protecting it very seriously. No spam!
- Pontoon Boats
- Personal Watercraft
- nauticalknowhow
- Nautical Knots
- Tools and Calculators
Types of Sailboats: Classification Guide
Sailboats can be divided into three basic types based on their hulls (catamaran, monohull or multihull) , their keel and their rigging, and then further subdivided from there. The result is that there are actually well over a dozen different kinds of sailboats out there.
Sailboat Hull Types

There are three main hull types that you’ll find in sailboats.
- Monohull: This is what most people think of when they think of a sail boat or any boat at all, really. A monohull sailboat has a single hulled structure that gives a boat that traditional boat shape we all instantly recognize. These are far and away the most common hull type for sailboats because they’re some of the oldest, they’re cheaper to produce, and they are fairly easy to maintain compared to the other options. You can do a lot more with the rigger in monohull sailboats and any sailing vessel with multiple masts is invariably going to be a monohull one. The downside of the monohull compared to the others is that they lack the stability.
- Catamaran: The second hull type you’ll find in sailboats is the catamaran . While technically a multihull vessel, they feature two hulls that are located on either side of the boat connected by a deck. Because it’s just the two, they get called catamarans rather than multihull which generally refers to three. Catamarans had been used by ancient peoples for years but never really caught on with “modern” boating for quite a long time. Now that we have fiberglass hulls and other advances, catamarans are much more commonplace than they were a hundred years ago. Catamarans offer great speed and stability but don’t have as much cabin space as a monohull.
- Trimaran/Multihull : This hull style features three hulls in a similar style to the catamaran with the addition of that third center hull. From the side you wouldn’t be able to tell a catamarans from trimaran sailboats. These boats are even faster and more stable than a catamaran and, by extension, a monohull. They have a very low center of gravity and a large beam. Space is still a drawback but the third hull increases room overall. There are also vessels with even more hulls, but they are exceedingly rare and also pretty expensive.
Sailboat Keel Types

Heading below the hull now and we’ll find the keel, which is what gives your sailboat added stability in the water. While multihull boats find stability in the additional hulls, a monohull boat will get stability from its keel. Though it’s nearly impossible to flip or capsize a trimaran, if it does happen it’s staying flipped or capsized. However, the keel on a monohull boat makes it even harder to flip because of the physics of resistance in the water. That isn’t to say a monohulled boat with a keel is unsinkable, quite the opposite, but you’re just not going to flip one upside down without a real fight. There are six main keel types you’ll find in sailboats.
- Bilge Keel: These are dual keels that can be like fin keels or even full keels extending the length of the vessel. They extend from the sides and can prevent the boat from rolling. They need to be symmetrical on both sides of the boat to work.
- Bulb Kee l: These are a kind of fin keel but they carry ballast in them. That allows them to have a little more stability. They operate like a hydrofoil
- Centerboard Keel: This type of keel actually pivots and can be changed depending on the depth of the water.
- Daggerboard Keel : Another kind of centerboard keel but the daggerboard can actually be pulled up into the hull. This allows you to alter its position for an increase or decrease in speed or stability as needed.
- Fin Kee l: If you’re into racing you’ll probably have a fin keel. They are thin but extend deep below the sailboat. This makes them great for speed but not really ideal for a comfortable ride. You wouldn’t want to be day sailing for fun and relaxation with a fin keel.
- Full Keel: This is the most common type of keel and it spans the entire length of the vessel. There will likely be a rudder built into the keel as well.
- Wing Keel : This is a variant on the fin keel. Wing keels have a small wing at the tip to allow better directional stability by reducing cross flow.
Sailboat Mast Configuration
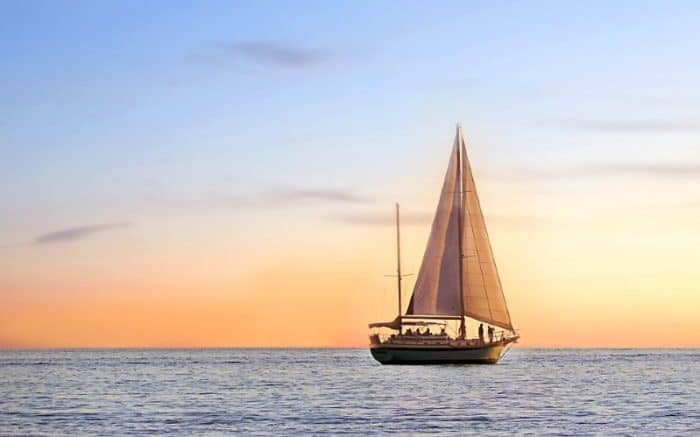

The mast of the sailboat is obviously that large pole onto which sails are rigged. Depending on your boat type you may have one mast, two masts, or more masts. How these masts are configured is where you can start distinguishing sailboat types you may recognize by name. These include:
Sloop: This is arguably the most popular type of sailboat mast type. A sloop has a single mast and two sails – the headsail and the mainsail. Being a single masted sailboat makes them easy to identify. These are probably the easiest to learn how to rig and how to sail. It’s versatile enough for cruising and for racing. Commonly these a gaff rig or a Bermuda rig. Another kind of sloop rig is the fractional rig sloop in which you can find one of the sails below the top of the mast.
Schooner: These can have multiple masts, not just two. The largest sailing vessels you’re likely to see, either in the present or in images from history, were schooners. Giant ships with six masts each bearing over 10 sails were schooners. An important detail is that the first mast on a schooner will always be shorter than the others. They are usually gaff-rigged
Cutter: This type of sailboat is very similar to the sloop and has a centrally located mast supporting three sails. Two headsails, the second called a staysail, is what distinguishes it most easily from the sloop. The rigging makes a cutter a bit harder to manage than a sloop.
Ketch : A ketch is a lot like a schooner but the two masts are arranged differently. On a ketch, the main mast is taller than the aft mast which is called the mizzen mast. The mizzen sail naturally is on the mizzen mast with the mizzen mast positioned aft.
Catboat : Also called a cat, a catboat has a single mast and a large, single gaff sail. The boats are usually short, stout boats that aren’t built for speed or for open seas. Best to be used in coastal waters
Yawl: This vessel is nearly identical to the ketch with one main difference. In a yawl, the helm is forward of the mizzen mast, while that is not the case in a ketch.
Other Types of Sailboats

Now that we have the basic configurations out of the way, let’s look at some of the more specific types of sailboats you may find at sea. In some cases you’ll see that these terms are not entirely specific and one term may actually apply to multiple kinds of sail boats in much the same way that something like SUV can describe multiple different vehicles that are similar but not all the same.
Sailing Dinghies
Like any dinghy, a sailing dinghy is going to be a small vessel. Typically made to accommodate just one or two people, they are under 15 feet and the smallest of which are often used by children. Optimist dinghies are raced professionally and must meet certain requirements to be officially registered as true Optimist boats. If you’re totally new to sailing, a sailing dinghy might be a good place to learn the ropes.
Daysailer generally refers to any sailboat that is not intended to either race other boats or keep you out on the water for an overnight stay. As such, it can cover a lot of ground. Typically, a daysailer will probably be between 14 feet and 20 feet. Usually you won’t get more than 4 people on board and there will be room for storing gear but not a sleeping berth. These are great beginner sailboats.

Pocket Cruisers
Like a daysailer, a pocket cruiser is more of a general label for boats rather than a specific kind. In this case, any sailboat under 30 feet could technically be considered a pocket cruiser. Basically it should be trailerable and used for either cruising or racing. They may contain a small cabin or berth. They could be outfitted for long offshore trips.
Trailer Sailer
Very similar to a pocket cruiser, a trailer sailer is a smaller vessel but still larger than a sailing dinghy. There is clear overlap between trailer sailers, daysailers, and pocket cruisers and the same name could technically be used for many different boats. The defining characteristic of a trailer sailer is that it can easily be transported by trailer behind your tow vehicle. Unlike a sailing dinghy, a trailer sailer would likely have a retractable keep like a centerboard or daggerboard.
Racing Sailboats
These boats can be very large, anywhere from 20 feet to over 70 feet, and they are designed to be light and fast on the water. Larger racing sailboats required a skilled crew to operate. These have keels intended to increase speed and even laminate sales to improve performance. Smaller racing boats can be manned by just one or two people. They don’t offer a lot of creature comforts and aren’t meant for relaxing trips at sea.
Beach Catamarans
Beach cats get their name from the fact they’re designed to be beached and can be launched again from the beach if you so desire. They are usually under 25 feet and not meant for extending sailing offshore, rather they are designed for daysailing. They are very agile and fast and take a good foundation of knowledge to control properly.
Cruising Catamarans
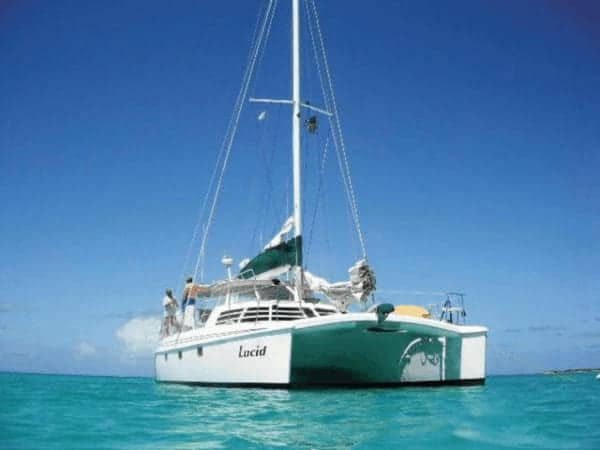

This is the larger style of catamaran designed for more serious boating. Like any catamaran they have a shallow draft but these can be between 25 feet and up to more than 50 feet. They’re designed for extended cruising offshore.
Cruising Sailboats
Boats like schooners quality as a cruising boat and they are typically at least 16 feet in length but may get well over 50 feet as well. Cruising sailboats include cabins for extended stays offshore and, if the boat is large enough, will likely have a fairly large living space below deck which includes a galley and a head in addition to sleeping berths. These are often called liveaboard sailboats .
Cruisers are often monohull but can just as easily be multihull. When properly outfitted they can be used for long, extended stays at sea that last weeks or more. Depending on rigging a cruising sailboat could easily be a sloop, a schooner, a cutter, a ketch or even a superyacht.
Racing Cruisers
This is essentially a hybrid of the cruising sailboat and the racing sailboat. It’s built for more speed than a cruiser but it will have better accommodations than a racing sailboat to allow for stays at sea. The end result is a lighter cruiser ideal for a few days at sea that can get some good speed.
Bluewater Cruising Boats
These are basically the next step up from a cruising sailboat. A bluewater cruiser is meant to sail across oceans, which is where the bluewater part of the name comes from. These are large sailboats and are best only sailed by skilled sailors. They can be outfitted for very long stays at sea and are able to handle rough weather better than smaller vessels.
Motorsailers
You don’t hear this term much anymore but it refers to a sailboat that also has an inboard motor so that they can travel under engine power or wind power. Typically these are larger vessels with accommodations below deck and designed for extended stays off shore. That said, because they mix both styles of boat, they fall somewhere short of either in terms of performance. The engine takes up space and adds weight, limiting your sailing abilities. Obviously traditional sailboats won’t include a motor.
The Bottom Line
There are a number of different kinds of sailboats and the easiest way to distinguish them is by comparing hull types, sail and mast configuration, and keels. Many terms you hear to describe sailboats can describe more than one kind, while others are very specific and the boat must meet certain requirements to merit the name. The only thing that truly unites every type of sailboat is the fact it must be powered by the wind, and even then there are hybrid versions that use motor power sometimes.
Learning the rigging of the different types of sailboats, including things like gaff rigs, standard rigging, and other rig types can be hard work and time consuming as some of these sailing boat rig types are far more complex than others.
My grandfather first took me fishing when I was too young to actually hold up a rod on my own. As an avid camper, hiker, and nature enthusiast I'm always looking for a new adventure.
Categories : Boats
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
More in Boats

What Is A Gunwale?

131 of the Best Hawaiian Boat Names

167 Patriotic Boat Names

The 138 Best Boat Names for Dog Lovers

The People’s Poncho Review and Ratings

Oru Lake Kayak Review

About Boatsafe
Established in 1998, BoatSafe is your independent guide into the world of boating, fishing, and watersports. We provide expert insights and detailed guides to help you find products tailored to your needs and budget.
Contact Boatsafe
- Address: 4021 West Walnut Street. Rogers, AR 72756
- Phone: (479)339-4795
- Email: [email protected]
Site Navigation
- How We Test
- Corrections Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Editorial Policy
- Affiliate Disclosure
Our Reviews

All content is © Copyright 2024. All rights reserved.

Types of Sailing Yachts: Pros, Cons and Comparison

There are many different types of sailing yachts, each with their own unique features and characteristics. Here, we will discuss some of the most popular types of sailing yachts and the features that set them apart.
Table of Contents
Cruiser/Racer

Cruiser/Racer sailing yachts are designed for both cruising and racing, making them versatile and popular among sailors of all skill levels. These yachts typically have a comfortable interior for longer trips and a more performance-oriented hull design for racing.
One of the key features of cruiser/racer yachts is their balance between comfort and performance. While they have the amenities and space needed for cruising, such as a comfortable interior, a large cockpit, and a variety of amenities for extended voyages, they also have a more performance-oriented hull design for racing. This allows sailors to enjoy the best of both worlds, whether they want to go for a leisurely cruise or participate in a racing event.
The hull design of cruiser/racer yachts is typically more hydrodynamic than traditional cruising yachts, which allows for better speed and manoeuvrability. Additionally, these yachts often have a more lightweight construction to help reduce drag and increase performance.
Another feature that sets cruiser/racer yachts apart is their modern sail plan. They are often equipped with larger and more powerful sails than traditional cruising yachts, which allows them to reach higher speeds and perform better in racing conditions.
Cruiser/Racer sailing yachts are popular among sailors who want to participate in racing events, but also want to take longer trips and enjoy the comfort and amenities of a cruising yacht. They are also popular among sailors who want to learn to race, but don’t want to sacrifice the comfort and space of a traditional cruising yacht.
Pros and Cons of Cruiser/Racer
Cruiser/Racer yachts are versatile sailing yachts that are designed for both cruising and racing, making them popular among sailors of all skill levels. However, like any type of yacht, they have their own set of pros and cons.
- Versatility: Cruiser/Racer yachts are designed for both cruising and racing, which makes them a great choice for sailors who want to do both. They have a comfortable interior for longer trips and a more performance-oriented hull design for racing, which allows sailors to enjoy the best of both worlds.
- Balance of comfort and performance: Cruiser/Racer yachts are designed to provide a balance of comfort and performance. They have the amenities and space needed for cruising, but also have a more performance-oriented hull design for racing, which allows them to perform well in racing conditions.
- Good for learning to race: Cruiser/Racer yachts are a great choice for sailors who want to learn to race, but don’t want to sacrifice the comfort and space of a traditional cruising yacht.
- Expensive: Cruiser/Racer yachts can be more expensive than other types of yachts, especially if they are designed and built to high specifications.
- Maintenance: Cruiser/Racer yachts require more maintenance than other types of yachts, as they have more complex systems and features.
- Not as comfortable as a cruiser: Cruiser/Racer yachts are not as comfortable as traditional cruising yachts, as they have more performance
Overall, Cruiser/Racer sailing yachts are a great choice for sailors looking for a versatile yacht that can handle both cruising and racing. With their comfortable interior, performance-oriented hull design, and modern sail plan, these yachts offer the perfect balance between comfort and performance.

Daysailer sailing yachts, as the name suggests, are designed for short trips and day sails. They are typically smaller and more compact than other types of yachts, and are often used for training or recreational sailing.
One of the key features of daysailers is their small size and simplicity. They typically have a smaller cockpit, a simple sailplan, and minimal amenities, which makes them easy to handle and maneuver for sailors of all skill levels. This makes them ideal for training, learning to sail, or for short trips where you don’t need to bring much gear or supplies.
Daysailers also typically have a more lightweight construction than other types of sailing yachts, which allows them to be more responsive and maneuverable on the water. This makes them ideal for racing and other competitive sailing events.
Another feature that sets daysailers apart is their affordability. They are often less expensive than other types of yachts, which makes them an accessible option for sailors who are just starting out or who are on a budget.
Daysailers are also popular among sailors who prefer the simplicity of day sailing and are not interested in overnight trips or longer cruises. They are also a great choice for sailors who want to enjoy the experience of sailing without the added responsibilities that come with owning a larger yacht.
Pros and Cons of Daysailers
Daysailer yachts are designed for short trips and day sails, and are typically smaller and more compact than other types of yachts. They are often used for training or recreational sailing. However, like any type of yacht, they have their own set of pros and cons.
- Affordable: Daysailers are often less expensive than other types of yachts, which makes them an accessible option for sailors who are just starting out or who are on a budget.
- Easy to handle: Daysailers typically have a small cockpit, a simple sail plan, and minimal amenities, which makes them easy to handle and maneuver for sailors of all skill levels. This makes them ideal for training, learning to sail, or for short trips where you don’t need to bring much gear or supplies.
- Lightweight construction: Daysailers have a more lightweight construction than other types of sailing yachts, which allows them to be more responsive and maneuverable on the water. This makes them ideal for racing and other competitive sailing events.
- Limited amenities: Daysailers have limited amenities, which means they are not designed for overnight stays or longer cruises.
- Limited space: Daysailers typically have limited space, which makes them less comfortable than larger yachts.
- Not suitable for long-distance cruising: Daysailers are not suitable for long-distance cruising or live-aboard cruising as they are not equipped for it.
Overall, Daysailer yachts are a great choice for sailors looking for a small, easy-to-handle, and affordable yacht that is ideal for day sailing and short trips. However, they are not suitable for overnight trips or long-distance cruising, and have limited amenities and space.
Racing Yacht

Racing yachts are designed specifically for speed and performance. They are typically much smaller than cruising yachts, and are built to be as lightweight and hydrodynamic as possible. They are often used in competitive sailing events, such as regattas and races.
One of the key features of racing yachts is their lightweight construction. They are typically made of materials such as carbon fiber or high-tech composites, which are both lightweight and strong. This allows them to reach high speeds and perform well in racing conditions.
Another feature that sets racing yachts apart is their hydrodynamic hull design. These yachts are built with a sharp bow, a narrow beam and a long waterline, which helps them to cut through the water more efficiently and reach higher speeds. They also tend to have a deep keel, which provides them with more stability and helps them to perform better in strong winds and rough seas.
Racing yachts also often have a more modern sail plan, with larger and more powerful sails that allow them to reach higher speeds and perform better in racing conditions. They also often have a smaller interior to keep weight down, which can make them less comfortable for overnight stays.
Racing yachts are popular among sailors who want to participate in competitive sailing events and races. They are also popular among sailors who want to experience the thrill of sailing at high speeds and pushing the limits of performance. However, it’s important to keep in mind that racing yachts are not as comfortable for long cruises as other types of sailing yachts and they can be expensive to maintain.
Pros and Cons of Racing yachts
Racing yachts are designed specifically for speed and performance, and are often used in competitive sailing events such as regattas and races. However, like any type of yacht, they have their own set of pros and cons.
- Speed: Racing yachts are built with lightweight construction and a hydrodynamic hull design, which allows them to reach high speeds and perform well in racing conditions.
- Maneuverability : Racing yachts are designed to be highly maneuverable, which allows them to perform well in tight and technical racing conditions.
- Modern sail plan : Racing yachts are often equipped with larger and more powerful sails than traditional cruising yachts, which allows them to reach higher speeds and perform better in racing conditions.
- Cost : Racing yachts can be expensive to purchase and maintain, especially if they are designed and built to high specifications.
- Comfort : Racing yachts typically have a smaller interior than other yachts, which can make them less comfortable for overnight stays.
- Maintenance : Racing yachts require more maintenance than other types of yachts, as they have more complex systems and features, and they are often pushed to the limits of their performance.
- Not suitable for long-distance cruising : Racing yachts are not suitable for long-distance cruising or live-aboard cruising as they are not equipped for it.
Overall, Racing yachts are a great choice for sailors looking for a high-performance sailing vessel that can be used in competitive sailing events. With their lightweight construction, hydrodynamic hull design, and modern sail plan, racing yachts are designed to reach high speeds and perform well in racing conditions. However, they can be expensive to purchase and maintain, and may not be as comfortable as other types of yachts for overnight stays or long-distance cruising.

Cruising yachts, also known as cruisers, are designed for longer trips and are typically larger and more comfortable than other types of yachts. They are built for extended voyages, and often have a spacious interior, a large cockpit, and a variety of amenities to make life on board more comfortable.
One of the key features of cruising yachts is their spacious interior. They are designed to have multiple cabins, a large salon, and a well-appointed galley, which makes them ideal for longer trips and live-aboard cruising. They also usually have a lot of storage space, so you can bring all the gear and supplies you’ll need for an extended voyage.
Another feature that sets cruising yachts apart is their stability and seaworthiness. They are designed to handle rough seas and strong winds, which allows them to be more comfortable and safer for longer trips. They also typically have a more comfortable motion, which helps to reduce fatigue for those on board.
Cruising yachts also often have a variety of amenities, such as air conditioning, generators, and refrigeration, which make them more comfortable and convenient for longer trips. They also often have a larger cockpit, which provides more space for relaxing and entertaining.
Cruising yachts are popular among sailors who want to take longer trips, live aboard or even cross oceans. They are also popular among sailors who want to experience the comfort and convenience of a well-appointed yacht. However, it’s worth noting that cruising yachts are typically more expensive than other types of yachts and they require more maintenance.
Overall, cruising yachts are a great choice for sailors looking for a comfortable and seaworthy yacht that can handle longer trips and live-aboard cruising. With their spacious interior, stability, and variety of amenities, cruising yachts are designed to make life on board as comfortable and convenient as possible.

A catamaran is a type of sailing yacht that has two parallel hulls, rather than one. They are known for their stability and spaciousness, making them popular for longer trips, live-aboard cruising, and charter vacations.
One of the key features of catamarans is their stability. With two hulls, the boat has a lower center of gravity and a wider beam, which makes them less likely to tip over in rough seas. This makes them a comfortable and safe option for longer trips and live-aboard cruising.
Another feature that sets catamarans apart is their spaciousness. They typically have a larger interior than monohulls of the same length, which allows for more living and storage space. This makes them ideal for bigger groups of people or for longer trips. They also usually have a larger cockpit, which provides more space for relaxing and entertaining.
Catamarans also often have a more shallow draft than monohulls, which allows them to navigate shallow waters, and anchor in more secluded bays. This can open up new opportunities for cruising, especially in areas where monohulls can’t access.
Catamarans are popular among sailors who want to take longer trips, live aboard, or who are looking for more stability and spaciousness. They are also popular among sailors who want to experience the comfort and convenience of a well-appointed yacht. However, it’s worth noting that catamarans are typically more expensive than other types of yachts and they require more maintenance.
Pros and cons of Catamaran
Catamarans are a type of sailing yacht that have two parallel hulls, which makes them known for their stability and spaciousness. They are popular for longer trips, live-aboard cruising, and charter vacations. However, like any type of yacht, they have their own set of pros and cons.
- Stability: Catamarans have a lower center of gravity and a wider beam than monohulls which make them less likely to tip over in rough seas. This makes them a comfortable and safe option for longer trips and live-aboard cruising.
- Space: Catamarans typically have a larger interior than monohulls of the same length, which allows for more living and storage space. This makes them ideal for bigger groups of people or for longer trips.
- Shallow draft: Catamarans also often have a more shallow draft than monohulls, which allows them to navigate shallow waters and anchor in more secluded bays.
- Cost: Catamarans can be more expensive than other types of yachts, especially if they are designed and built to high specifications.
- Maintenance: Catamarans require more maintenance than other types of yachts, as they have more complex systems and features.
- Not suitable for racing: Catamarans are not typically used for racing as they are not as fast as monohulls.
- Can be affected by wind direction: Catamarans can be affected by the wind direction, as the wind can hit the hulls from the side and can cause them to heel over.
Overall, Catamarans are a great choice for sailors looking for a stable and spacious yacht that can handle longer trips and live-aboard cruising. With their stability, spaciousness, and shallow draft, Catamarans are designed to provide a comfortable and safe sailing experience. However, they can be expensive and require more maintenance, they are

A trimaran is a type of sailing yacht that has three hulls, two smaller amas (outrigger hulls) and a central main hull, rather than one. They are known for their speed and stability, and are often used for racing and long-distance cruising.
One of the key features of trimarans is their speed. The two smaller amas, which are located on the sides of the main hull, increase the waterline length and provide more surface area for the sails to push against. This allows them to reach higher speeds and perform better in racing conditions.
Another feature that sets trimarans apart is their stability. With three hulls, the boat has a lower center of gravity and a wider beam, which makes them less likely to tip over in rough seas. This makes them a comfortable and safe option for longer trips and live-aboard cruising.
Trimarans also often have a more shallow draft than monohulls, which allows them to navigate shallow waters, and anchor in more secluded bays. This can open up new opportunities for cruising, especially in areas where monohulls can’t access.
Trimarans are popular among sailors who want to participate in racing events, and also want to take longer trips and enjoy the comfort and amenities of a cruising yacht. They are also popular among sailors who want to experience the thrill of sailing at high speeds and pushing the limits of performance. However, it’s worth noting that trimarans can be expensive to maintain and they also need more space to store.
Overall, trimarans are a great choice for sailors looking for a high-performance sailing vessel that can handle both racing and long-distance cruising. With their speed, stability, and shallow draft, trimarans are designed to provide a comfortable and safe sailing experience while reaching high speeds and performing well in racing conditions.
Pros and Cons of Trimaran
Trimarans have several advantages over monohull boats:
- Faster: Trimarans have a wider beam (the width of the boat) than monohulls, which gives them more stability and allows them to sail faster.
- Shallower draft: Because the majority of the weight is on the main hull, trimarans have a shallower draft (the depth of the boat in the water) than monohulls, which allows them to navigate in shallower waters.
- More space: Trimarans have more space on deck and inside the boat, which makes them more comfortable for longer trips.
- Less comfortable in rough seas: Trimarans can be less comfortable in rough seas because the smaller hulls can be affected by the waves.
- More difficult to handle: Trimarans can be more difficult to handle than monohulls because they have a larger sail area and a wider beam.
- More expensive: Trimarans are generally more expensive to build and maintain than monohulls.
In summary, Trimarans are faster, more stable, and have more space, but they can be less comfortable in rough seas and are more difficult to handle. They are also more expensive than monohulls.
Classic Yacht

A classic yacht is a type of sailing yacht that is typically older and has been restored or maintained in its original condition. These yachts often have a timeless aesthetic and are often made of wood, they are often used for historical sailing events and regattas.
One of the key features of classic yachts is their unique and timeless design. They often have a traditional and elegant aesthetic, with classic lines, and a beautiful woodwork finish. These yachts are often one of a kind, as many of them were custom-built for their original owners.
Another feature that sets classic yachts apart is their history. Many of these yachts have a rich and interesting past, and have often been sailed by famous sailors, or have participated in significant sailing events. This can add to the charm and allure of owning and sailing a classic yacht.
Classic yachts also often have a more traditional sail plan and rigging, which can add to the sailing experience. Sailing a classic yacht can be a unique and rewarding experience, as it allows sailors to connect with the rich history of sailing and to appreciate the craftsmanship of these yachts.
Classic yachts are popular among sailors who appreciate the beauty and craftsmanship of traditional sailing yachts, and who want to experience the unique sailing experience that these yachts offer. They are also popular among sailors who want to participate in historical sailing events and regattas. However, it’s worth noting that classic yachts can be expensive to maintain, and require more expertise and care to keep in good condition.
Pros and Cons of Classic Yacht
Classic yachts are a type of sailing yacht that are typically older and have been restored or maintained in their original condition. They often have a timeless aesthetic and are often made of wood. They are often used for historical sailing events and regattas. However, like any type of yacht, they have their own set of pros and cons.
- Timeless design: Classic yachts often have a traditional and elegant aesthetic, with classic lines and beautiful woodwork finish. These yachts are often one of a kind, as many of them were custom-built for their original owners.
- History: Many classic yachts have a rich and interesting past, and have often been sailed by famous sailors or have participated in significant sailing events. This can add to the charm and allure of owning and sailing a classic yacht.
- Traditional sailing experience: Classic yachts often have a more traditional sail plan and rigging, which can add to the sailing experience. Sailing a classic yacht can be a unique and rewarding experience, as it allows sailors to connect with the rich history of sailing and to appreciate the craftsmanship of these yachts.
- Maintenance: Classic yachts require more maintenance than other types of yachts, as they are often older and may require more repairs and restoration.
- Expensive: Classic yachts can be expensive to purchase, maintain, and restore, especially if they are in high demand or have a rich history.
- Limited amenities: Classic yachts often have limited amenities, which can make them less comfortable than newer yachts. They may not have modern features such as air conditioning, generators, and refrigeration, which can be a drawback for longer trips or live-aboard cruising.
- Limited performance: Classic yachts are not built for speed and performance, as they were not designed for racing and competitive sailing events. They may not perform as well as newer yachts in racing conditions.
- Limited availability: Classic yachts are not as readily available as newer yachts, and it can be difficult to find one that fits your needs and budget.
Overall, classic yachts are a great choice for sailors who appreciate the beauty and craftsmanship of traditional sailing yachts, and want to experience the unique sailing experience that these yachts offer. However, they can be expensive to purchase and maintain, and may not have the same level of amenities and performance as newer yachts. They also require more maintenance and expertise to keep in good condition.
No matter what type of sailing yacht you choose, it is important to consider the features and characteristics that are most important to you, and to choose a yacht that will suit your needs and preferences. Whether you’re a seasoned sailor or a beginner, there is a yacht out there that will fit your needs.
Steven T. Anderson
Steven Taylor Anderson is an experienced sailor and author who writes for sailingbetter.com. He has been sailing for over 20 years across the USA and has taken several courses to improve his skills. He has also navigated throughout the world on various boats and yachts. His passion for sailing and knowledge of the sport shines through in his writing, making him a respected authority on the subject.
Recent Posts
Lagoon vs Leopard Catamaran: Which Sailboat Is Right for You?
Introduction When it comes to cruising on the open waters, catamarans have gained immense popularity for their stability, space, and comfort. Two of the leading catamaran manufacturers, Lagoon and...
How to Determine Sailboat Weight: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction Sailing is a thrilling and adventurous activity that has captivated humans for centuries. Whether you are a seasoned sailor or a novice looking to set sail for the first time,...

Sail Rigs And Types - The Only Guide You Need

A well-designed sailboat is a thing of pure beauty. Whether you're a proud owner of one, a guest on one, or a shore-side admirer, you'll fall in love with the gliding sails, the excitement of a race, and the eco-friendly nature of these sophisticated yet magnificent vessels. With good sails, great design, and regular maintenance, sails and rigs are an important part of a sailboat.
If you’re thinking about going sailing, one of the first things you have to understand is the variety of modern sail plans. Unlike old sailboats, modern sailboats don't need huge, overlapping headsails and multiple masts just to get moving. In the past, when sailboats were heavy, keels were long, the only way to get the boat moving was with a massive relative sail area. You needed as much square footage as you could just to get your sailboat moving. But with the invention of fiberglass hulls, aluminum or composite masts, high-tensile but low diameter lines and stats, and more efficient sails, sailboats no longer need to plan for such large sail plans.. Still, there are various rig styles, from the common sloop, to the comfortable cat-rig, to the dual masted ketch and schooner, there are various sail types and rigs to choose from. The most important thing is to know the different types of sails and rigs and how they can make your sailing even more enjoyable.
There are different types of sails and rigs. Most sailboats have one mainsail and one headsail. The mainsail is generally fore-and-aft rigged and is triangular shaped. Various conditions and courses require adjustments to the sails on the boats, and, other than the mainsail, most boats can switch out their secondary sail depending on various conditions.. Do you want to sail upwind or go downwind? You cannot hoist just any sail and use it. It's, therefore, of great importance to understand how and when to use each sail type.
In this in-depth article, we'll look at various sail types and rigs, and how to use them to make your sailing more enjoyable.
Table of contents
Different Sail Types
It is perhaps worth noting that a sailboat is only as good as its sails. The very heart of sailing comes in capturing the wind using artfully trimmed sails and turning that into motion. . Ask any good sailor and he'll tell you that knowing how and when to trim the sails efficiently will not only improve the overall performance of your boat but will elevate your sailing experience. In short, sails are the driving force of sailboats.
As such, it's only natural that you should know the different types of sails and how they work. Let's first highlight different sail types before going into the details.
- Jib - triangular staysail
- Spinnaker - huge balloon-shaped downwind sail for light airs
- Genoa - huge jib that overlaps the mainsail
- Gennaker - a combination of a spinnaker and genoa
- Code zero - reaching genoa for light air
- Windseeker - tall, narrow, high-clewed, and lightweight jib
- Drifter - versatile light air genoa made from particularly lightweight cloth
- Storm jib - a smaller jib meant for stormy conditions
- Trysail - This is a smaller front-and-aft sail for heavy weather
The mainsail is the principal sail on a boat. It's generally set aft of the mainmast. Working together with the jib, the mainsail is designed to create the lift that drives the sailboat windward. That being said, the mainsail is a very powerful component that must always be kept under control.
As the largest sail, and the geometric center of effort on the boat, the mainsail is tasked with capturing the bulk of the wind that's required to propel the sailboat. The foot, the term for the bottom of any sail, secures to the boom, which allows you to trim the sail to your heading. The luff, the leading edge of the sail, is attached to the mast. An idealized mainsail would be able to swing through trim range of 180°, the full semi-circle aft of the mast, though in reality, most larger boats don’t support this full range of motion, as a fully eased sail can occasionally be unstable in heavy breeze.
. As fully controlling the shape of the mainsail is crucial to sailing performance, there are many different basic mainsail configurations. For instance, you can get a full-batten mainsail, a regular mainsail with short battens, or a two-plus-two mainsail with two full-length battens. Hyper-high performance boats have even begun experimenting with winged sails which are essentially trimmable airplane wings! Moreover, there are numerous sail controls that change the shape by pulling at different points on the sail, boom, or mast. Reefing, for instance, allows you to shorten the sail vertically, reducing the amount of sail area when the boat is overpowered.
Features of a Mainsail
Several features will affect how a particular sail works and performs. Some features will, of course, affect the cost of the sail while others may affect its longevity. All in all, it's essential to decide the type of mainsail that's right for you and your sailing application.
Sail Battens, the Roach, and the Leech
The most difficult part of the sail to control, but also the most important, are the areas we refer to as the leech and the roach. The roach is the part of the sail that extends backwards past the shortest line between the clew, at the end of the boom, and the top of the mast. It makes up roughly the back third of the sail. The leech is the trailing edge of the sail, the backmost curve of the roach. Together, these two components control the flow of the air off the back of the sail, which greatly affects the overall sail performance. If the air stalls off the backside of the sail, you will find a great loss in performance. Many sail controls, including the boom vang, backstay, main halyard, and even the cunningham, to name a few, focus on keeping this curve perfect.
As for parts of the sail itself, battens control the overall horizontal shape of the sail. Battens are typically made from fiberglass or wood and are built into batten pockets. They're meant to offer support and tension to maintain the sail shape Depending on the sail technology you want to use, you may find that full battens, which extend from luff to leech, or short battens, just on the trailing edge, are the way to go. Fully battened sails tend to be more expensive, but also higher performance.
Fully Battened Mainsails
They're generally popular on racing multihulls as they give you a nice solid sail shape which is crucial at high speeds. In cruising sailboats , fully battened mainsails have a few benefits such as:
- They prevent the mainsail from ragging. This extends the life of the sail, and makes maneuvers and trimming easier for the crew.
- It provides shape and lift in light-air conditions where short-battened mainsails would collapse.
On the other hand, fully-battened mainsails are often heavier, made out of thicker material, and can chafe against the standing rigging with more force when sailing off the wind.
Short Battens
On the other hand, you can choose a mainsail design that relies mostly on short battens, towards the leech of the sail. This tends to work for lighter cloth sails, as the breeze, the headsail, and the rigging help to shape the sail simply by the tension of the rig and the flow of the wind. The battens on the leech help to preserve the shape of the sail in the crucial area where the air is flowing off the back of the sail, keeping you from stalling out the entire rig.
The only potential downside is that these short battens deal with a little bit of chafe and tension in their pockets, and the sail cloth around these areas ought to be reinforced. If your sails do not have sufficient reinforcement here, or you run into any issues related to batten chafe, a good sail maker should be able to help you extend the life of your sails for much less than the price of a new set.
How to Hoist the Mainsail
Here's how to hoist the mainsail, assuming that it relies on a slab reefing system and lazy jacks and doesn't have an in-mast or in-boom furling system.
- Maintain enough speed for steeragewhile heading up into the wind
- Slacken the mainsheet, boom vang, and cunningham
- Make sure that the lazy jacks do not catch the ends on the battens by pulling the lazy jacks forward.
- Ensure that the reefing runs are free to run and the proper reefs are set if necessary.
- Raise the halyard as far as you can depending on pre-set reefs.
- Tension the halyard to a point where a crease begins to form along the front edge
- Re-set the lazy jacks
- Trim the mainsail properly while heading off to your desired course
So what's Right for You?
Your mainsail will depend on how you like sailing your boat and what you expect in terms of convenience and performance. That being said, first consult the options that the boatbuilder or sailmakers suggest for your rig. When choosing among the various options, consider what you want from the sail, how you like to sail, and how much you're willing to spend on the mainsail.
The headsail is principally the front sail in a fore-and-aft rig. They're commonly triangular and are attached to or serve as the boat’s forestay. They include a jib and a genoa.
A jib is a triangular sail that is set ahead of the foremost sail. For large boats, the roto-furling jib has become a common and convenient way to rig and store the jib. Often working in shifts with spinnakers, jibs are the main type of headsails on modern sailboats. Jibs take advantage of Bournoulli’s Principle to break the incoming breeze for the mainsail, greatly increasing the speed and point of any boat. By breaking the incoming wind and channeling it through what we call the ‘slot,’ the horizontal gap between the leech of the jib and the luff of the mainsail, the jib drastically increases the efficiency of your mainsail. It additionally balances the helm on your rudder by pulling the bow down, as the mainsail tends to pull the stern down. .
The main aim of the jib is to increase the sail area for a given mast size. It improves the aerodynamics of the mainsails so that your sailboat can catch more wind and thereby sail faster, especially in light air
Using Jibs on Modern Sailboats
In the modern contexts, jib’s mainly serve increase the performance and overall stability of the mainsail. The jib can also reduce the turbulence of the mainsail on the leeward side.
On Traditional Vessels
Traditional vessels such as schooners have about three jibs. The topmast carried a jib topsail, the main foresail is called the jib, while the innermost jib is known as the staysail. The first two were employed almost exclusively by clipper ships.
How to Rig the Jibs
There are three basic ways to rig the jib.
Track Sheets - A relatively modern approach to the self-tacking jib, this entails placing all the trimming hardware on a sliding track forward of the mast. This means that on each tack, the hardware slides from one side of the boat to the other. This alleviates the need to switch sheets and preserves the trim angle on both sides, though it can be finnicky and introduce friction.
Sheet up the Mast - This is a very popular approach and for a good reason. Hoist the jib sheet up the mast high enough to ensure that there's the right tension through the tack. Whether internally or externally, the sheet returnsto the deck and then back to the cockpit just like the rest of the mast baselines. The fact the hardware doesn't move through the tacks is essential in reducing friction.
Sheet Forward - This method revolves around ensuring that the jib sheet stays under constant pressure so that it does not move through the blocks in the tacks. This is possible if the through-deck block is extremely close to the jib tack. Your only challenge will only be to return the sheet to the cockpit. This is, however, quite challenging and can cause significant friction.
Dual Sheeting - The traditional method, especially on smaller dinghies, though it is not self-tacking. This requires a two ended or two separate sheet system, where one sheet runs to a block on starboard, and the other to port. Whenever you tack or gybe, this means you have to switch which sheet is active and which is slack, which is ok for well crewed boats, but a potential issue on under-crewed boats.
Another important headsail, a genoa is essentially a large jib that usually overlaps the mainsail or extends past the mast, especially when viewed from the other side. In the past, a genoa was known as the overlapping jib and is technically used on twin-mast boats and single-mast sloops such as ketches and yawls. A genoa has a large surface area, which is integral in increasing the speed of the vessel both in moderate and light winds.
Genoas are generally characterized by the percentage they cover. In most cases, sail racing classes stipulate the limit of a genoa size. In other words, genoas are usually classified by coverage.
Top-quality genoa trim is of great importance, especially if the wind is forward of the beam. This is because the wind will first pass over the genoa before the mainsail. As such, a wrongly sheeted genoa can erroneously direct the wind over the mainsail,spelling doom to your sailing escapades. While you can perfectly adjust the shape of a genoa using the mast rake, halyard tension, sheet tension, genoa car positioning, and backstay tension, furling and unfurling a genoa can be very challenging, especially in higher winds.
That being said, here are the crucial steps to always keep in mind.
- Unload and ease the loaded genoa sheet by going to a broad reach
- Do not use the winch; just pull on the furling line
- Keep a very small amount of pressure or tension on the loaded genoa sheet
- Secure the furling line and tighten the genoa sheets
- Get on the proper point of sail
- Have the crew help you and release the lazy genoa sheets
- Maintain a small tension while easing out the furling line
- Pull-on a loaded genoa sheet
- Close or cleat off the rope clutch when the genoa is unfurled
- Trim the genoa
To this end, it's important to note that genoas are popular in some racing classes. This is because they only categorize genoas based on the fore-triangle area covered, which essentially allows a genoa to significantly increase the actual sail area. On the contrary, keep in mind that tacking a genoa is quite a bit harder than a jib, as the overlapping area can get tangled with the mast and shrouds. It's, therefore, important to make sure that the genoa is carefully tended, particularly when tacking.
Downwind Sails
Modern sailboats are a lot easier to maneuver thanks to the fore-and-aft rig. Unfortunately, when sailing downwind they catch less wind, and downwind sails are a great way of reducing this problem. They include the spinnaker and the gennaker.
A spinnaker will, without a doubt, increase your sailing enjoyment. But why are they often buried in the cabin of cruising boats? Well, the first few attempts to rig and set a spinnaker can be difficult without enough help and guidance. Provided a solid background, however, spinnakers are quite straightforward and easy to use and handle with teamwork and enough practice. More importantly, spinnakers can bring a light wind passage to life and can save your engine.
Spinnakers are purposely designed for sailing off the wind; they fill with wind and balloon out in front of your sailboat. Structured with a lightweight fabric such as nylon, the spinnaker is also known as a kite or chute, as they look like parachutes both in structure and appearance.
A perfectly designed spinnaker should have taut leading edges when filled. This mitigates the risk of lifting and collapsing. A spinnaker should have a smooth curve when filled and devoid of depressions and bubbles that might be caused by the inconsistent stretching of the fabric. The idea here is that anything other than a smooth curve may reduce the lift and thereby reduce performance.
Types of Spinnakers
There are two main types of spinnakers: symmetric spinnakers and asymmetric spinnakers.
Asymmetric Spinnakers
Flown from a spinnaker pole or bowsprit fitted to the bow of the boat, asymmetric spinnakers resemble large jibs and have been around since the 19th century. The concept of asymmetric spinnaker revolves around attaching the tack of the spinnaker at the bow and pulling it around during a gybe.
Asymmetric spinnakers have two sheets just like a jib., These sheets are attached at the clew and never interact directly with the spinnaker pole. This is because the other corner of the spinnaker is fixed to the bowsprit. The asymmetric spinnaker works when you pull in one sheet while releasing the other. This makes it a lot easier to gybe but is less suited to sailing directly downwind. There is the loophole of having the asymmetric spinnaker gybed to the side opposite of the boom, so that the boat is sailing ‘wing-on-wing,’ though this is a more advanced maneuver, generally reserved for certain conditions and tactical racing situations.
On the contrary, the asymmetric spinnaker is perfect for fast planing dinghies. This is because such vessels have speeds that generate apparent wind forward. Because asymmetrics, by nature, prefer to sail shallower downwind angles, this apparent wind at high speeds makes the boat think that it is sailing higher than it really is, allowing you to drive a little lower off the breeze than normal. . In essence, the asymmetric spinnaker is vital if you're looking for easy handling.
Symmetric Spinnakers
Symmetric spinnakers are a classic sail type that has been used for centuries for controlling boats by lines known as a guy and a sheet. The guy, which is a windward line, is attached to the tack of the sail and stabilized by a spinnaker pole. The sheet, which is the leeward line, is attached to the clew of the spinnaker and is essential in controlling the shape of the spinnaker sail.
When set correctly, the leading edges of the symmetric spinnaker should be almost parallel to the wind. This is to ensure that the airflow over the leading edge remains attached. Generally, the spinnaker pole should be at the right angles to the apparent wind and requires a lot of care when packing.
The main disadvantage of this rig is the need to gybe the spinnaker pole whenever you gybe the boat. This is a complicated maneuver, and is one of the most common places for spinnakers to rip or get twisted. If, however, you can master this maneuver, you can sail at almost any angle downwind!
How to Use Spinnaker Effectively
If you decide to include the spinnakers to your sailboat, the sailmaker will want to know the type of boat you have, what kind of sailing you do, and where you sail. As such, the spinnaker that you end up with should be an excellent and all-round sail and should perform effectively off the breeze
The type of boat and where you'll be sailing will hugely influence the weight of your spinnaker cloth. In most cases, cruising spinnakers should be very light, so if you've decided to buy a spinnaker, make sure that it's designed per the type of your sailboat and where you will be sailing. Again, you can choose to go for something lighter and easier to set if you'll be sailing alone or with kids who are too young to help.
Setting up Spinnakers
One of the main reasons why sailors distrust spinnakers is because they don't know how to set them up. That being said, a perfectly working spinnaker starts with how you set it up and this revolves around how you carefully pack it and properly hook it up. You can do this by running the luff tapes and ensuring that the sails are not twisted when packed into the bag. If you are using large spinnakers, the best thing to do is make sure that they're set in stops to prevent the spinnakers from filling up with air before you even hoist them fully.
But even with that, you cannot fully set the spinnaker while sailing upwind. Make sure to bear away and have your pole ready to go as you turn downwind. You should then bear away to a reach before hoisting. Just don't hoist the spinnakers from the bow as this can move the weight of the crew and equipment forward.
Used when sailing downwind, a gennaker is asymmetric sail somewhere between a genoa and a spinnaker. It sets itself apart because it gennaker is a free-flying asymmetric spinnaker but it is tacked to the bowsprit like the jib.
Let's put it into perspective. Even though the genoa is a great sail for racing and cruising, sailors realized that it was too small to be used in a race or for downwind sail and this is the main reason why the spinnaker was invented. While the spinnakers are large sails that can be used for downwind sail, they are quite difficult to handle especially if you're sailing shorthanded. As such, this is how a gennaker came to be: it gives you the best of both worlds.
Gennakers are stable and easy to fly and will add to your enjoyment and downwind performance.
The Shape of a Gennaker
As we've just noted, the gennaker is asymmetrical. It doesn't attach to the forestay like the genoa but has a permanent fitting from the mast to bow. It is rigged exactly like a spinnaker but its tack is fastened to the bowsprit. This is fundamentally an essential sail if you're looking for something to bridge the gap between a genoa and a spinnaker.
Setting a Gennaker
When cruising, the gennaker is set with the tack line from the bow, a halyard, and a sheet that's led to the aft quarter. Attach the tack to a furling unit and attach it to a fitting on the hull near the very front of the sailboat. You can then attach the halyard that will help in pulling it up to the top of the mast before attaching it to the clew. The halyard can then run back to the winches to make the controlling of the sail shape easier, just like when using the genoa sail.
In essence, a gennaker is a superb sail that will give you the maximum versatility of achieving the best of both a genoa and a spinnaker, especially when sailing downwind. This is particularly of great importance if you're cruising by autopilot or at night.
Light Air Sails
Even though downwind sails can be used as light air sails, not all light air sails can be used for downwind sailing. In other words, there's a level of difference between downwind sails and light air sails. Light air sails include code zero, windseeker, and drifter reacher.
A cross between an asymmetrical spinnaker and a genoa, a code zero is a highly modern sail type that's generally used when sailing close to the wind in light air. Although the initial idea of code zero was to make a larger genoa, it settled on a narrow and flat spinnaker while upholding the shape of a genoa.
Modern boats come with code zero sails that can be used as soon as the sailboat bears off close-hauled even a little bit. It has a nearly straight luff and is designed to be very flat for close reaching. This sail is designed to give your boat extra performance in light winds, especially in boats that do not have overlapping genoas. It also mitigates the problem of loss of power when you are reaching with a non-overlapping headsail. Really, it is closer to a light air jib that sacrifices a little angle for speed.
In many conditions, a code zero sail can go as high as a sailboat with just a jib. By hoisting a code zero, you'll initially have to foot off about 15 degrees to fill it and get the power that you require to heel and move the boat. The boat will not only speed up but will also allow you to put the bow up while also doing the same course as before you set the zero. In essence, code zero can be an efficient way of giving your boat about 30% more speed and this is exactly why it's a vital inventory item in racing sailboats.
When it comes to furling code zero, the best way to do it is through a top-down furling system as this will ensure that you never get a twist in the system.
Generally used when a full size and heavier sail doesn't stay stable or pressurized, a windseeker is a very light sail that's designed for drifting conditions. This is exactly why they're designed with a forgiving cloth to allow them to handle these challenging conditions.
The windseeker should be tacked at the headstay with two sheets on the clew. To help this sail fill in the doldrums, you can heel the boat to whatever the apparent leeward side is and let gravity help you maintain a good sail shape while reaching.The ideal angle of a windseeker should be about 60 degrees.
Though only used in very specific conditions, the windseeker is so good at this one job that it is worth the investment if you plan on a long cruise. Still, you can substitute most off the breeze sails for this in a pinch, with slightly less performance gain, likely with more sacrifices in angle to the breeze.
Drifter Reacher
Many cruising sailors often get intimidated by the idea of setting and trimming a drifter if it's attached to the rig at only three corners or if it's free-flying. But whether or not a drifter is appropriate for your boat will hugely depend on your boat's rig, as well as other specific details such as your crew's ability to furl and unfurl the drifter and, of course, your intended cruising grounds.
But even with that, the drifter remains a time-honored sail that's handy and very versatile. Unlike other light air sails, the drifter perfectly carries on all points of sails as it allows the boat to sail close-hauled and to tack. It is also very easy to control when it's set and struck. In simpler terms, a drifter is principally a genoa that's built of lightweight fabric such as nylon. Regardless of the material, the drifter is a superb sail if you want to sail off a lee shore without using the genoa.
Generally stronger than other regular sails, stormsails are designed to handle winds of over 45 knots and are great when sailing in stormy conditions. They include a storm jib and a trysail.
If you sail long and far enough, chances are you have or will soon be caught in stormy conditions. Under such conditions, storm jibs can be your insurance and you'll be better off if you have a storm jib that has the following features:
- Robustly constructed using heavyweight sailcloth
- Sized suitably for the boat
- Highly visible even in grey and white seas
That's not all; you should never go out there without a storm jib as this, together with the trysail, is the only sails that will be capable of weathering some of nature's most testing situations.
Storm jibs typically have high clews to give you the flexibility of sheet location. You can raise the sail with a spare halyard until its lead position is closed-hauled in the right position. In essence, storm jib is your insurance policy when out there sailing: you should always have it but always hope that you never have to use it.
Also known as a spencer, a trysail is a small, bright orange, veritably bullet-proof, and triangular sail that's designed to save the boat's mainsail from winds over 45 knots and works in the same way as a storm jib. It is designed to enable you to make progress to windward even in strong and stormy winds.
Trysails generally use the same mast track as the mainsail but you have to introduce the slides into the gate from the head of the trysail.
There are two main types of rigs: the fore-and-aft rig and the square rigg.
Fore-and-aft Rig
This is a sailing rig that chiefly has the sails set along the lines of the keel and not perpendicular to it. It can be divided into three categories: Bermuda rig, Gaff rig, and Lateen rig.
Bermuda Rig - Also known as a Marconi rig, this is the typical configuration of most modern sailboats. It has been used since the 17th century and remains one of the most efficient types of rigs. The rig revolves around setting a triangular sail aft of the mast with the head raised to the top of the mast. The luff should run down the mast and be attached to the entire length.
Gaff Rig - This is the most popular fore-and-aft rig on vessels such as the schooner and barquentine. It revolves around having the sail four-cornered and controlled at its peak. In other words, the head of the mainsail is guided by a gaff.
Lateen Rig - This is a triangular fore-and-aft rig whereby a triangular sail is configured on a long yard that's mounted at a given angle of the mast while running in a fore-and-aft direction. Lateen rig is commonly used in the Indian Ocean and the Mediterranean.
Square Rigged
This is a rig whereby the mainsails are arranged in a horizontal spar so that they're square or vertical to the mast and the keel of the boat. The square rig is highly efficient when sailing downwind and was once very popular with ocean-going sailboats.
Unquestionably, sailing is always pleasurable. Imagine turning off the engine of your boat, hoisting the sails, and filling them with air! This is, without a doubt, a priceless moment that will make your boat keel and jump forward!
But being propelled by the noiseless motion of the wind and against the mighty currents and pounding waves of the seas require that you know various sail types and how to use them not just in propelling your boat but also in ensuring that you enjoy sailing and stay safe. Sails are a gorgeous way of getting forward. They remain the main fascination of sailboats and sea cruising. If anything, sails and boats are inseparable and are your true friends when out there on the water. As such, getting to know different types of sails and how to use them properly is of great importance.
All in all, let's wish you calm seas, fine winds, and a sturdy mast!
Related Articles
Daniel Wade
I've personally had thousands of questions about sailing and sailboats over the years. As I learn and experience sailing, and the community, I share the answers that work and make sense to me, here on Life of Sailing.
by this author
Learn About Sailboats
Sailboat Parts
Most Recent

What Does "Sailing By The Lee" Mean?
October 3, 2023

The Best Sailing Schools And Programs: Reviews & Ratings
September 26, 2023
Important Legal Info
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies.
Similar Posts

Affordable Sailboats You Can Build at Home
September 13, 2023

Best Small Sailboat Ornaments
September 12, 2023

Discover the Magic of Hydrofoil Sailboats
December 11, 2023
Popular Posts

Best Liveaboard Catamaran Sailboats
December 28, 2023

Can a Novice Sail Around the World?
Elizabeth O'Malley
June 15, 2022

4 Best Electric Outboard Motors

How Long Did It Take The Vikings To Sail To England?

10 Best Sailboat Brands (And Why)
December 20, 2023

7 Best Places To Liveaboard A Sailboat
Get the best sailing content.
Top Rated Posts
© 2024 Life of Sailing Email: [email protected] Address: 11816 Inwood Rd #3024 Dallas, TX 75244 Disclaimer Privacy Policy
ACTIVE STORM TRACKER Hurricane and Tropical Storm Information Learn more

Service Locator
- Angler Endorsement
- Boat Towing Coverage
- Mechanical Breakdown
- Insurance Requirements in Mexico
- Agreed Hull Value
- Actual Cash Value
- Liability Only
- Insurance Payment Options
- Claims Information
- Towing Service Agreement
- Membership Plans
- Boat Show Tickets
- BoatUS Boats For Sale
- Membership Payment Options
- Consumer Affairs
- Boat Documentation Requirements
- Installation Instructions
- Shipping & Handling Information
- Contact Boat Lettering
- End User Agreement
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Vessel Documentation
- BoatUS Foundation
- Government Affairs
- Powercruisers
- Buying & Selling Advice
- Maintenance
- Tow Vehicles
- Make & Create
- Makeovers & Refitting
- Accessories
- Electronics
- Skills, Tips, Tools
- Spring Preparation
- Winterization
- Boaters’ Rights
- Environment & Clean Water
- Boat Safety
- Navigational Hazards
- Personal Safety
- Batteries & Onboard Power
- Motors, Engines, Propulsion
- Books & Movies
- Cockpit Confessions
- Communication & Etiquette
- Contests & Sweepstakes
- Colleges & Tech Schools
- Food, Drink, Entertainment
- New To Boating
- Travel & Destinations
- Watersports
- Anchors & Anchoring
- Boat Handling
- ← New & Used Boats
Types of Sailboats and Their Uses
Advertisement

Beach Catamaran
These are generally 14–20 feet in length primarily used for daysailing. They are fast boats that require some agility to sail. They have shallow drafts when the dagger boards are up for beaching.

Cruising Catamaran
A larger relative of the beach catamaran, they share more in common with a cruising mono-hull with accommodation for extended cruising. They are stable platforms with shallow drafts and are 25–50+ feet in length.

Cruising Sailboat
Generally 16–50+ feet in length, these boats are cabins for extended cruising. Boats larger than 26 feet usually have standing headroom down below. Many of the more popular models have large fleets and are raced or have fleet associations for group cruising.

These boats are generally 14–20 feet in length. They can seat up to 4 passengers. As the name implied they are intended for day use with a small cuddy cabin for storing gear. Many can accommodate a small outboard. They make a great choice for new boaters.

Motorsailer
Motorsailers are sailboats powered with inboard engines allowing long cruises under power or sail. They have luxury accommodations and usually 35 feet and over. They are a compromise giving up sailing speed due to a smaller rig and added weight for the engine and larger gas and water tanks.

Racer-Cruiser
This is a hybrid of the cruising boat built to accommodate overnight cruising but trimmed with the equipment for competitive racing. They are generally 25 feet and over.

Racing Sailboats
Similar to cruising boats but have more equipment and are built lighter, with spartan accommodations. They are not intended to be a comfortable ride, just a fast one. Usually 20–70+ feet in length. Just as these are related to cruising boats, there are smaller, faster cousins of sailing dinghies that are also raced.

Sailing Dinghies
Small (under 15 feet) these boats are usually one or two person boats. These are boats that guarantee a wet ride. Many are competitively raced. They are a great choice for those that are new to boating.
Related Articles
The truth about ceramic coatings for boats.
Our editor investigates the marketing claims of consumer-grade ceramic coatings.
Fine-Tune Your Side Scan Fishfinder
Take your side-scanning fishfinder off auto mode, and you’ll be spotting your prey from afar in no time
DIY Boat Foam Decking
Closed-cell foam flooring helps make boating more comfortable. Here’s how to install it on your vessel
Click to explore related articles
BoatUS Editors
Contributor, BoatUS Magazine
Award-winning BoatUS Magazine is the official publication of Boat Owners Association of The United States. The magazine provides boating skills, DIY maintenance, safety, news and more from top experts.
BoatUS Magazine Is A Benefit Of BoatUS Membership
Membership Benefits Include:
Subscription to the print version of BoatUS Magazine
4% back on purchases from West Marine stores or online at WestMarine.com
Discounts on fuel, transient slips, repairs and more at over 1,200 businesses
Deals on cruises, charters, car rentals, hotel stays and more…
All for only $25/year!
We use cookies to enhance your visit to our website and to improve your experience. By continuing to use our website, you’re agreeing to our cookie policy.

Types of Sailboats by Type of Rig
16 December 2015
To have a better idea of which types of sailboats would best suit your needs, your Allied Yachting broker can advise you on the various options available on the market for new or second-hand vessels as well as new construction. In the meantime, here is a summarized guide to the different categories of sailing yachts by type of rig , whether they are monohull (single hull) or multihull , as they’re called in the Mediterranean.
Sailboats by rig type: hulls, masts

Single masted sailboat with monohull
The most common monohull modern sailing yacht is the sloop, which features one mast and two sails, thus sloops are single-masted sailboats. If they have just two sails — a foresail and a headsail — then they’re a Bermudan sloop, the purest type of sailboat. This simple configuration is very efficient for sailing into the wind.
Sailing sloops with moderate rigs are probably the most popular of all cruising sailboats. Just a single-masted sailboat with two sails (a foresail or headsail, and a mainsail) and the minimum of rigging and sail control lines they are relatively simple to operate and less expensive than rigs with multiple masts.
Sloops are adapted for cruising as well as racing, depending on the height and size of their rig.
The cutter sailing yacht is also a monohull similar to a sloop with a single mast and mainsail but generally carries the mast further aft to allow for a jib and staysail to be attached to the head stay and inner forestay, respectively. Once a common racing configuration, today it gives versatility to cruising boats, especially in allowing a small staysail to be flown from the inner stay in high winds.
Thus, a cutter-rig sailboat has an additional sail (the staysail) set on its own stay between the foresail and the headsail.
Cutters are mostly adapted for cruising, but capable of good performance while racing as well.
A ketch is a two-masted sailboat, the main-mast forward and a shorter mizzen mast aft.
But not all two-masted sailboats are ketches — they might be yawls.
A ketch may also carry a staysail, with or without a bowsprit, in which case it would be known as a cutter-rigged ketch.
Ketches are also monohulls, but there is a second shorter mast astern of the mainmast, but forward of the rudder post. The second sailboat mast is called the mizzen mast and its sail is called the mizzen sail.
Yawls have their origins as old-time sail fishing boats, where the small mizzen sail was trimmed to keep the vessel steady when hauling the nets.
Similar to a ketch, the difference being that the yawl has the mizzen mast positioned aft of the rudder post whereas the ketch has its mizzen mast ahead of the rudder post.
Thus, a yawl is also a monohull, similar to a ketch, with a shorter mizzen mast carried astern the rudderpost more for balancing the helm than propulsion.
Schooners are generally the largest monohull sailing yachts.

Monohull two masts sailing boat
A schooner has a mainmast taller than its foremast, distinguishing it from a ketch or a yawl. A schooner can have more than two masts, with the foremast always lower than the foremost main. Traditional topsail schooners have topmasts allowing triangular topsails sails to be flown above their gaff sails; many modern schooners are Bermuda rigged.
A schooner is a two-(or more) masted sailboat, in which the aft-most mast – the mainmast – is the same height or taller than the foremast. Many sailors agree that of all the different types of sailboats, a schooner under full sail is one of the most beautiful sights afloat.
Gaffed-rigged sailboats, or “gaffers”, have their mainsail supported by a spar – the “gaff” – which is hauled up the mast by a separate halyard. Often these types of sailboats are rigged with a topsail. The gaff rig is no longer seen on modern production yachts.
A catamaran (‘cat’ for short) is a multihull yacht consisting of two parallel hulls of equal size.
A catamaran is geometry-stabilized, that is, it derives its stability from its wide beam, rather than having a ballasted keel like a monohull. Being ballast-free and lighter than a monohull, a catamaran can have a very shallow draught. The two hulls will be much finer than a monohull’s, allowing reduced drag and faster speeds in some conditions, although the high wetted surface area is detrimental in lower wind speeds, but allows much more accommodations, living and entertaining space in stability and comfort.
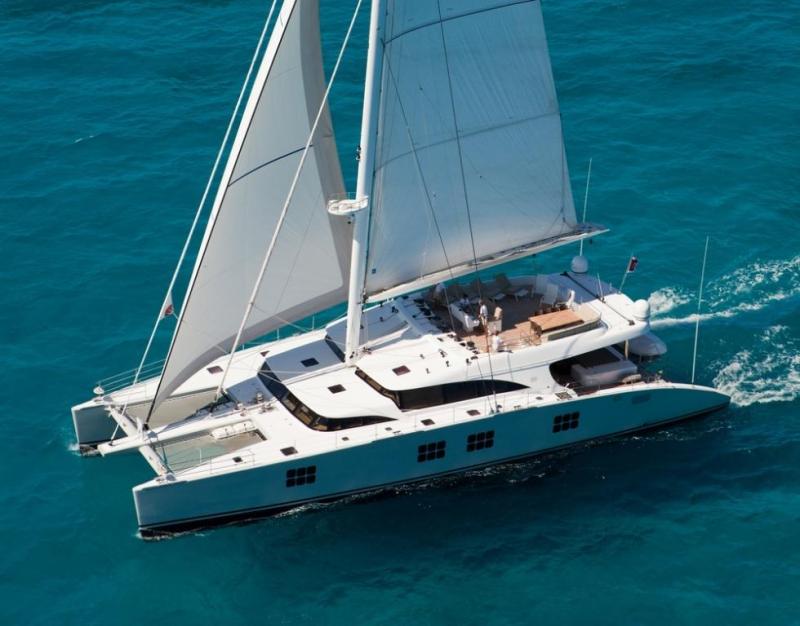

Two parallel hulls sailing catamaran
The speed and stability of these catamarans have made them a popular pleasure craft in Europe, most high-quality catamarans are built in France, but careful since their wide beams aren’t easy (or cheap) to berth in the French Riviera.
Racing catamarans technology has made them today’s leading racing sailboats of the world, like in the latest editions of America’s cup or other renowned transoceanic races.
Please surf through our website listings of sailing catamarans .
OTHER MULTIHULLS
Even harder to berth in the Mediterranean, and most commonly designed for around-the-globe racing rather than cruising, the trimarans have also been gaining some popularity in the western hemisphere, especially by naval designers with futuristic projects.
A trimaran is a multihull boat that comprises a main hull and two smaller outrigger hulls (or ‘floats’) which are attached to the main hull with lateral beams.
MOTORSAILER
A motorsailer or “motorsailor”, is a type of sailing vessel, typically a pleasure yacht, that derives propulsion from its sails and engine(s) in equal measure.
While the sailing yacht appeals primarily to the purist sailing enthusiast, the motorsailer is more suited for long-distance cruising, as a home for ‘live-aboard’ yachtsmen. The special features of the motorsailer (large engine, smaller sails, etc.) mean that, while it may not be the fastest boat under sail, the vessel is easily handled by a small crew. As such, it can be ideal for retired people who might not be entirely physically able to handle large sail areas. In heavy weather, the motorsailer’s large engine allows it to punch into a headwind when necessary to make landfall, without endless tacking to windward.
The Turkish word gulet is a loanword from the French goélette, meaning ‘schooner’.
A gulet is a traditional design of a two-masted (more common) or even three-masted wooden sailing vessel from the southwestern coast of Turkey, particularly built in the coastal towns of Bodrum and Marmaris; although similar vessels can be found all around the eastern Mediterranean. For considerations of crew economy, Diesel power is commonly used on these vessels, similar to a motorsailer. Today, this type of vessel, varying in size from 14 to 45 meters, is very popular and affordable for tourist charters in Turkey, the Aegean, Greece and up to Croatia in the Adriatic.
Please surf through our website listings of cruising sailing yachts by type of rig.
OUR YACHT LISTINGS:
- New Yachts for Sale
- Pre-owned Yachts for Sale
- Yachts for Charter
You might also like

Yachting Consultants
Sale-Charter-Brokerage-Management
Headquarters:
34 Rue Caffarelli 06000 Nice, France
Front Office:
Boulevard de La Croisette – Port Canto 06400 Cannes, France
T.: +33 493 43 82 83 Email: [email protected] Website: www.alliedyachting.com

Sail Types: A Comprehensive Guide to 8 Types of Sails
Sailboats come in all shapes and sizes. And that means there are many types of sails on the market! For those who might not know, sails are made of canvas and use wind power to propel sailboats through the water.
Understandably, different sails are required for different types of sailboats . And sailboats are categorized by the number of hulls they have. Monohulls have a single-hull design, catamarans have two hulls, and trimarans have three. Generally, sailors use catamarans for upwind sailing (but they can be used to sail downwind in certain conditions).
The type of sail you'll need for your sailboat depends on the kind of sailboat you have. Additionally, sails are highly dependent on the wind and weather conditions. Therefore, it's always a good idea to have different types of sails on board to navigate the ever-changing weather conditions.

8 Types of Sails for Sailboats
As mentioned, you should carry multiple sails when sailing to prepare for various weather conditions. Here's a brief overview of the types of sails for sailboats:
1. Mainsails
The mainsail is the largest and most important sail. Therefore, it's probably the first sail to come to mind when you think of camping. Typically, it's situated directly behind the mast — connected to the boom — and uses wind energy to move the vessel. The mainsail plays a significant role in tacking and gybing, making it essential for any voyage.
Since the mainsail is a larger sail, it doesn't require wind to propel it forward. And the fact that it can be moved by moving the boom makes it uber-easy to operate.
Learn More About Sailing
2. Headsail
The headsail often accompanies the mainsail, though it is smaller in size. Regardless of your sailboat type, the headsail is positioned at the front of the mast – over the sailboat's bow.
Because headsails are small, they are helpful when navigating through windy conditions. Smaller sails catch less wind, preventing them from propelling your boat as strongly as larger sails. Additionally, headsails help lift, balance, and protect the vessel from inclement weather conditions.
While the term 'headsail' refers to any sail in front of the mast, the jib is the most common type of headsail. (And when a jib is so large that it overlaps the mast, it's called a genoa.)
Learn More About Sailboats
3. Genoa
The genoa is a large sail that attaches to the front of the forestay. (In this instance, it's similar to a headsail.) However, the genoa is larger than the headsail and overlaps the mainsail partially or completely to help the boat go faster.
Genoa sails are useful when sailing through light or medium wind. You can also use it when the wind comes directly from the rear. If you use a Genoa sail during high winds, you'll probably start sailing too quickly and put yourself and your boat at risk.
4. Spinnaker
The spinnaker is a large and whimsical (often colorful) sail. Spinnaker sails are usually symmetrical, allowing them to reach different points of sail. Generally, these are lighter sails and don't cover the mast like the genoa.
Because spinnaker sails are on the larger side, you have to be incredibly careful with them. Don't use them in rough conditions. Instead, save them for sailing in low winds and calm seas.
5. Gennaker
As the name suggests, the Gennaker sail combines a spinnaker and a Genoa sail. They are as large as the spinnaker, although they're not symmetrical.
They come in handy whenever the wind changes from a pure dead run to a reaching point of sail, as sailors can navigate various wind types with the same sail. It's still only meant for lighter and milder winds, but it's more versatile than the spinnaker and genoa.
6. Light Air Sails
Light air sails are useful in calmer conditions when the headsail and mainsail alone aren't cutting it. They include:
- Code Zero : A code zero sail is a gennaker sail ideal for sailing in light to mild winds. It's designed to create lift and boost boat speed whenever regular sails don't generate enough power. For that reason, many racers and cruisers use code zero sails to improve performance and gain control in various situations.
- Windseeker : This small, special sail is reserved for no wind or light wind. Essentially, it helps boats remain maneuverable in extremely calm conditions. And for that reason, it's valuable to long-distance sailors.
7. Storm Jib
Storm jibs can be used as a headsail whenever the weather is particularly rough and windy. Because it functions as a safety seal, it prevents boats from capsizing by reducing the sail area exposed to the wind. Therefore, it's a necessary sail for every sailor.
Read Next: Boating in Inclement Weather
During strong winds and storms, sailors can raise a trysail — a small, triangular sail near the boat's stern — for better control and stability. Generally, sailors do this whenever the mainsail becomes too large and challenging to maneuver.
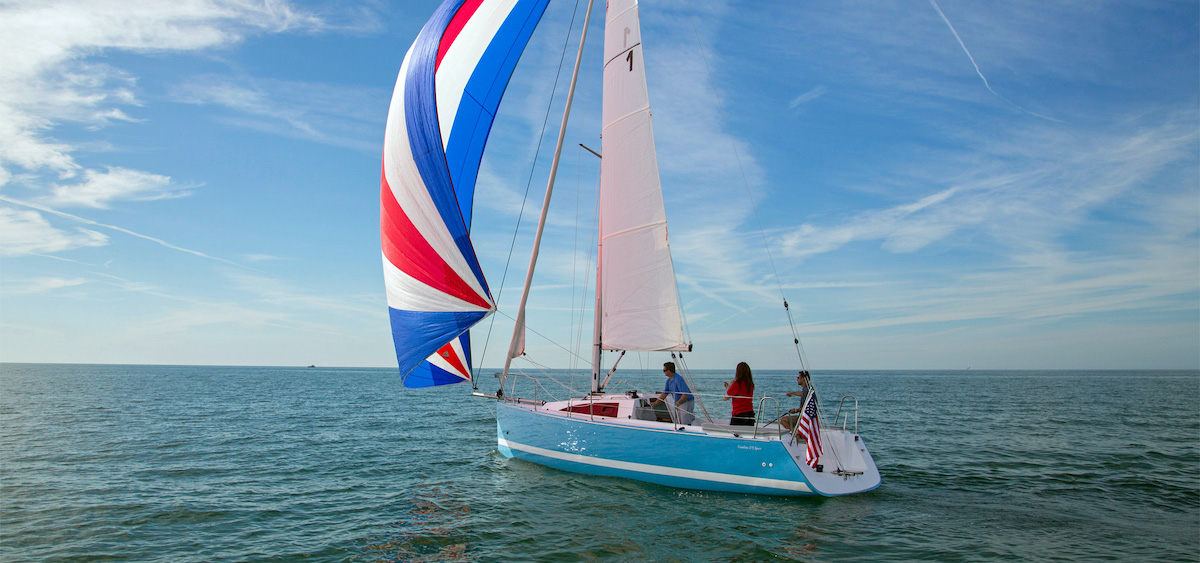

Join Our Newsletter!
Get community news, buying bargains, and how-to guides at your fingertips.

The Different Types Of Sails And When To Use Them – Complete Guide

Sail forms an integral part of a sailboat. When you sail on the open water and observe other boats (in various sizes), you’d have noticed how each boat type has a specific model of sail. If you’re a beginner in boating, you must know that there are a ton of different sails and they each have their own purpose.
As a general setup, sailboats will use three common sails, including headsail, mainsail, and specialty sail. Due to the varying wind conditions and the model of the sailboat, there are many types of sails including jib, genoa, trysail, storm jib, code zero, gennaker, and spinnaker.
While that sounds like too many models of sails, you can easily differentiate between them and choose the ideal model based on your purpose. This article guides you on this aspect. Let’s begin!
Different Types of Sails & When To Use Them
1. mainsail.
Mainsail is by far the most widely spotted sail model, and it’s usually fixed to the boom and fitted behind the mast. This offers the highest mileage to your sailboat, thereby maximizing speed and performance.
You can use a mainsail if:
- You’re concerned about the performance
- You need to go faster and utilize all wind power
- You need to steer your boat irrespective of the wind’s status
- You’ve a large boat and can offer adequate space to this sail.
This mainsail displays a wide surface area to make the most out of the available wind condition. As a result, you can steer your boat quite easily. However, the downside is its size. It is very large and hard to store if you need to take it down for some reason.
Check out my other article all about maintaing sails!
2. Headsail
Similar to a mainsail, it’s very easy to spot a head sail. Just look at the bow of the boat and see if there is a sail. If you see one then yes that’s a headsail. Also called a jib or genoa, a headsail is smaller in size compared to a mainsail and attaches in front of the mast to the forestay. The Foresail will not have a boom for the clew of the sail to attach to. The clew will be attached to the foresails sheet. It can be used without the mainsail in certain conditions but for the most part the two sails are used together. The foresail is always forward of the main.
The headsail comes in many different forms such as a jib, genoa, spinnaker or storm jib. The most common headsail is a jib or genoa.
You can use a headsail if:
- Your sailboat is set up for it.
- You don’t want to use the mainsail at this time.
- Your mainsail is not usable.
The biggest advantage of a headsail is the option to protect yourself even if the wind turns unpredictable or wild. This all depends on the type of headsail you are using.
So, what are the different types of headsails? Let’s take a look!
As more boaters chose to use a headsail for their boats, the jib was introduced as one of its forms. The Jib is a form of headsail that is attached to a shackle present on the deck’s front region.
The Jib is a sail that does not go past the mast when it is raised and in use. If it goes past the mast then you probably have a genoa.
You can use a jib if:
- You are out for a normal day of sailing in moderate wind speeds
- You have a roller furling. Which is a sail that wraps up around itself.
Some weather conditions can make maneuvering harder or tighter than usual. As a result, it’s essential to use a jib in such cases. It functions well with boats containing a roller furling as the jib handles different positions and tackles the movement of the boat at ease.
2.2 Genoa
Just when you’ve got acquainted with the jib, genoa comes into the picture as a larger version of the jib. If you’re boating along a coastal region, the genoa sail is the one widely used and is attached to the front area of the deck as well.
Here’s a quick trick to find out if a boat has a genoa sail. This genoa is usually larger than a Jib. This means that the genoa effortlessly overlaps and extends itself beyond the mast, thereby covering the mainsail as well.
You should use a genoa sail if:
- You’re planning to sail in minimum wind conditions. Less wind means you need more sail.
- You find the wind to originate from the rear area.
- You own a large boat. Remember that genoa can partially or completely cover the mainsail too. Larger sails for larger boats!
While it’s great for sailing in regular conditions, there are downsides associated with it. A genoa can put you in a dangerous situation if you are sailing in high wind conditions and don’t have the ability to furl in the sail. Furling in the sail will reduce the area of the sail and catch less wind.
Genoas do come in many sizes as well such as 110% or 120%.
The next section of the sail list are ones that aren’t necessary but can be helpful in certain situations. Let’s look at specialty sails!
3. Specialty Sail
While headsails and mainsails are quite commonly used, there are also specialty sails in the market to address specific requirements. Some of the widely seen specialty sails are spinnakers, storm jibs, and code zeros.
3.1 Spinnakers
Spinnaker is a sail dedicated to downwind and is quite large. Think of a beautifully covered parachute.
It’s easy to spot spinnakers as they resemble kites or parachutes. However, it crosses the bow of the boat and isn’t attached to the forestay.
Unlike the genoa sail that covers the mast, a spinnaker fails to do so. The advantage of a spinnaker is the surface area. When the wind is light, the spinnaker can catch a lot more wind giving you more speed. The Spinnaker is usually fixed to three points – pole, halyard, and sheet.
You should use a spinnaker if:
- You have minimal wind on a run.
- You are trying to harness as much wind power as you can.
While it has a wide surface area, the downside is its inability to steer the boat during strong wind conditions. It can even put the passengers at risk when the wind is at high speeds.
Make sure you have experience before trying out the spinnaker.
3.2 Storm Jibs
Storm jib is another type of specialty sail meant exclusively for rough weather. It’s a tiny, triangular structure that helps during offshore racing or cruising. Just think of it as a smaller jib.
You should use a storm jib if:
- You’re going to sail in heavy weather conditions.
- You anticipate high wind speeds.
- You’re going to be in an offshore race and they are an approved sail type.
Note: In the case of an offshore racing requirement, it’s critical to take prior permission from the regulatory authority for using a storm jib.
3.3 Code Zeros
Code zero is another updated version of a spinnaker that’s meant to be a combination of genoa and gennaker sails. It resembles the look of a genoa but is a lot bigger.
You should use a code zero if:
- You’re looking for an overlapping flying headsail.
- You’re sailing only in light air conditions.
- You’re looking for an alternative to a Genoa.
Having said that, a code zero or a screecher does the job of a genoa with better efficiencies.
3.4 Trysail
Trysail is another type of specialty sail that’s tiny, triangular, and can be fixed right above a gooseneck on the sailboat.
The Trysail is less known in the market as most boaters go ahead with common mainsails and headsails. It’s essential to acknowledge trysail as a front-and-aft mainsail model. It offers excellent performance and contains a permanent pennant in it.
You should use a trysail if:
- You’re sailing in heavy weather conditions.
- You’re looking for a storm replacement.
- You are experienced with using them.
The quadrilateral sail in a trysail is usually turned and bent to a mast, and this helps in heading the vessel during windy conditions.
3.5 Gennakers
If you’ve been able to spot genoa and spinnaker in the past, identifying a gennaker is incredibly easy. A gennaker is a hybrid sail form that is small, slow, and requires no pole attached to the mast.
You should use a gennaker if:
- You’re looking for a smaller version of a spinnaker.
- You’ve no space to fix a pole to the mast.
- You require the sail to be easily manageable.
- You’re sailing in a region requiring minimum downwind levels.
Choosing a hybrid sail has a lot of benefits as it combines the usefulness of 2 sail models. However, being aware of their cons is critical to planning a safe sail.
As you begin using these sails, you can also look for better customizations. There are drifters, wind seekers, and other jib types that are meant to handle different wind conditions.
How Many Sails On A Sailboat ?
In general, a sailboat contains two sails. Two sails is the typical setup for the best performance of the boat during different wind conditions. It’s essential to pick your two sails based on your sailing plan.
Why Are There Two Sails On A Sailboat?
A sailboat uses two sails because the wind left over by the first sail is easily caught by the second sail. This helps in steering the sailboat to a better extent and gives the sailboat more power.
Final Thoughts
Sails are one of the major assets of a sailboat. From managing wind to maximizing the performance and longevity of a sailboat, the type of sails you use, plays a huge role. From the various sail types listed in this article, you can choose the best model that fits your sailing routine. Just make sure to remember to check and make sure they are the correct size for your vessel.
Make sure to plan ahead and have the right sails for your sailing weekend. Cheers!
Boatlifehq owner and author/editor of this article.
Recent Posts
How to Repair a Sailboat Hull: Step-by-Step Guide
Maintaining your sailboat's hull is crucial for ensuring its longevity and performance on the water. Hull damage can occur due to various reasons, such as collisions, grounding, or general wear and...
10 Steps For Anchoring Your Sailboat
Anchoring a sailboat is a fundamental skill every sailor must master. Proper anchoring ensures your boat remains secure, preventing it from drifting and potentially causing damage. Whether you're...
Different Types of Sailing and Racing Explained
You can literally sail on any type of water: whatever floats your boat. I wanted to know exactly what it's called when crossing an ocean, so I did some research. Here's what I came up with.
What are the different types of sailing? Inland sailing is freshwater sailing, on rivers and lakes. River delta sailing, so in brackish water, is called estuary. Oceanic sailing is divided into coastal (in sight of land), offshore sailing (out of sight of land, but within range), and bluewater sailing (out of sight of land and out of range).
But it's not just your location or the sort of water you're in. Intention also plays a part in determining what kind of sailing you're doing. For example: when does it stop to be offshore, and start to be bluewater sailing? It's a bit of a grey area.
Apart from the type of sailing, you can also participate in all kinds of racing, which I'll go over below as well.

On this page:
More on sailing types, more on racing types, related questions.
There are two types of sailing: cruising and racing (scrolls down ). The most common type of sailing is inland cruising, as most people simply want to enjoy their boats on safe and predictable waters.
There are five different types in total, which depend on where you are and what your intentions are. The further out you go, the more adventurous it gets.
Here are the different types of sailing:
- Inland - best for beginners
- Estuary - rivers that lead to sea
- Coastal - in sight of land
- Off Shore - out of sight of land
- Ocean - blue water or intercontinental
Freshwater generally offers the easiest conditions, and is the easiest on your boat. It's the cheapest and easiest to get started, requires the least amount of equipment and also the least amount of maintenance.
Saltwater generally offers more difficult conditions like stronger winds and higher waves. You need larger and more expensive equipment, and the salt is harder on your gear and boat, so you need to do a lot more maintenance.
The differences between each type of sailing:
| Inland | Estuary | Coastal | Off Shore | Ocean |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| enclosed water | river deltas | in sight of land | out of sight of land | oceanic crossings |
| freshwater | brackish water | saltwater | saltwater | saltwater |
| all boat types | keel boats | keel boats | keel boats | keel boats |
| all hull lengths | all hull lengths | > 26 feet (8 m) | > 30 feet (9 m) | > 30 feet (9 m) |
| low maintenance | medium maintenance | medium mantenance | high maintenance | high maintenance |
| no tides | tides | tides | tides | tides |
| medium waves | medium waves | high waves | high waves | high waves |
| good support | good support | good support | medium support | no support |
Inland sailing
The easiest sailing is on inland waters . All water that is enclosed by land is called inland water. These are lakes, rivers, canals, and so on. Freshwater rivers are pretty safe. In typical lake sailing you won't find yourself drifting for weeks on end because you got hit by a storm. Generally there are more people around that can help you out.
It's important to say that ponds and small lakes can be treacherous. The winds can be unpredictable coming from land (for example due to nearby hills). So these small and seemingly innocent waters may require some real seamanship.
Inland sailing is definitely the best kind of sailing for beginners. You don't have to account for tides, the waves are not as high and you don't have to stock up on supplies since there's always a harbor nearby. It's also the easiest on your boat: inland waters are mostly freshwater, which means maintenance is low.
So great news for beginners on a budget: you can use any boat type: flat bottom, keel, aluminum, wood: whatever you like to sail most.
Estuary sailing
Estuary means the delta or tidal mouth of a river. It's partially enclosed water. Like inland sailing, estuary areas have a lot of oversight. With the Coast Guard keeping a close eye on everybody, the chance that something really bad happens is extremely small. You have to account for some tidal changes and the current can be strong.

There will typically will be good weather forecasts for river deltas, so there shouldn't be a lot of sudden surprises. However, you want to be prepared in case the weather changes. Maybe you want to have a keel for this type of water, and you should definitely wear a PFD. There are some boats that have a keel you can lower if needed; this way you won't permanently increase your draft, but you'll be able to sail coastal and estuary regions.
Because river delta water is brackish, there's more salt in the water. So it's a bit harder on your boat. You probably need to increase your maintenance. Maybe you want a fiberglass hull, but you probably won't need to convert your entire boat.
Coastal sailing
Coastal sailing is a form of oceanic sailing where you're still in sight of land, but also in partially protected waters. Protected waters are sheltered waters that have stable weather conditions and have Coast Guard support. Mostly, coastal sailing requires a bit more skill and better equipment.
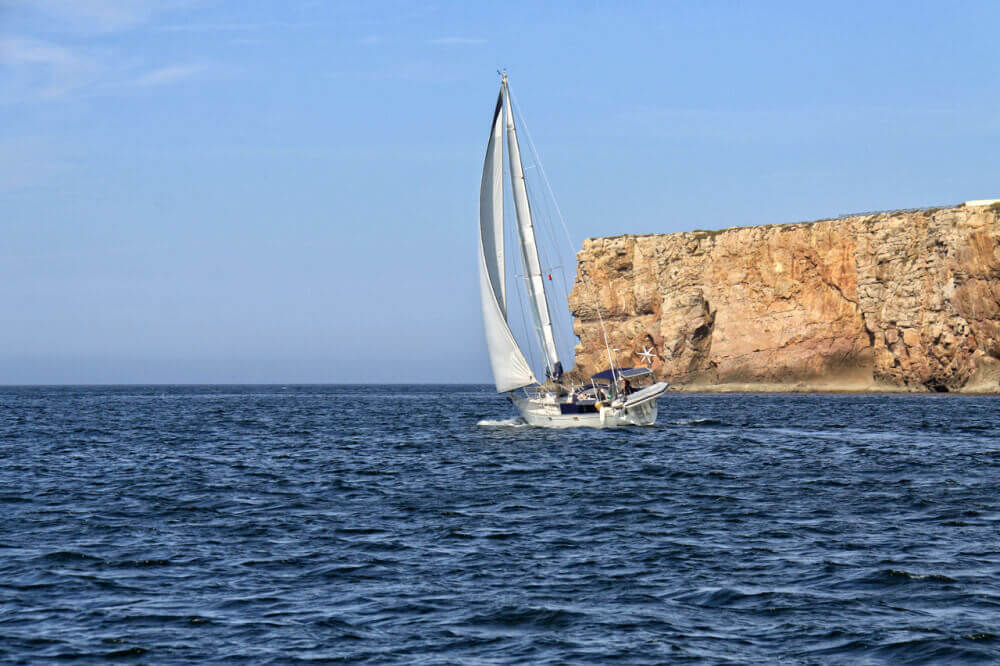

You will need a keelboat to sail coastal waters, and the hull needs to be strong enough to deal with larger waves. The forces you have to deal with are just a level up compared to freshwater conditions. If you go overboard, the consequences can be quite severe, because there can be a strong current, so make sure to wear your PFD.
But, the water is quite shallow and there are reliable weather forecasts. If you don't go out in heavy weather, you'll have enough time to get back to safe harbor when the weather starts to change.
You can use smaller sailboats without problem, but make sure the boat is safe, and you have all necessary safety equipment on board. You may also need to convert your boats engine to help it deal with galvanic corrosion.
If you want to know everything about the systems used in saltwater boats, I really recommend you read my article on boat conversion (opens in new tab ).
Off Shore sailing
You're sailing off shore when you're out of sight of land, but you're not crossing an ocean. Anything under 15 miles of the coast is regarded as off shore, but if you're going out 20 miles and turning back to return for port afterwards, that's still off shore sailing and not bluewater.

Off shore sailing can be very challenging. Sea conditions can get very rough: the weather gets more unpredictable where land meets water, and the current can get very strong. Generally off shore is more rough than open seas (except for the hurricane season). If you plan on sailing off shore, you definitely need a good strong keel boat that's a bit longer, ideally over 24 - 30 feet (7 - 9 m).
A mistake can have huge consequences. Off shore is being watched pretty closely by the Coast Guard as well, so if something goes wrong, help will be on the way. But it really makes a huge difference whether you're 12 or 20 miles out. Response time for Coast Guard is about 8 minutes at 12 miles, but it's 20 minutes at 20 miles. Drifting around in cold water for 20 minutes can be dangerous. More importantly: they have to find you out there.
So please make sure you have the right safety equipment on board. If you're unsure what you need, check out my post about USCG safety requirements here (opens a new tab ).
Bluewater sailing
Blue water sailing is definitely one of the most advanced types of sailing.
Contrary to popular belief, the open seas aren't always rough. They can be, but it's mostly the off shore areas that suffer from heavy weather. Outside the hurricane season, they're mostly pretty calm. If you use the trade winds, wind conditions are pretty reliable.

It is recommend to use a mid-sized boat (most sailors go for 30' (9 m) or up), not just for comfort but also to be able to carry enough supplies to last for at least a couple of weeks. Typically you'll need to bring roughly 40 - 60 gallons (200 - 300 liters) of water per person and 60 gallons (250 liters) of fuel.
The hardest part of bluewater sailing is being completely self reliable.
You're out on the open ocean alone, sometimes for multiple weeks on end. The Atlantic crossing takes about three weeks, for example. The longest passage there is about 12 days. During that period, if anything breaks, you need to be able to fix it. If you don't, you won't be able to continue. If something goes wrong - you get injured, for example - you're the one that needs to put on a bandage.
Some people can handle this kind of stress pretty well. Others break down because of it. It's recommended to find out what kind of person you are before getting on that boat and using the trade winds to blast it to the middle of the ocean. Where you hit a dead zone. You're now helplessly floating around in the middle of nothingness on a 100 square foot (10 square meters) piece of plastic. It's just not the best of times to meet your true self.
If you want to learn more about what it takes to do ocean crossings, consider to read my article about bluewater sailing here (opens a new tab ).
Besides cruising, you can also participate in sailing races, which can be great fun. There are a lot of racing types, and you can invent your own rules and competition methods.
The type of race isn't just determined by the kind of water (like with cruising) but also the kind of event, the kind of course, and the competition method (which are the rules and requirements).
Here are the different types of racing styles:
- windward/leeward - racing course with one windward and leeward leg
- passage or course - maneuvering around multiple marks (for example buoys)
- fleet racing - the most common race form where a fleet of sailboats go around a course
- match racing - identical yachts trying to finish first in a single race
- team racing - two sailing teams with multiple boats compete to win a series of races
- one-design - competitive racing at high speeds, based on class requirements: identical models with same rigging and crew
- offshore or oceanic racing - races of multiple days or weeks in open waters over a distance of 800 miles
And this are some different types of racing events:
- twilight racing - social racing events in the summer organized by individual sailors
- club racing - social racing events organized by the local yacht club
- regatta - multiple day event with an overall event winner, typically organized by the class association
- disabled or Para World sailing - official racing events that are organized for disabled people
Competition methods
There are four primary competition methods in sailboat racing: one design and handicap.
- handicap racing - different boats, time gets corrected based on features
- one-design racing - identical boats, real time wins
- formula class - different boats with certain identical features (ie. hull speed)
- development class - different boats that meet specific requirements (ie. length, hull type, etc.)
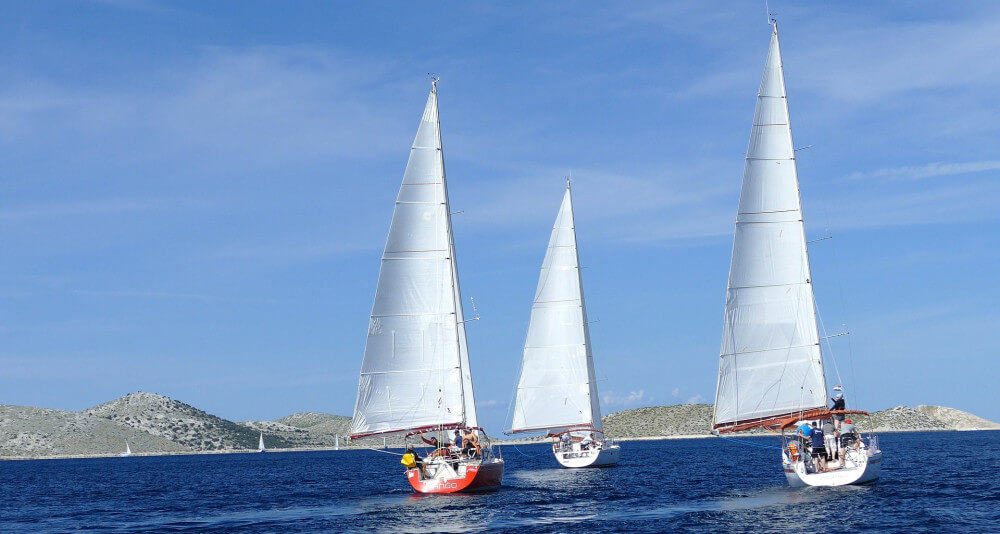

In handicap racing , time is added or subtracted based on the hull type, materials used, and other design factors. The handicap gets calculated using standardized formulas. So the winner is determined by correcting the time mathematically after the race. In these races you'll see all kinds of boat models, rigging, crews, and so on. The difference between the individual boats makes the handicap.
There are different handicap rating systems. A popular system is PHRF (Performance Handicap Racing Fleet).
In one-design racing , identical boats race for the best time. The first boat to cross the finish line wins. All boats that take part must adhere to the class requirements. So you won't see any different models or hull types in one-design racing. The class requirements determine all kinds of stuff, like the number of crew allowed, the type of rigging, amount of sails, and boat requirements.
There are a couple of other approaches. The development class is a middle way that's right in between handicap and OD racing. The boats in this class are not identical, but typically have the same length. They are all built to meet certain requirements An example is the America's Cup 12-meter.
The formula class allows different boats to compete without using a handicap system. They keep a couple of specs the same (ie. hull speed) to ensure they all have a fair chance of winning.
What are protected waters? Protected waters are sheltered waters that meet certain stability criteria, such as stable water conditions and emergency support by the Coast Guard. These water bodies pose no special hazards to the people sailing them. Most inland waters, like rivers and lakes, are protected waters, but also harbors and most coastal waters.
What are the most common types of racing sailboats? The most-used sailboats for racing are keel boats, centerboard boats (dinghy), multi-hulls (catamaran or trimaran), and tower ship (also called tall ships). Most keel boats are racing yachts between 24' and 50' (7 - 15 m). One of the most well-known sailboat races is the America's Cup 12-meter, which is a 40' class.
Leave a comment
You may also like, the ultimate guide to sail types and rigs (with pictures).
What's that sail for? Generally, I don't know. So I've come up with a system. I'll explain you everything there is to know about sails and rigs in this article.

The Difference Between Freshwater and Saltwater Boats

17 Sailboat Types Explained: How To Recognize Them

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
one mast. triangular mainsail (called a Bermuda sail) a foresail (also called the jib) fore-and-aft rigged. medium-sized (12 - 50 ft) Fore-and-aft rigged just means "from front to back". This type of rigging helps to sail upwind. Any sailboat with one mast and two sails could still be a sloop.
For day sailing, small sailboats such as sailing dinghies, day sailers, and pocket cruisers are ideal options. These boats usually range between 12 and 25 feet in length and offer simplicity, ease of handling, and portability. Examples of common day sailing boats include the Sunfish, Laser, and O'Day Mariner.
The most common kind of sailboat is the sloop, as it's simple to operate and versatile. Other common sailboat types include the schooner, cutter, cat, ketch, schooner, catamaran, and trimaran. Other sailboat variations include pocket cruisers, motorsailers, displacement, and shoal-draft vessels. The information found in this article is sourced ...
June 17, 2024. Sailboats are powered by sails using the force of the wind. They are also referred to as sailing dinghies, boats, and yachts, depending on their size. Sailboats range in size, from lightweight dinghies like the Optimist dinghy (7'9") all the way up to mega yachts over 200 feet long. The length is often abbreviated as LOA (length ...
List of sailing boat types. A Windmill sailing dinghy. The following is a partial list of sailboat types and sailing classes, including keelboats, dinghies, and multihull (catamarans and trimarans).
Cruising in sailing boats is by far the most popular activity and is enjoyed in many different ways, using the full range of sailing boats on many different types of water, from lakes, rivers and canals, to coastal waters and even across oceans. Given the huge number of different varieties of sailing activity, it's perhaps no surprise that there's a huge number of different styles of a boat.
Sailboat Shapes And Hull Types. Sailboat hulls differ in their total number and shape. They can be monohulls (one hull), catamarns (two hulls) and trimarans (three hulls). The shape of a sailboat not only changes the way it is commanded, but also how it performs on different points of sail and in different conditions.
This observation alone will enable you to identify the five main types of sailboats — sloops, cutters, ketches, yawls and schooners - all of which are described here. But apart from the various rig types, you can describe types of sailboats from a different viewpoint - sailing dinghies, dayboats, motorsailors, monohulls, catamarans and ...
Sailboat Rig Types. Sailboat rigging includes: the mast (s); boom (s); and the shrouds or stays that hold up the mast. A sailboat with one mast is usually a sloop with one mainsail and one headsail. A cutter rig usually has one mast but two or more headsails. This rig "cuts" the foretriangle between the head (forward) stay and the main mast.
Contents show. Several factors determine the types of sailboats, including the hull type, keel type, mast configuration, and sails and rigging. The hull is the boat's body and can be either a monohull, catamaran, or trimaran. The keel is the underwater part of the hull that provides stability and can be either a fin keel, wing keel, bilge ...
Monohull sailboats. Monohulls are the most common type of sailboat and are designed with a single hull, and have a long, narrow shape which makes them fast and easy to maneuver. Monohulls are typically designed for recreational sailing, and are great for long-distance cruising, coastal sailing, and racing. As they can be relatively inexpensive ...
The luxury yachts are ideal to experience sailing in comfort and style. These vessels are known for their remarkable craftsmanship and innovative design. The most common type of sailboat is the racing sailboat, used in sailing competitions around the world.
Leave a Reply. Sailboats can be divided into three basic types based on their hulls (catamaran, monohull or multihull), their keel and their rigging, and then further subdivided from there. The result is that there are actually well over a dozen different kinds of sailboats out there. Sailboat Hull Types There are three….
A trimaran is a type of sailing yacht that has three hulls, two smaller amas (outrigger hulls) and a central main hull, rather than one. They are known for their speed and stability, and are often used for racing and long-distance cruising. One of the key features of trimarans is their speed. The two smaller amas, which are located on the sides ...
In front of the main mast is called a foremast. The 5 most common two-masted rigs are: Lugger - two masts (mizzen), with lugsail (cross between gaff rig and lateen rig) on both masts. Yawl - two masts (mizzen), fore-and-aft rigged on both masts. Main mast much taller than mizzen. Mizzen without mainsail.
A sailboat or sailing boat is a boat propelled partly or entirely by sails and is smaller than a sailing ship. Distinctions in what constitutes a sailing boat and ship vary by region and maritime culture. ... A great number of sailboat-types may be distinguished by size, hull configuration, keel type, purpose, number and configuration of masts ...
Bermuda Rig - Also known as a Marconi rig, this is the typical configuration of most modern sailboats. It has been used since the 17th century and remains one of the most efficient types of rigs. The rig revolves around setting a triangular sail aft of the mast with the head raised to the top of the mast.
Racing Sailboats. Similar to cruising boats but have more equipment and are built lighter, with spartan accommodations. They are not intended to be a comfortable ride, just a fast one. Usually 20-70+ feet in length. Just as these are related to cruising boats, there are smaller, faster cousins of sailing dinghies that are also raced.
A trimaran is a multihull boat that comprises a main hull and two smaller outrigger hulls (or 'floats') which are attached to the main hull with lateral beams. MOTORSAILER. A motorsailer or "motorsailor", is a type of sailing vessel, typically a pleasure yacht, that derives propulsion from its sails and engine(s) in equal measure.
3. Genoa. The genoa is a large sail that attaches to the front of the forestay. (In this instance, it's similar to a headsail.) However, the genoa is larger than the headsail and overlaps the mainsail partially or completely to help the boat go faster. Genoa sails are useful when sailing through light or medium wind.
The rig consists of the sail and mast hardware. The sail rig and sail type are both part of the sail plan. We usually use the sail rig type to refer to the type of boat. Let's start by taking a look at the most commonly used modern sail rigs. Don't worry if you don't exactly understand what's going on. At the end of this article, you'll ...
As a general setup, sailboats will use three common sails, including headsail, mainsail, and specialty sail. Due to the varying wind conditions and the model of the sailboat, there are many types of sails including jib, genoa, trysail, storm jib, code zero, gennaker, and spinnaker. While that sounds like too many models of sails, you can easily ...
Here are the different types of sailing: Inland - best for beginners. Estuary - rivers that lead to sea. Coastal - in sight of land. Off Shore - out of sight of land. Ocean - blue water or intercontinental. Freshwater generally offers the easiest conditions, and is the easiest on your boat.